# 53. Maximum Subarray
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Example:
- Input:
[-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] - Output:
6 - Explanation: The subarray
[4,-1,2,1]has the maximum sum of6.
# Thought Process
We previously solved this using a greedy algorithm during our discussion on greedy methods, Greedy Algorithm: Maximum Subarray (opens new window).
This time, let's analyze it using dynamic programming.
The dynamic programming methodology consists of the following five steps:
Define the
dparray (dp table) and the meaning of its indicesdp[i]: The maximum sum of a contiguous subarray ending at indexi(includingnums[i]).Define the recursive formula
dp[i]can be derived from two options:dp[i - 1] + nums[i], i.e.,nums[i]joins the current contiguous subarray sum.nums[i], i.e., start a new contiguous subarray sum from scratch.
We choose the maximum:
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]).Initialize the
dparrayFrom the recursive formula, it's clear that
dp[i]depends on the state ofdp[i - 1], makingdp[0]the foundation of the formula.dp[0]is evident from its definition to benums[0]; thusdp[0] = nums[0].Determine the traversal order
The recursive formula indicates that
dp[i]depends on the state ofdp[i - 1], hence we need to traverse from front to back.Example trace of the
dparrayFor example, given
nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4], the correspondingdpstates are as follows:
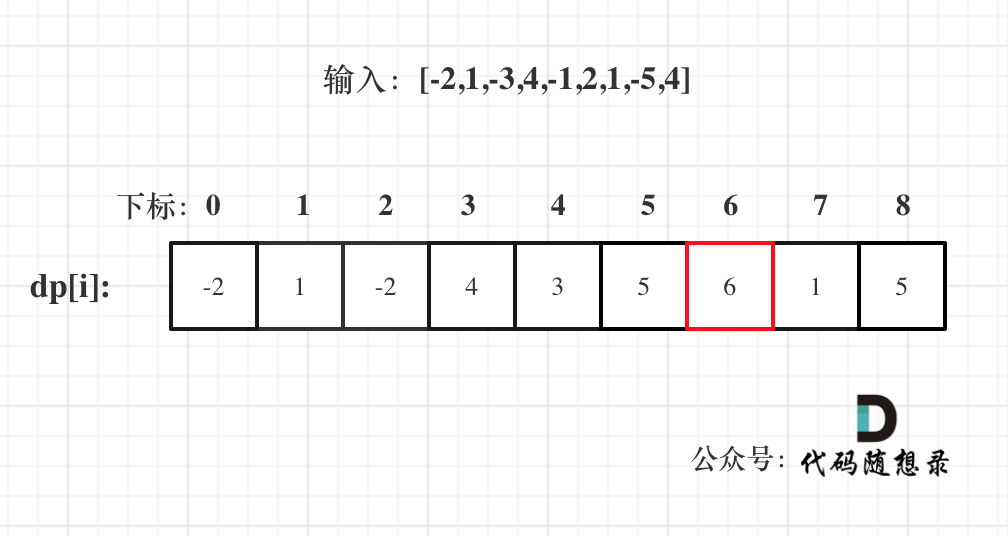
Note that the result is not
dp[nums.size() - 1]!, but ratherdp[6].Revisit the definition:
dp[i]is the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray ending at indexi.Therefore, we must find the maximum of all
dp[i]to determine the largest contiguous subarray sum.Thus, during the recursion formula, we can directly choose the maximal
dp[i].
Now that we've completed the dynamic programming analysis, here is the complete code:
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
vector<int> dp(nums.size());
dp[0] = nums[0];
int result = dp[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]); // State transition formula
if (dp[i] > result) result = dp[i]; // `result` keeps the maximum value of `dp[i]`
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
# Summary
The greedy approach is also clever, though a bit intricate and requires cautious thought. If you wish to revisit the greedy method, check here: Greedy Algorithm: Maximum Subarray (opens new window)
The dynamic programming solution is straightforward.
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
/**
* 1. `dp[i]` represents the maximum sum at the current index
* 2. Recurrence formula: dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i]), res = max(res,dp[i])
* 3. Initialization: all zeros
* 4. Traversal direction: from front to back
* 5. Example walkthrough...
*
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int res = nums[0];
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
res = res > dp[i] ? res : dp[i];
}
return res;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// Because the recurrence formula `dp[i]` only depends on the previous value, a variable can replace the `dp` array, reducing space complexity to O(1)
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int pre = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
pre = Math.max(pre + nums[i], nums[i]);
res = Math.max(res, pre);
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Python:
class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [0] * len(nums)
dp[0] = nums[0]
result = dp[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i]) # State transition formula
result = max(result, dp[i]) # Result keeps the maximum value of dp[i]
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Go:
// Solution
// 1, dp
// 2, greedy
func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
n := len(nums)
// Here dp[i] indicates the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray including element num[i]
dp := make([]int, n)
// Initialization, as the recurrence formula depends on dp[0]
dp[0] = nums[0]
// Initialize the maximum sum
mx := nums[0]
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
// Here the state transition formula seeks the maximum sum
// It can include or not include the previous sum
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+nums[i], nums[i])
mx = max(mx, dp[i])
}
return mx
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# JavaScript:
const maxSubArray = nums => {
// Array length and dp initialization
const len = nums.length;
let dp = new Array(len).fill(0);
dp[0] = nums[0];
// Initialize the maximum as `dp[0]`
let max = dp[0];
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
// Update the maximum
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
return max;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Scala:
object Solution {
def maxSubArray(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {
var dp = new Array[Int](nums.length)
var result = nums(0)
dp(0) = nums(0)
for (i <- 1 until nums.length) {
dp(i) = math.max(nums(i), dp(i - 1) + nums(i))
result = math.max(result, dp(i)) // Update the maximum
}
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# TypeScript:
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
const len = nums.length
if (len === 1) return nums[0]
const dp: number[] = new Array(len)
let resMax: number = dp[0] = nums[0]
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i])
// Pay attention to negative values
if (dp[i] > resMax) resMax = dp[i]
}
return resMax
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
