Leverage the properties of Binary Search Trees!
# 530. Minimum Absolute Difference in BST
LeetCode problem link (opens new window)
Given a binary search tree with non-negative values, find the minimum absolute difference between values of any two nodes.
Example:

Note: There are at least two nodes in the BST.
# Approach
The task is to find the minimum absolute difference between any two nodes in a binary search tree.
Remember, it is a binary search tree, which is ordered.
Whenever you need to find max, min, or differences in a binary search tree, think of it as an ordered array, which simplifies the problem.
# Recursive Approach
An in-order traversal of a binary search tree results in an ordered array.
Finding the minimum difference between two numbers in an ordered array is straightforward.
The most intuitive idea is to convert the binary search tree into an ordered array and then iterate through the array to find the minimum difference.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> vec;
void traversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
traversal(root->left);
vec.push_back(root->val); // Convert the BST into an ordered array
traversal(root->right);
}
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
vec.clear();
traversal(root);
if (vec.size() < 2) return 0;
int result = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) { // Find the minimum difference in the ordered array
result = min(result, vec[i] - vec[i-1]);
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
In the above code, we convert the binary search tree into an ordered array. We can calculate the difference as we traverse the tree.
We need to use a pre node to remember the previous node for this purpose.
As shown in the diagram:
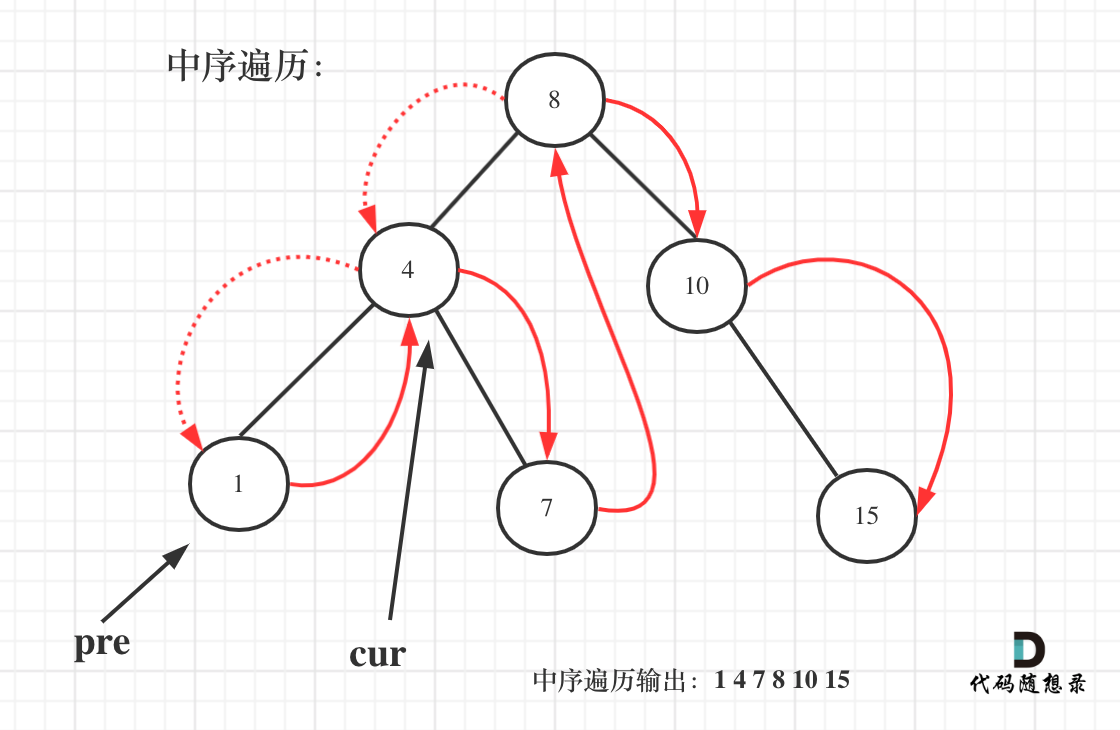
Some might not know how to maintain a pointer to the previous node in a recursive traversal. It's simple to implement and can be mastered once understood.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
private:
int result = INT_MAX;
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
void traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
traversal(cur->left); // Left
if (pre != NULL){ // Middle
result = min(result, cur->val - pre->val);
}
pre = cur; // Record previous
traversal(cur->right); // Right
}
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Doesn't seem too complex, right?
