# 583. Delete Operation for Two Strings
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to make word1 and word2 the same, where in each step you can delete one character in either string.
Example:
- Input: "sea", "eat"
- Output: 2
- Explanation: First step delete 's' from "sea" to get "ea", and then delete 't' from "eat" to get "ea".
# Solution
# Dynamic Programming Approach One
This problem is similar to 0115.Distinct Subsequences (opens new window), but here we can delete characters from both strings, adding a bit more complexity while keeping the overall idea unchanged.
# Dynamic Programming Approach Two
This problem is also very similar to 1143.Longest Common Subsequence (opens new window). We simply need to find the longest common subsequence between the two strings; all characters not part of this subsequence must be deleted. Subtracting the length of the longest common subsequence from the total length of both strings gives the minimum number of steps required for deletion.
# DP Array Definition
Define
dp[i][j]as the minimum number of deletion operations needed to make the stringsword1of lengthiandword2of lengthjthe same.Recursive Formula
- If
word1[i-1]equalsword2[j-1], thendp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]; - If
word1[i-1]is not equal toword2[j-1], we have:- Remove
word1[i-1]:dp[i-1][j] + 1 - Remove
word2[j-1]:dp[i][j-1] + 1 - Remove both
word1[i-1]andword2[j-1]:dp[i-1][j-1] + 2
- Remove
Therefore, the recursive formula in the case where
word1[i-1]is not equal toword2[j-1]is:dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j] + 1, dp[i][j-1] + 1);- If
DP Array Initialization
dp[i][0] = imeans deleting allicharacters from word1 to match an empty word2.dp[0][j] = jmeans deleting alljcharacters from word2 to match an empty word1.
Traversal Order
- We process the dp array from top to bottom, left to right, ensuring each
dp[i][j]is calculated based on its neighbors: top, left, and top-left.
- We process the dp array from top to bottom, left to right, ensuring each
Example Walkthrough
- For
word1 = "sea"andword2 = "eat", the state of the dp array will be as illustrated:
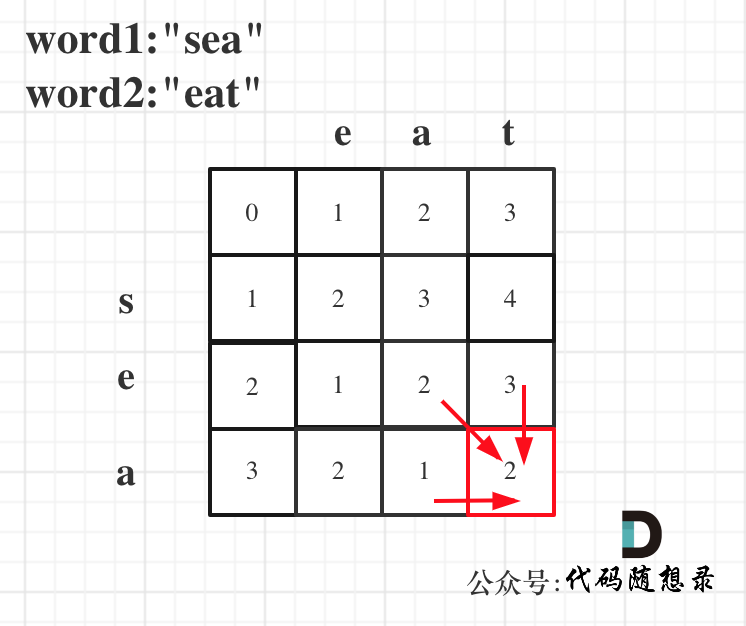
- For
The solution in C++ is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(word1.size() + 1, vector<int>(word2.size() + 1));
for (int i = 0; i <= word1.size(); i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= word2.size(); j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[word1.size()][word2.size()];
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- Time Complexity: O(n * m)
- Space Complexity: O(n * m)
The approach in Java is as follows:
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int[][] dp = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < word1.length() + 1; i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < word2.length() + 1; j++) dp[0][j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i < word1.length() + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < word2.length() + 1; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()];
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
The Python implementation is:
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
dp = [[0] * (len(word2)+1) for _ in range(len(word1)+1)]
for i in range(len(word1)+1):
dp[i][0] = i
for j in range(len(word2)+1):
dp[0][j] = j
for i in range(1, len(word1)+1):
for j in range(1, len(word2)+1):
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
else:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j] + 1, dp[i][j-1] + 1)
return dp[-1][-1]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
The Go implementation is:
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
dp := make([][]int, len(word1)+1)
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, len(word2)+1)
}
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
dp[i][0] = i
}
for j := 0; j < len(dp[0]); j++ {
dp[0][j] = j
}
for i := 1; i < len(dp); i++ {
for j := 1; j < len(dp[i]); j++ {
if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j] + 1, dp[i][j-1] + 1)
}
}
}
return dp[len(dp)-1][len(dp[0])-1]
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
And in JavaScript:
var minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
let dp = Array.from(new Array(word1.length + 1), () =>
Array(word2.length + 1).fill(0)
);
for (let i = 1; i <= word1.length; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (let j = 1; j <= word2.length; j++) {
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for (let i = 1; i <= word1.length; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= word2.length; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(
dp[i - 1][j] + 1,
dp[i][j - 1] + 1
);
}
}
}
return dp[word1.length][word2.length];
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
For TypeScript:
function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
const length1: number = word1.length,
length2: number = word2.length;
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length1 + 1).fill(0)
.map(_ => new Array(length2 + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i <= length1; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (let i = 0; i <= length2; i++) {
dp[0][i] = i;
}
for (let i = 1; i <= length1; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= length2; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] === word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(
dp[i - 1][j] + 1,
dp[i][j - 1] + 1
);
}
}
}
return dp[length1][length2];
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
In Rust:
impl Solution {
pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
for i in 0..word1.len() {
dp[i + 1][0] = i + 1;
}
for j in 0..word2.len() {
dp[0][j + 1] = j + 1;
}
for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
if char1 == char2 {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j];
} else {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].min(dp[i + 1][j]) + 1;
}
}
}
dp[word1.len()][word2.len()] as i32
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
