# 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

Return its maximum depth 3.
# Approach
After reading this section, you can proceed to solve the following two problems:
- 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (opens new window)
- 559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree (opens new window)
# Recursive Approach
For this problem, both pre-order (root-left-right) and post-order traversal (left-right-root) can be used. With pre-order traversal, you get the depth, and with post-order traversal, you get the height.
- The depth of a node in a binary tree is the number of edges or nodes from the root node to the node (depending on whether depth starts at 0 or 1).
- The height of a node in a binary tree is the number of edges or nodes from the node to the leaf node (depending on whether height starts at 0 or 1).
The height of the root node is the maximum depth of the binary tree, so in this problem, we determine the maximum depth by finding the height of the root node using a post-order traversal.
This is a point that many students do not fully understand and many solutions do not explain clearly.
Let's first calculate the tree's height using post-order traversal (left-right-root).
- Determine the parameters and return value of the recursive function: The parameter is the root node of the tree, and the return value is the depth of this tree, so the return type is
int.
int getdepth(TreeNode* node)
- Determine the termination condition: If the node is null, return 0, meaning the height is 0.
if (node == NULL) return 0;
- Determine the logic of a single layer of recursion: First find the depth of its left subtree, then the right subtree. Finally, take the maximum of the left and right depths and add 1 (the 1 accounts for the current root node), which is the depth of the tree with the current node as the root.
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // left
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // right
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // root
return depth;
2
3
4
Thus, the complete C++ code is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // left
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // right
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // root
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
The C++ code after simplification is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right));
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
The simplified code does not reveal which traversal method is used, nor does it show the steps of the recursive trio. Therefore, if you're not yet familiar with operations on binary trees, try to avoid directly learning from simplified code.
This problem can also be solved using pre-order traversal, as shown below: (clearly demonstrating the depth calculation and backtracking process)
class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // root
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // left
depth++; // Increment depth
getdepth(node->left, depth);
depth--; // Backtrack, decrement depth
}
if (node->right) { // right
depth++; // Increment depth
getdepth(node->right, depth);
depth--; // Backtrack, decrement depth
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == NULL) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Using pre-order traversal (root-left-right) sequence, this is the true logic for finding depth!
Notice that the above code is to make the details clear, simplify the code as follows:
class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // root
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // left
getdepth(node->left, depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) { // right
getdepth(node->right, depth + 1);
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == NULL) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Iterative Approach
When using an iterative approach, level-order traversal is the most suitable, because the maximum depth is the number of levels in the binary tree, which aligns very well with level-order traversal.
In a binary tree, traversing the tree level by level and recording the number of levels gives the depth of the binary tree, as shown in the diagram:
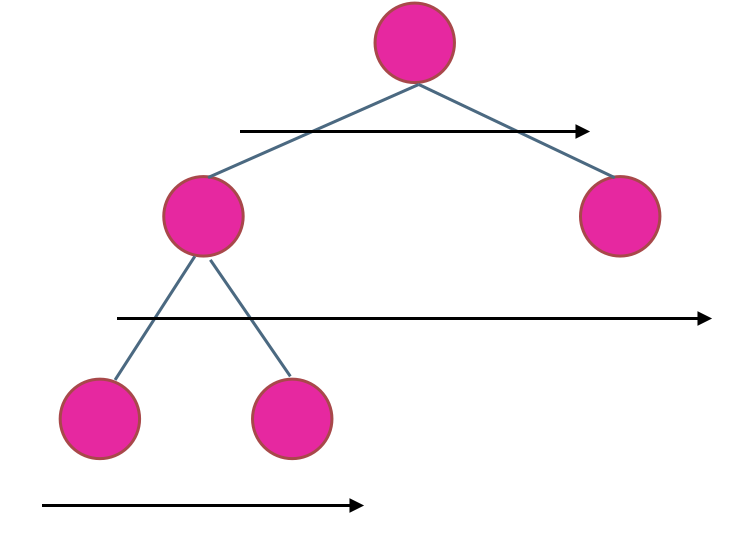
Thus, the iterative solution to this problem is a template problem, which can be solved using the binary tree level-order traversal template.
If you're still unclear about level-order traversal, you can refer to this article: 0102.Binary Tree Level Order Traversal (opens new window)
Below is the C++ code:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // Record depth
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Now we can conveniently solve the maximum depth of an n-ary tree problem.