# Iterative Approach
After reading these two articles: Binary Tree: Anything Recursion Can Do, the Stack Can Do Too! (opens new window) and Binary Tree: Can’t We Unify the Methods of Preorder, Inorder, and Postorder Traversals? (opens new window), it's not hard to write the iterative in-order traversal for this problem.
Below is one way of writing the in-order traversal iteratively:
class Solution {
public:
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
int result = INT_MAX;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // Visit nodes by pointers, down to the bottom
st.push(cur); // Add the visited nodes to the stack
cur = cur->left; // Left
} else {
cur = st.top();
st.pop();
if (pre != NULL) { // Middle
result = min(result, cur->val - pre->val);
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->right; // Right
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Summary
When asked to find max/min value differences in a binary search tree, always think about the fact that a binary search tree is ordered and leverage that property.
Also, learn the small trick of maintaining two pointers during recursive traversal — once learned, it’s quite beneficial.
Next, I'll introduce a series of problems utilizing binary search tree properties.
# Other Language Versions
# Java
Recursive
class Solution {
TreeNode pre; // Record the previously visited node
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
// Left
traversal(root.left);
// Middle
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(result, root.val - pre.val);
}
pre = root;
// Right
traversal(root.right);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Unified Iterative Traversal
class Solution {
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (root != null)
stack.add(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.peek();
if (curr != null) {
stack.pop();
if (curr.right != null)
stack.add(curr.right);
stack.add(curr);
stack.add(null);
if (curr.left != null)
stack.add(curr.left);
} else {
stack.pop();
TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
if (pre != null)
result = Math.min(result, temp.val - pre.val);
pre = temp;
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Iterative In-order Traversal
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;
Stack<TreeNode> stack;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(result, cur.val - pre.val);
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Python
Recursive Version 1 - Using in-order traversal to build a sorted list
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.vec = []
def traversal(self, root):
if root is None:
return
self.traversal(root.left)
self.vec.append(root.val) # Convert the BST into an ordered array
self.traversal(root.right)
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
self.vec = []
self.traversal(root)
if len(self.vec) < 2:
return 0
result = float('inf')
for i in range(1, len(self.vec)):
# Find min difference in ordered array
result = min(result, self.vec[i] - self.vec[i - 1])
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Recursive Version 2 - Using in-order traversal to find the minimum difference
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.result = float('inf')
self.pre = None
def traversal(self, cur):
if cur is None:
return
self.traversal(cur.left) # Left
if self.pre is not None: # Middle
self.result = min(self.result, cur.val - self.pre.val)
self.pre = cur # Record previous node
self.traversal(cur.right) # Right
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
self.traversal(root)
return self.result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Iterative Approach
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
stack = []
cur = root
pre = None
result = float('inf')
while cur is not None or len(stack) > 0:
if cur is not None:
stack.append(cur) # Add visited nodes to stack
cur = cur.left # Left
else:
cur = stack.pop()
if pre is not None: # Middle
result = min(result, cur.val - pre.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right # Right
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# Go
Building a sorted array from the binary tree:
// Calculate minimum value during in-order traversal
func getMinimumDifference(root *TreeNode) int {
// Keep a pointer to the previous node
var prev *TreeNode
// Define a very large value
min := math.MaxInt64
var travel func(node *TreeNode)
travel = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
travel(node.Left)
if prev != nil && node.Val - prev.Val < min {
min = node.Val - prev.Val
}
prev = node
travel(node.Right)
}
travel(root)
return min
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# JavaScript
Recursive - First converting to a sorted array
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var getMinimumDifference = function (root) {
let arr = [];
const buildArr = (root) => {
if (root) {
buildArr(root.left);
arr.push(root.val);
buildArr(root.right);
}
}
buildArr(root);
let diff = arr[arr.length - 1];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (diff > arr[i] - arr[i - 1])
diff = arr[i] - arr[i - 1];
}
return diff;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
Recursive - Finding the minimum during traversal
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
let res = Infinity
let preNode = null
const inorder = (node) => {
if(!node) return
inorder(node.left)
if(preNode) res = Math.min(res, node.val - preNode.val)
preNode = node
inorder(node.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Iterative - In-order traversal
