# 1143. Longest Common Subsequence
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
For example, "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde" but "aec" is not a subsequence of "abcde". A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that appears in both strings.
If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
Example 1:
- Input:
text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" - Output:
3 - Explanation: The longest common subsequence is
"ace"and its length is 3.
Example 2:
- Input:
text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc" - Output:
3 - Explanation: The longest common subsequence is
"abc"and its length is 3.
Example 3:
- Input:
text1 = "abc", text2 = "def" - Output:
0 - Explanation: There is no common subsequence, therefore the result is 0.
Constraints:
1 <= text1.length <= 10001 <= text2.length <= 1000- The input strings consist of lowercase English characters only.
# Approach
This problem differs from 0718. Maximum Length of Repeated Subarray (opens new window) because the subsequences here need not be contiguous, but must maintain relative ordering, i.e., "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde", but "aec" is not.
Analyzing this problem using the dynamic programming framework:
- Define the dp array and its meaning
dp[i][j]: the longest common subsequence of text1[0, i-1] and text2[0, j-1] is dp[i][j].
Some might ask why define it as text1[0, i-1] and not text1[0, i]. This is purely for code simplicity later on. If you insist on defining it as text1[0, i], that works too, which I elaborate on in the expansion section (opens new window) of that problem. The choice primarily simplifies the initialization of the first row and column of the dp array.
- Establish the recurrence relation
The main scenarios are: when text1[i-1] matches text2[j-1], and when they don't match.
If text1[i-1] matches text2[j-1], we've found a common element. Thus, dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;.
If text1[i-1] doesn't match text2[j-1], then we determine the maximum from dp[i-1][j] or dp[i][j-1].
Namely: dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);.
Here's the code:
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
2
3
4
5
- Initialize the dp array
First, let's determine the values of dp[i][0].
The longest common subsequence of text1[0, i-1] and the empty string is naturally 0, so dp[i][0] = 0;.
Similarly, dp[0][j] is also 0.
Other indices will be gradually calculated using the recurrence relation and can start as any value, so let's initialize them all as 0.
Code:
vector<vector<int>> dp(text1.size() + 1, vector<int>(text2.size() + 1, 0));
- Determine the traversal order
The recurrence relation reveals that three directions can derive dp[i][j]:
![Directions for dp[i][j]](https://file1.kamacoder.com/i/algo/20210204115139616.jpg)
Thus, to ensure all three directions have been calculated, we traverse the matrix from top to bottom and left to right.
- Example walkthrough for the dp array
Take the input: text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" as an example, the dp state is illustrated below:
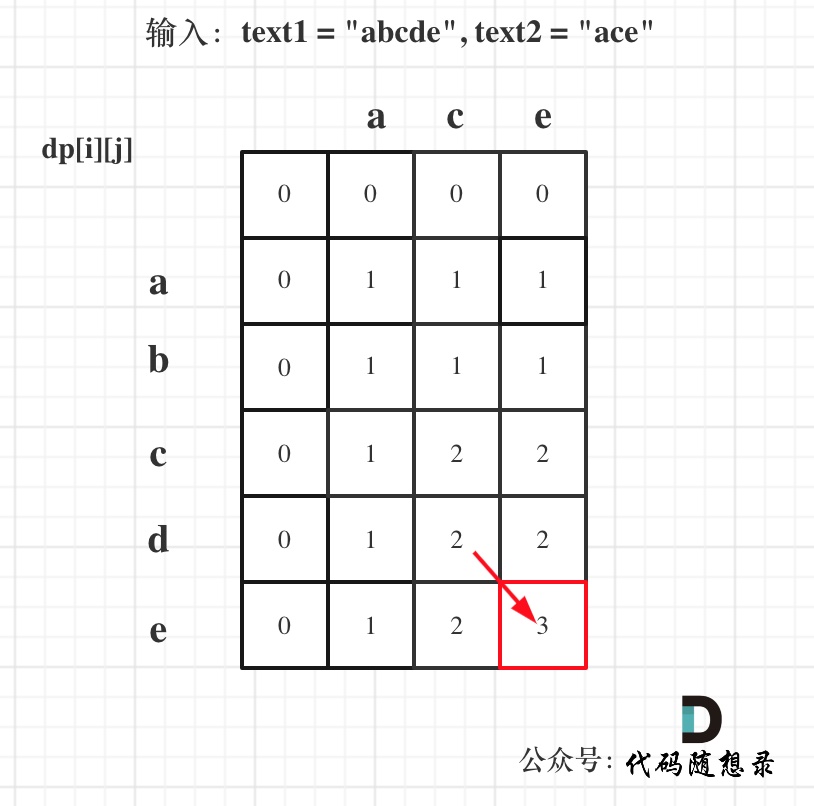
Finally, dp[text1.size()][text2.size()] in the red box is the result.