# Related Problem Recommendation
# 559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given an n-ary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
For example, given a 3-ary tree:
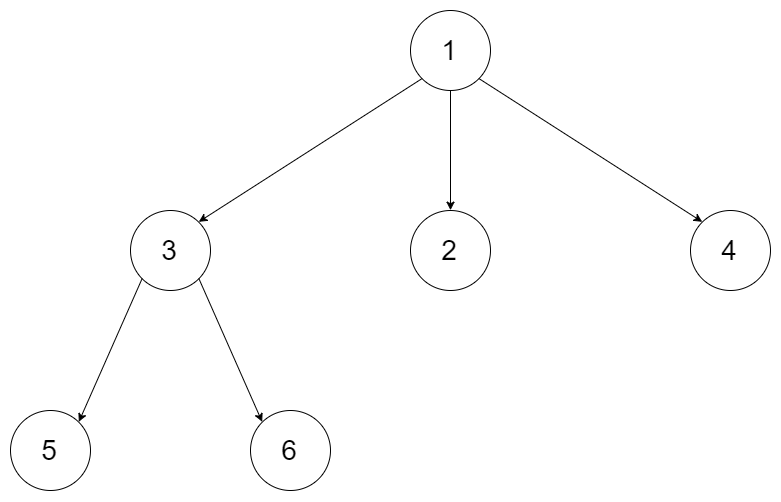
The tree's maximum depth is 3.
# Approach
Again, we can provide recursive and iterative solutions for this problem, the approach is similar to that used for binary trees. Directly provide the code as follows:
# Recursive Approach
C++ code:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == 0) return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
depth = max(depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Iterative Approach
Still use level-order traversal, code as follows:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // Record depth
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < node->children.size(); j++) {
if (node->children[j]) que.push(node->children[j]);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
class Solution {
/**
* Recursive Approach
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
/**
* Recursive Approach (For Depth Calculation)
*/
//Define maximum depth
int maxnum = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
ans(root,0);
return maxnum;
}
//Recursive method to solve maximum depth
void ans(TreeNode tr,int tmp){
if(tr==null) return;
tmp++;
maxnum = maxnum<tmp?tmp:maxnum;
ans(tr.left,tmp);
ans(tr.right,tmp);
tmp--;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class Solution {
/**
* Iterative Approach, using level-order traversal
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
deque.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
class Solution {
/* Recursive Approach, post-order traversal to calculate the height of root node */
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
if (root.children != null){
for (Node child : root.children){
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(child));
}
}
return depth + 1; // root node
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Solution {
/**
* Iterative Approach, using level-order traversal
*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
Queue<Node> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while (!que.isEmpty())
{
depth ++;
int len = que.size();
while (len > 0)
{
Node node = que.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < node.children.size(); i++)
if (node.children.get(i) != null)
que.offer(node.children.get(i));
len--;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# Python :
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Recursive Approach:
class Solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
return self.getdepth(root)
def getdepth(self, node):
if not node:
return 0
leftheight = self.getdepth(node.left) # left
rightheight = self.getdepth(node.right) # right
height = 1 + max(leftheight, rightheight) # root
return height
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Recursive Approach: Simplified Code
class Solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return 1 + max(self.maxdepth(root.left), self.maxdepth(root.right))
2
3
4
5
Level-Order Traversal Iterative Approach:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
depth = 0
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return depth
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
Recursive Approach:
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
max_depth = 1
for child in root.children:
max_depth = max(max_depth, self.maxDepth(child) + 1)
return max_depth
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Iterative Approach:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
depth = 0
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
for child in node.children:
queue.append(child)
return depth
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Using a Stack
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
max_depth = 0
stack = [(root, 1)]
while stack:
node, depth = stack.pop()
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
for child in node.children:
stack.append((child, depth + 1))
return max_depth
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Go:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
/**
* definition for a binary tree node.