var getMinimumDifference = function(root) {
let stack = []
let cur = root
let res = Infinity
let pre = null
while(cur || stack.length) {
if(cur) {
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
} else {
cur = stack.pop()
if(pre) res = Math.min(res, cur.val - pre.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# TypeScript
Using auxiliary array to solve
function getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let helperArr: number[] = [];
function recur(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) return;
recur(root.left);
helperArr.push(root.val);
recur(root.right);
}
recur(root);
let resMin: number = Infinity;
for (let i = 0, length = helperArr.length; i < length - 1; i++) {
resMin = Math.min(resMin, helperArr[i + 1] - helperArr[i]);
}
return resMin;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Solving in recursion
function getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let preNode: TreeNode | null= null;
let resMin: number = Infinity;
function recur(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) return;
recur(root.left);
if (preNode !== null) {
resMin = Math.min(resMin, root.val - preNode.val);
}
preNode = root;
recur(root.right);
}
recur(root);
return resMin;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Iterative In-order Traversal
function getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode | null): number {
const helperStack: TreeNode[] = [];
let curNode: TreeNode | null = root;
let resMin: number = Infinity;
let preNode: TreeNode | null = null;
while (curNode !== null || helperStack.length > 0) {
if (curNode !== null) {
helperStack.push(curNode);
curNode = curNode.left;
} else {
curNode = helperStack.pop()!;
if (preNode !== null) {
resMin = Math.min(resMin, curNode.val - preNode.val);
}
preNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode.right;
}
}
return resMin;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Scala
Creating a sorted array from the binary tree:
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode): Int = {
val arr = mutable.ArrayBuffer[Int]()
def traversal(node: TreeNode): Unit = {
if (node == null) return
traversal(node.left)
arr.append(node.value)
traversal(node.right)
}
traversal(root)
var result = Int.MaxValue
for (i <- 1 until arr.size) {
result = math.min(result, arr(i) - arr(i - 1))
}
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Recording previous node during recursion:
object Solution {
def getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var result = Int.MaxValue
var pre: TreeNode = null
def traversal(cur: TreeNode): Unit = {
if (cur == null) return
traversal(cur.left)
if (pre != null) {
result = math.min(result, cur.value - pre.value)
}
pre = cur
traversal(cur.right)
}
traversal(root)
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Iterative solution:
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def getMinimumDifference(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var result = Int.MaxValue
var pre: TreeNode = null
var cur = root
var stack = mutable.Stack[TreeNode]()
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
} else {
cur = stack.pop()
if (pre != null) {
result = math.min(result, cur.value - pre.value)
}
pre = cur
cur = cur.right
}
}
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Rust
Building a sorted array from the binary tree:
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn get_minimum_difference(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut vec = vec![];
Self::traversal(root, &mut vec);
let mut min = i32::MAX;
for i in 1..vec.len() {
min = min.min(vec[i] - vec[i - 1])
}
min
}
pub fn traversal(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, v: &mut Vec<i32>) {
if root.is_none() {
return;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::traversal(node.left.clone(), v);
v.push(node.val);
Self::traversal(node.right.clone(), v);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
Calculating minimum during recursion
impl Solution {
pub fn get_minimum_difference(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut pre = None;
let mut min = i32::MAX;
Self::inorder(root, &mut pre, &mut min);
min
}
pub fn inorder(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, pre: &mut Option<i32>, min: &mut i32) {
if root.is_none() {
return;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::inorder(node.left.clone(), pre, min);
if let Some(pre) = pre {
*min = (node.val - *pre).min(*min);
}
*pre = Some(node.val);
Self::inorder(node.right.clone(), pre, min);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Iterative
impl Solution {
pub fn get_minimum_difference(mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let mut stack = vec![];
let mut pre = -1;
let mut res = i32::MAX;
while root.is_some() || !stack.is_empty() {
while let Some(node) = root {
root = node.borrow().left.clone();
stack.push(node);
}
let node = stack.pop().unwrap();
if pre >= 0 {
res = res.min(node.borrow().val - pre);
}
pre = node.borrow().val;
root = node.borrow().right.clone();
}
res
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# C#
// Recursive
public class Solution
{
public List<int> res = new List<int>();
public int GetMinimumDifference(TreeNode root)
{
Traversal(root);
return res.SelectMany((x, i) => res.Skip(i + 1).Select(y => Math.Abs(x - y))).Min();
}
public void Traversal(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return;
Traversal(root.left);
res.Add(root.val);
Traversal(root.right);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