With the analysis complete, here's the C++ code:
class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(text1.size() + 1, vector<int>(text2.size() + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= text1.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= text2.size(); j++) {
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[text1.size()][text2.size()];
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- Time Complexity: O(n * m), where n and m are the lengths of
text1andtext2 - Space Complexity: O(n * m)
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
/*
2D dp array
*/
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int[][] dp = new int[text1.length() + 1][text2.length() + 1];
// Initialize the dp array
for (int i = 1 ; i <= text1.length() ; i++) {
char char1 = text1.charAt(i - 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= text2.length(); j++) {
char char2 = text2.charAt(j - 1);
if (char1 == char2) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[text1.length()][text2.length()];
}
}
/**
1D dp array
*/
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int n1 = text1.length();
int n2 = text2.length();
int[] dp = new int[n2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
int pre = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
int cur = dp[j];
if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[j] = pre + 1;
} else {
dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - 1]);
}
pre = cur;
}
}
return dp[n2];
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# Python:
2D DP
class Solution:
def longestCommonSubsequence(self, text1: str, text2: str) -> int:
dp = [[0] * (len(text2) + 1) for _ in range(len(text1) + 1)]
for i in range(1, len(text1) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(text2) + 1):
if text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
return dp[len(text1)][len(text2)]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1D DP
class Solution:
def longestCommonSubsequence(self, text1: str, text2: str) -> int:
m, n = len(text1), len(text2)
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
for i in range(1, m + 1):
prev = 0
for j in range(1, n + 1):
curr = dp[j]
if text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]:
dp[j] = prev + 1
else:
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - 1])
prev = curr
return dp[n]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Go:
func longestCommonSubsequence(text1 string, text2 string) int {
t1 := len(text1)
t2 := len(text2)
dp := make([][]int, t1+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, t2+1)
}
for i := 1; i <= t1; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= t2; j++ {
if text1[i-1] == text2[j-1] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
}
}
}
return dp[t1][t2]
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# JavaScript:
const longestCommonSubsequence = (text1, text2) => {
let dp = Array.from(Array(text1.length+1), () => Array(text2.length+1).fill(0));
for(let i = 1; i <= text1.length; i++) {
for(let j = 1; j <= text2.length; j++) {
if(text1[i-1] === text2[j-1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] +1;;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
}
}
}
return dp[text1.length][text2.length];
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# TypeScript:
function longestCommonSubsequence(text1: string, text2: string): number {
/**
dp[i][j]: length of the longest common subsequence of the first i-1 characters of text1 and the first j-1 characters of text2
*/
const length1: number = text1.length,
length2: number = text2.length;
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length1 + 1).fill(0)
.map(_ => new Array(length2 + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= length1; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= length2; j++) {
if (text1[i - 1] === text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[length1][length2];
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn longest_common_subsequence(text1: String, text2: String) -> i32 {
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; text2.len() + 1]; text1.len() + 1];
for (i, c1) in text1.chars().enumerate() {
for (j, c2) in text2.chars().enumerate() {
if c1 == c2 {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1;
} else {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].max(dp[i + 1][j]);
}
}
}
dp[text1.len()][text2.len()]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1D:
impl Solution {
pub fn longest_common_subsequence(text1: String, text2: String) -> i32 {
let mut dp = vec![0; text2.len() + 1];
for c1 in text1.chars() {
let mut prev = 0;
for (j, c2) in text2.chars().enumerate() {
let temp = dp[j + 1];
if c1 == c2 {
dp[j + 1] = prev + 1;
} else {
dp[j + 1] = dp[j + 1].max(dp[j]);
}
prev = temp;
}
}
dp[text2.len()]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# C:
#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
int longestCommonSubsequence(char* text1, char* text2) {
int text1Len = strlen(text1);
int text2Len = strlen(text2);
int dp[text1Len + 1][text2Len + 1];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof (dp));
for (int i = 1; i <= text1Len; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= text2Len; ++j) {
if(text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[text1Len][text2Len];
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Cangjie
func longestCommonSubsequence(text1: String, text2: String): Int64 {
let n = text1.size
let m = text2.size
let dp = Array(n + 1, {_ => Array(m + 1, repeat: 0)})
for (i in 1..=n) {
for (j in 1..=m) {
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
}
}
}
return dp[n][m]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
