# The Ultimate Summary of Dynamic Programming!
Now that 42 classic problems on dynamic programming with a total of 50 articles have been discussed, it is time to make a summary.
Regarding dynamic programming, in the first article of the topic Dynamic Programming Fundamentals (opens new window), the five steps of dynamic programming were introduced and emphasized as crucial for solving dynamic programming problems!
These are the distilled pearls of wisdom Carl has gathered from completing over one hundred dynamic programming problems. If you've followed along with the "Coding Thoughts" series on dynamic programming, you'll deeply appreciate the significance of these five steps.
The five steps of dynamic programming are:
- Define the dp array (dp table) and the meaning of its indices.
- Determine the transition formula.
- Initialize the dp array.
- Decide on the order of traversal.
- Deduce the dp array through examples.
At the start of the dynamic programming section, the problems discussed were relatively simple. Many readers mentioned that these simple problems seemed to be over-explained and could be solved directly by figuring out the transition formula.
Carl's perspective has always been that simple problems are meant to reinforce methodology. Simple problems can be tackled by intuition, but slightly more difficult problems are likely to defy such an approach.
Throughout the dynamic programming discussion, the importance of these five steps has consistently been highlighted.
Some readers believe that discovering the transition formula is the most challenging and crucial step, and once it's found, the rest follows easily.
However, if you think this way, your understanding of dynamic programming is likely incomplete.
In dynamic programming, if any of these steps are unclear, the problem can hardly be solved; even if it is, it hasn't been thoroughly understood, and the process feels foggy at best.
- If the specific meaning of the dp array is unclear, how can you discuss a transition formula? You may even make mistakes during initialization.
- For example, in 0063.Unique Paths II (opens new window), initialization is the key focus.
- If you've reviewed the knapsack series, especially the complete knapsack, the ordering of the two for loops can certainly confuse many people, while the transition formula is straightforward.
- As for the importance of deducing the dp array, it's almost always emphasized in each article within the dynamic programming section: when the program's output is incorrect, you must deduce the formula yourself to check it against the program's logs.
Great, let's revisit the content we've covered in the dynamic programming section.
# Basics of Dynamic Programming
- Dynamic Programming Fundamentals (opens new window)
- 0509.Fibonacci Number (opens new window)
- 0070.Climbing Stairs (opens new window)
- 0746.Min Cost Climbing Stairs (opens new window)
- 0062.Unique Paths (opens new window)
- 0063.Unique Paths II (opens new window)