* type treenode struct {
* val int
* left *treenode
* right *treenode
* }
*/
func max (a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a;
}
return b;
}
// Recursive
func maxdepth(root *treenode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0;
}
return max(maxdepth(root.left), maxdepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
// Iterative
func maxdepth(root *treenode) int {
levl := 0;
queue := make([]*treenode, 0);
if root != nil {
queue = append(queue, root);
}
for l := len(queue); l > 0; {
for ;l > 0;l-- {
node := queue[0];
if node.left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.left);
}
if node.right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.right);
}
queue = queue[1:];
}
levl++;
l = len(queue);
}
return levl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
q := list.New()
q.PushBack(root)
depth := 0
for q.Len() > 0 {
n := q.Len()
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
node := q.Remove(q.Front()).(*Node)
for j := range node.Children {
q.PushBack(node.Children[j])
}
}
depth++
}
return depth
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# JavaScript :
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
var maxdepth = function(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
return 1 + Math.max(maxdepth(root.left), maxdepth(root.right))
};
2
3
4
Recursive Binary Tree Maximum Depth
var maxdepth = function(root) {
//Using a recursive method, three steps for recursion
//1. Determine the parameters and return value of the recursive function
const getdepth = function(node) {
//2. Determine the termination conditions
if(node === null) {
return 0;
}
//3. Determine the logic of a single layer
let leftdepth = getdepth(node.left);
let rightdepth = getdepth(node.right);
let depth = 1 + Math.max(leftdepth, rightdepth);
return depth;
}
return getdepth(root);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Binary Tree Maximum Depth Level-Order Traversal
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let count = 0
const queue = [root]
while(queue.length) {
let size = queue.length
/* Level +1 */
count++
while(size--) {
let node = queue.shift();
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return count
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
Recursive Implementation of Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let depth = 0
for(let node of root.children) {
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(node))
}
return depth + 1
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Level-Order Traversal for Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) return 0
let count = 0
let queue = [root]
while(queue.length) {
let size = queue.length
count++
while(size--) {
let node = queue.shift()
for (let item of node.children) {
item && queue.push(item);
}
}
}
return count
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# TypeScript:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
// Post-order Traversal (Bottom-Up)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
if (root === null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
};
// Pre-order Traversal (Top-Down)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
function recur(node: TreeNode | null, count: number) {
if (node === null) {
resMax = resMax > count ? resMax : count;
return;
}
recur(node.left, count + 1);
recur(node.right, count + 1);
}
let resMax: number = 0;
let count: number = 0;
recur(root, count);
return resMax;
};
// Level-Order Traversal (Iterative)
function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let helperQueue: TreeNode[] = [];
let resDepth: number = 0;
let tempNode: TreeNode;
if (root !== null) helperQueue.push(root);
while (helperQueue.length > 0) {
resDepth++;
for (let i = 0, length = helperQueue.length; i < length; i++) {
tempNode = helperQueue.shift()!;
if (tempNode.left) helperQueue.push(tempNode.left);
if (tempNode.right) helperQueue.push(tempNode.right);
}
}
return resDepth;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
// Post-order Traversal (Bottom-Up)
function maxDepth(root: Node | null): number {
if (root === null) return 0
let depth = 0
for (let i = 0; i < root.children.length; i++) {
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(root.children[i]))
}
return depth + 1
}
// Pre-order Traversal (Top-Down)
function maxDepth(root: Node | null): number {
if (root === null) return 0
let depth: number = 0
const queue: Array<Node | null> = []
queue.push(root)
while (queue.length > 0) {
let len = queue.length
depth++
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// Traverse the current level
let curNode: Node | null = queue.shift()!
for (let j = 0; j < curNode.children.length; j++) {
if (curNode.children[j]) queue.push(curNode.children[j])
}
}
}
return depth
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# C:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Binary Tree Maximum Depth Recursion
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
// If the input node is NULL, return 0
if(!root)
return 0;
// Calculate the depth of the left subtree
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
// Calculate the depth of the right subtree
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
// Take the maximum of the depths of the left and right subtrees
int max = left > right ? left : right;
// Return the maximum depth plus 1 (1 represents the current level)
return max + 1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Binary Tree Maximum Depth Iteration
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
// If the input root node is NULL, return 0
if(!root)
return 0;
int depth = 0;
// Allocate queue space
struct TreeNode** queue = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 6000);
int queueFront = 0;
int queueEnd = 0;
// Enqueue the root node
queue[queueEnd++] = root;
int queueSize;
// Calculate the number of elements in the current queue
while(queueSize = queueEnd - queueFront) {
int i;
// If the current node in the queue has left and right subtrees, enqueue them too
for(i = 0; i < queueSize; i++) {
struct TreeNode* tempNode = queue[queueFront + i];
if(tempNode->left)
queue[queueEnd++] = tempNode->left;
if(tempNode->right)
queue[queueEnd++] = tempNode->right;
}
// Update the front of the queue
queueFront += queueSize;
// Increment depth
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
Binary Tree Maximum Depth Iteration—Post-order Traversal
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return 0;
struct TreeNode *stack[10000] = {};
int top = -1;
struct TreeNode *p = root, *r = NULL; // r points to the last visited node
int depth = 0, maxDepth = -1;
while(p != NULL || top >= 0)
{
if(p != NULL)
{
stack[++top] = p;
depth++;
p = p->left;
}
else
{
p = stack[top];
if(p->right != NULL && p->right != r) // Right subtree not visited