- 0343.Integer Break (opens new window)
- 0096.Unique Binary Search Trees (opens new window)
# Knapsack Problem Series
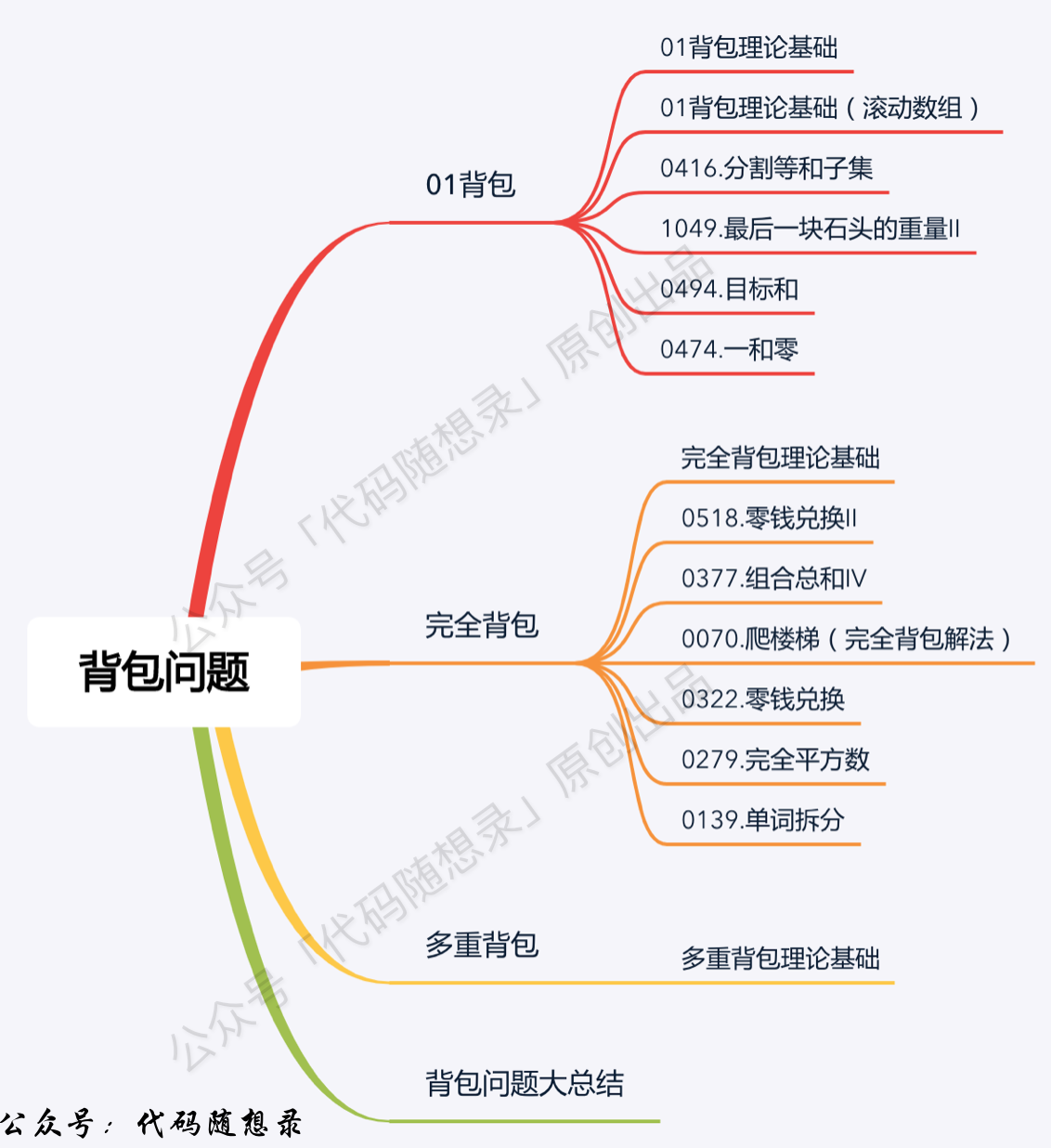
- Knapsack Theory 01 Knapsack-1 (opens new window)
- Knapsack Theory 01 Knapsack-2 (opens new window)
- 0416.Partition Equal Subset Sum (opens new window)
- 1049.Last Stone Weight II (opens new window)
- 0494.Target Sum (opens new window)
- 0474.Ones and Zeroes (opens new window)
- Knapsack Problem Theory Basics Complete Knapsack (opens new window)
- 0518.Coin Change II (opens new window)
- 0377.Combination Sum IV (opens new window)
- 0070.Climbing Stairs Complete Knapsack Version (opens new window)
- 0322.Coin Change (opens new window)
- 0279.Perfect Squares (opens new window)
- 0139.Word Break (opens new window)
- Knapsack Problem Theory Basics - Multiple Knapsack (opens new window)
- Knapsack Summary (opens new window)
# House Robbery Series
- 0198.House Robber (opens new window)
- 0213.House Robber II (opens new window)
- 0337.House Robber III (opens new window)
# Stock Series
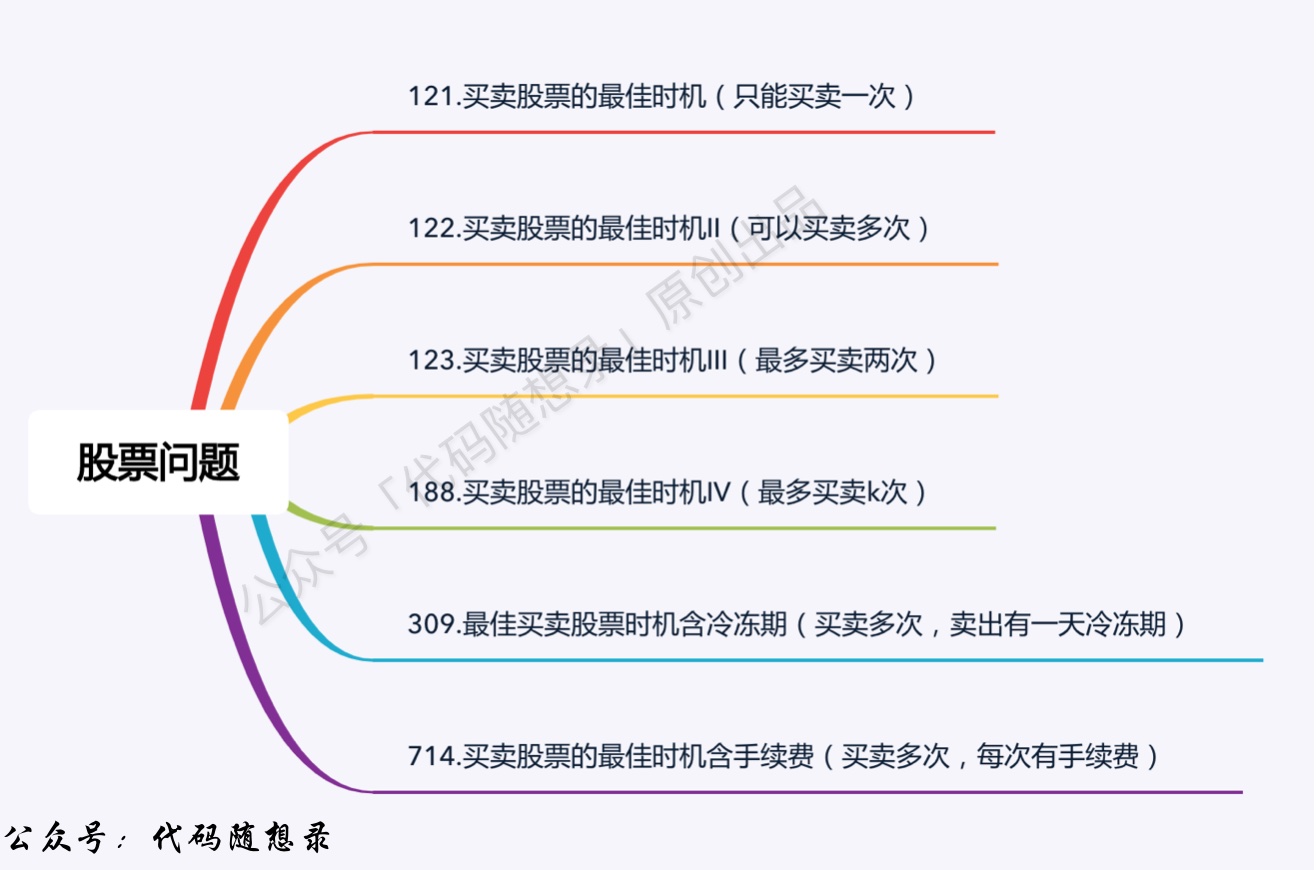
- 0121.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock (opens new window)
- Dynamic Programming-Stock Problem Summary (opens new window)
- 0122.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II (Dynamic Programming) (opens new window)
- 0123.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III (opens new window)
- 0188.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV (opens new window)
- 0309.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown (opens new window)
- 0714.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Transaction Fee (Dynamic Programming) (opens new window)
# Subsequence Series
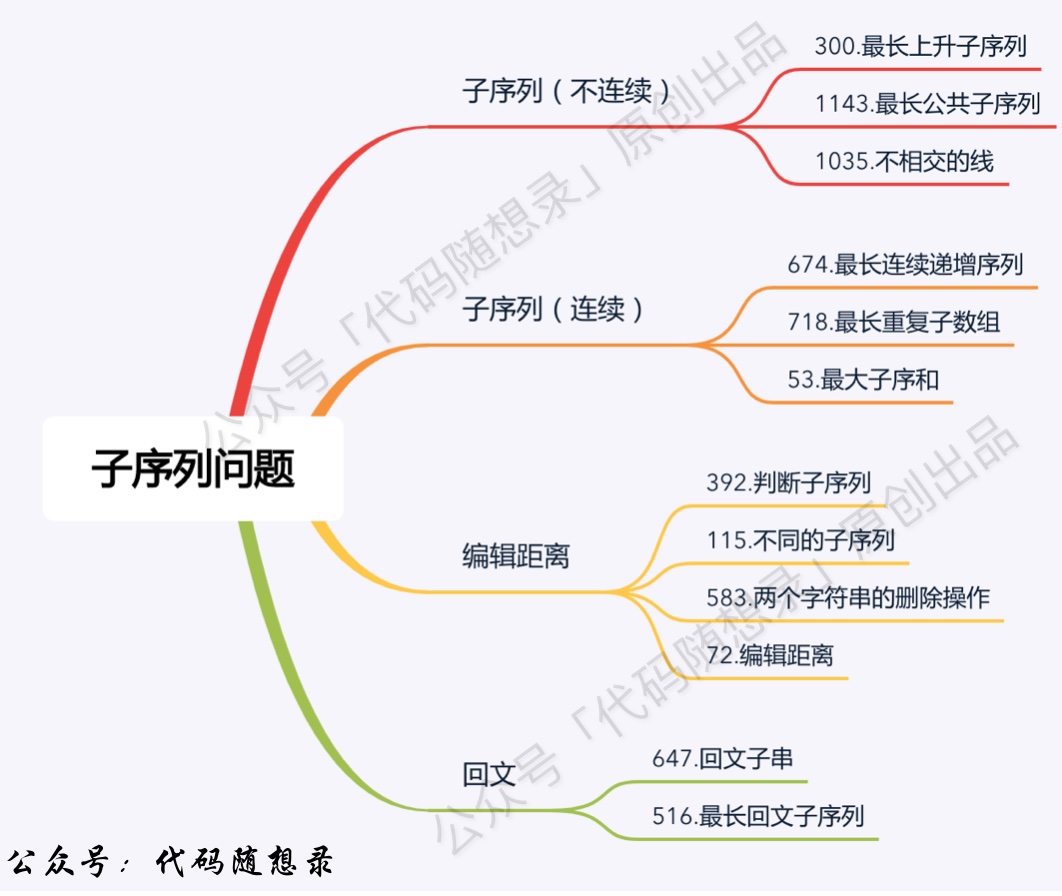
- 0300.Longest Increasing Subsequence (opens new window)
- 0674.Longest Continuous Increasing Subsequence (opens new window)
- 0718.Maximum Length of Repeated Subarray (opens new window)
- 1143.Longest Common Subsequence (opens new window)
- 1035.Uncrossed Lines (opens new window)
- 0053.Maximum Subarray (Dynamic Programming) (opens new window)
- 0392.Is Subsequence (opens new window)
- 0115.Distinct Subsequences (opens new window)
- 0583.Delete Operation for Two Strings (opens new window)
- 0072.Edit Distance (opens new window)
- Edit Distance in Three Steps by Karl (opens new window)
- 0647.Palindromic Substrings (opens new window)
- 0516.Longest Palindromic Subsequence (opens new window)
# Concluding Remarks on Dynamic Programming
Beyond dynamic programming, there are other types such as Tree DP (with one problem shown in the House Robbery series), Digit DP, Interval DP, Probability DP, Game DP, State Compression DP, etc. I won’t be explaining these; their occurrence in interviews is quite low.
If you thoroughly research all the problems listed in this article, your level of understanding of dynamic programming will be very high. It will be more than sufficient for interviews!