p = p->right;
else
{
if(depth >= maxDepth) maxDepth = depth;
p = stack[top--];
depth--;
r = p;
p = NULL;
}
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# Swift:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
// Recursion - Post-order
func maxDepth1(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
return _maxDepth1(root)
}
func _maxDepth1(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
let leftDepth = _maxDepth1(root!.left)
let rightDepth = _maxDepth1(root!.right)
return 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth)
}
// Level-Order
func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
var queue = [TreeNode]()
queue.append(root)
var res: Int = 0
while !queue.isEmpty {
res += 1
for _ in 0 ..< queue.count {
let node = queue.removeFirst()
if let left = node.left {
queue.append(left)
}
if let right = node.right {
queue.append(right)
}
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
// Recursion
func maxDepth(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
var depth = 0
for node in root.children {
depth = max(depth, maxDepth(node))
}
return depth + 1
}
// Iterative-Level Order Traversal
func maxDepth1(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
guard let root = root else {
return 0
}
var depth = 0
var queue = [Node]()
queue.append(root)
while !queue.isEmpty {
let size = queue.count
depth += 1
for _ in 0 ..< size {
let node = queue.removeFirst()
for child in node.children {
queue.append(child)
}
}
}
return depth
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# Scala:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Recursive Approach:
object Solution {
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
def process(curNode: TreeNode): Int = {
if (curNode == null) return 0
// Recursively call the left and right nodes and return the maximum value, then add 1
math.max(process(curNode.left), process(curNode.right)) + 1
}
// Call the recursive method, the return keyword can be omitted
process(root)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Iterative Approach:
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def maxDepth(root: TreeNode): Int = {
var depth = 0
if (root == null) return depth
val queue = mutable.Queue[TreeNode]()
queue.enqueue(root)
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
val len = queue.size
for (i <- 0 until len) {
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
if (curNode.left != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.left)
if (curNode.right != null) queue.enqueue(curNode.right)
}
depth += 1 // Increment depth when there is a level
}
depth
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
Recursive Approach:
object Solution {
def maxDepth(root: Node): Int = {
if (root == null) return 0
var depth = 0
for (node <- root.children) {
depth = math.max(depth, maxDepth(node))
}
depth + 1
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Iterative Approach: (Level-Order Traversal)
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def maxDepth(root: Node): Int = {
if (root == null) return 0
var depth = 0
val queue = mutable.Queue[Node]()
queue.enqueue(root)
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
val len = queue.size
depth += 1
for (i <- 0 until len) {
val curNode = queue.dequeue()
for (node <- curNode.children) queue.enqueue(node)
}
}
depth
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Rust:
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Recursive:
impl Solution {
pub fn max_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
std::cmp::max(
Self::max_depth(root.clone().unwrap().borrow().left.clone()),
Self::max_depth(root.unwrap().borrow().right.clone()),
) + 1
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Iterative:
impl Solution {
pub fn max_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if root.is_none(){
return 0;
}
let mut max_depth: i32 = 0;
let mut stack = vec![root.unwrap()];
while !stack.is_empty() {
let num = stack.len();
for _i in 0..num{
let top = stack.remove(0);
if top.borrow_mut().left.is_some(){
stack.push(top.borrow_mut().left.take().unwrap());
}
if top.borrow_mut().right.is_some(){
stack.push(top.borrow_mut().right.take().unwrap());
}
}
max_depth+=1;
}
max_depth
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# C#
- Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
// Recursive Approach
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = MaxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = MaxDepth(root.right);
return 1 + Math.Max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// Pre-order Traversal
int result = 0;
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return result;
GetDepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
public void GetDepth(TreeNode root, int depth)
{
result = depth > result ? depth : result;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return;
if (root.left != null)
GetDepth(root.left, depth + 1);
if (root.right != null)
GetDepth(root.right, depth + 1);
return;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// Iterative Approach
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
{
int depth = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> que = new();
if (root == null) return depth;
que.Enqueue(root);
while (que.Count != 0)
{
int size = que.Count;
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
var node = que.Dequeue();
if (node.left != null) que.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null) que.Enqueue(node.right);
}
}
return depth;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree Recursive Approach
/*
Recursive Approach
*/
public class Solution {
public int MaxDepth(Node root) {
int res = 0;
/* Termination condition */
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
/* Logic */
// Traverse the child nodes of the current node
for (int i = 0; i < root.children.Count; i++)
{
res = Math.Max(res, MaxDepth(root.children[i]));
}
return res + 1;
}
}
// @lc code=end
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Iterative Approach (Level-Order Traversal)
/*
Iterative Approach
*/
public class Solution
{
public int MaxDepth(Node root)
{
Queue<Node> que = new Queue<Node>(); // Use a generic queue to store nodes
int res = 0;
if(root != null){
que.Enqueue(root); // Enqueue the root node
}
while (que.Count > 0)
{
int size = que.Count; // Get the number of nodes at the current level
res++; // Increment depth
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
// Traverse each level
var curNode = que.Dequeue(); // Dequeue the node
for (int j = 0; j < curNode.children.Count; j++)
{
if (curNode.children[j] != null)
{
que.Enqueue(curNode.children[j]); // Enqueue the child node
}
}
}
}
return res; // Return the maximum depth of the tree
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