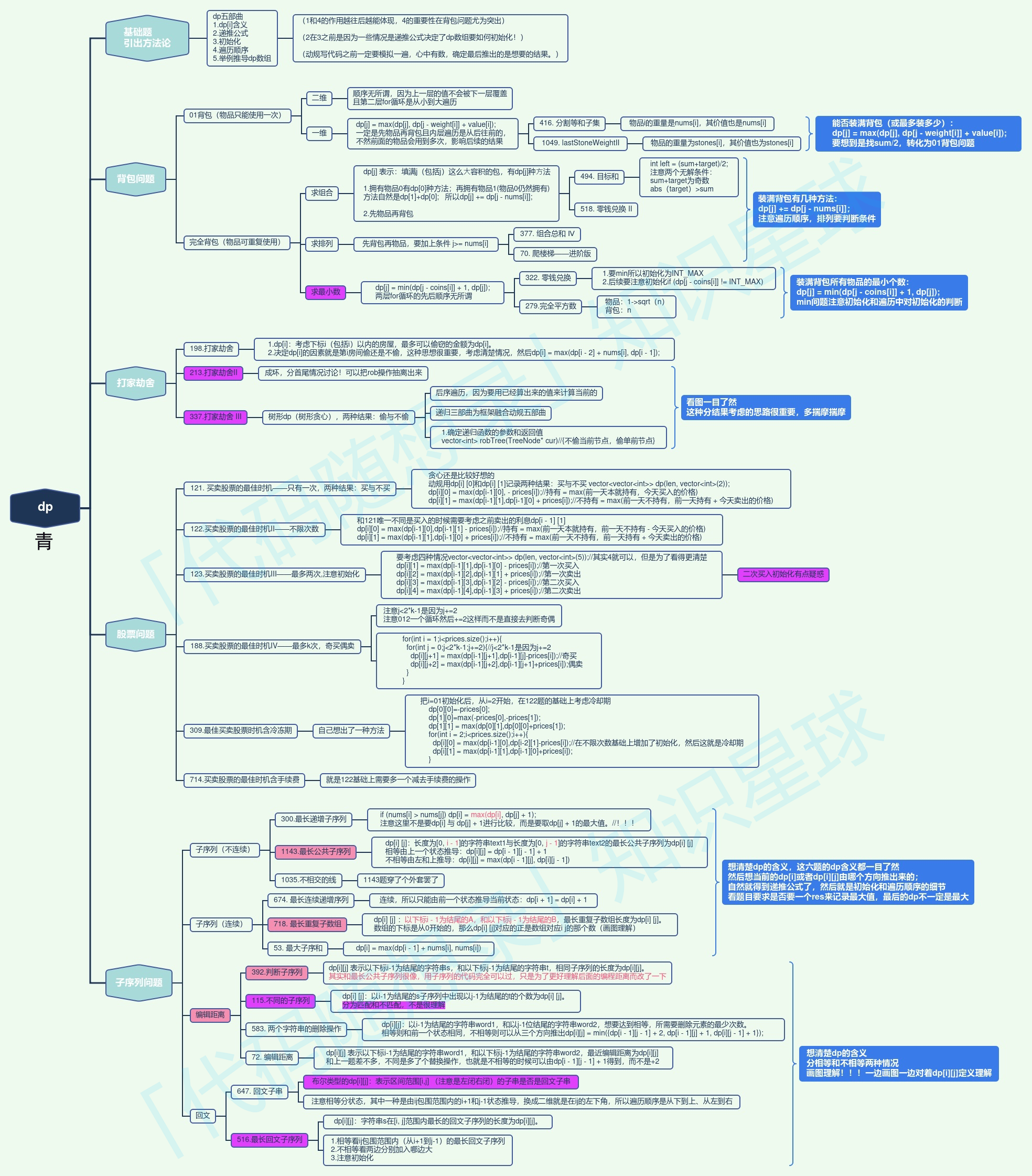
This diagram is created by a member Qing (opens new window) from the Coding Thoughts Knowledge Community (opens new window). It’s beautifully summarized and I'd like to share it with everyone.
This should be the most detailed explanation series on dynamic programming available online.
In fact, if you search online, you'll find that there are very few resources that can explain dynamic programming clearly because it is indeed challenging! Explaining it to others is even harder!
In "Sword Offer Background," dynamic programming problems are scarce; the classic algorithm book "Algorithm 4" does not discuss dynamic programming, and "Introduction to Algorithms" covers it at a level that could be quite discouraging.
Explaining a single problem clearly is easy, explaining two problems clearly is easy, but thoroughly elucidating dynamic programming in its entirety and implementing it with a consistent methodology throughout is extremely difficult.
Therefore, Carl has devoted significant efforts to sharing his complete understanding of dynamic programming to help you avoid detours. Keep going!
