# 51. N-Queens
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
The N-Queens problem is about placing n queens on an n×n chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the placement of the n queens, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
Example 1:
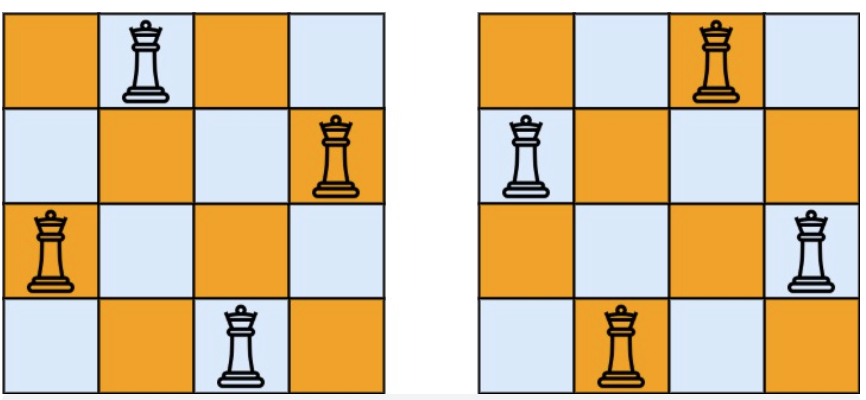
- Input: n = 4
- Output: [[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
- Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens problem as shown above.
Example 2:
- Input: n = 1
- Output: [["Q"]]
# Approach
It is well known that the n-queens problem is typically solved using backtracking, but the presence of a 2D matrix while applying this technique can still be overwhelming after handling combinations, cuttings, subsets, and permutation problems.
Let's first consider the constraints associated with placing queens:
- They must not be placed in the same row.
- They must not be placed in the same column.
- They must not be placed on the same diagonal.
Having the constraints clearly defined, consider how to go about searching for the positions to place queens. The search for queens' positions can be visualized as a tree.
For example, using a 3x3 chessboard and abstracting the search process to a tree structure:
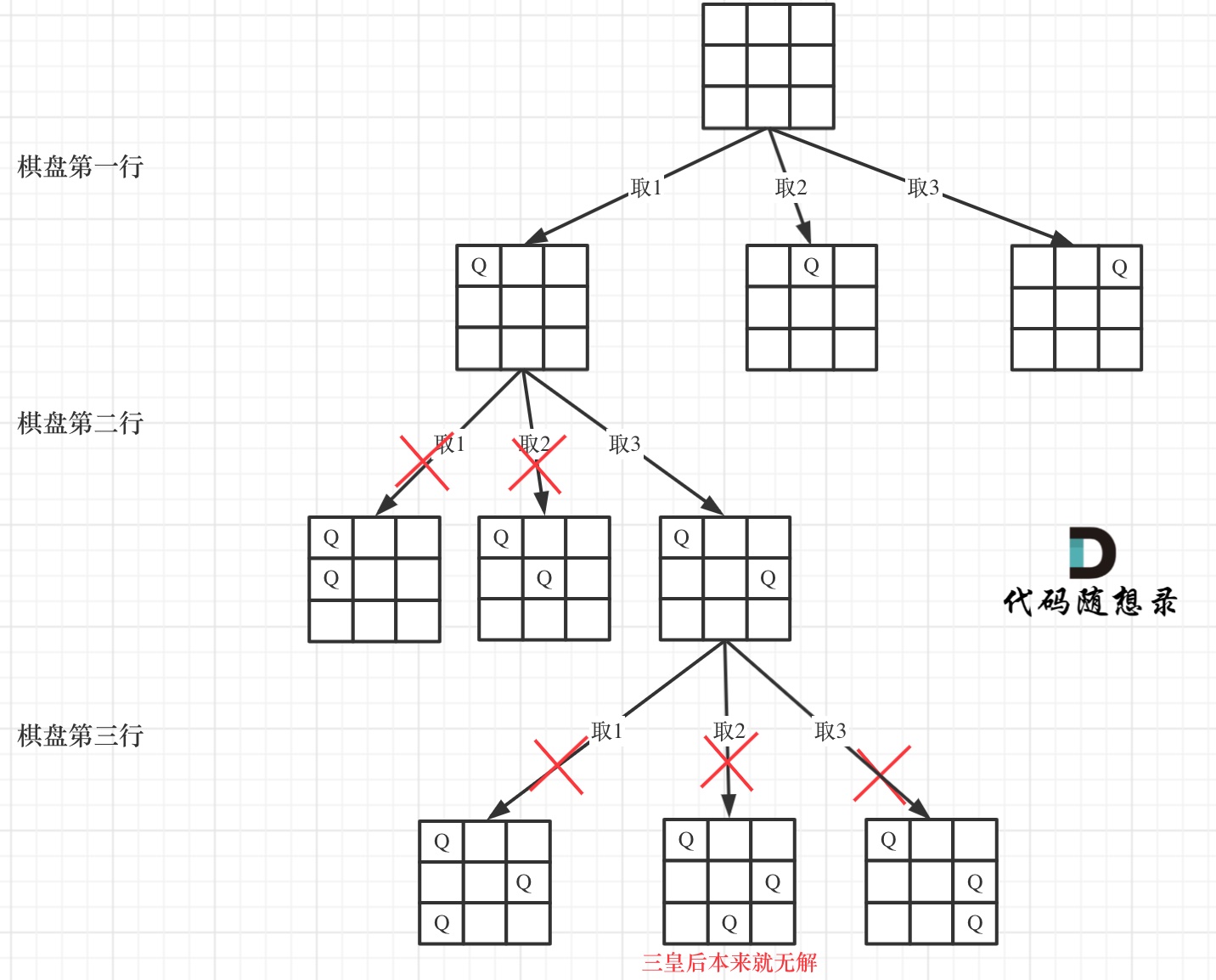
From the tree, it is apparent that the matrix's height corresponds to the tree height, and the matrix width corresponds to the width of each level in the tree structure.
We traverse this tree guided by the constraints until we reach the leaf nodes, where a valid placement for the queens is found.
# Backtracking in Three Steps
Following the established template for backtracking, let's explore it systematically:
void backtracking(parameters) {
if (termination condition) {
store result;
return;
}
for (choice: choices in current layer (number of child nodes equals the number of choices)) {
process the node;
backtracking(path, choice list); // recursion
backtrack to remove the current decision's impact
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- Recursive Function Parameters
Here, a global variable result, a 2D array, is used to store the final outcome.
The parameter n represents the size of the chessboard, while row tracks the current row being processed.
Code:
vector<vector<string>> result;
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
2
- Termination Condition for Recursion
As evident from the tree structure diagram:

Upon reaching the tree's bottom level (the leaf nodes), collect the results and return.
Code:
if (row == n) {
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
2
3
4
- Logic for Single Layer Search
The recurrence depth indicated by row traverses the board row-by-row, while the for loop on col controls the columns for each row, thereby determining the position to place a queen.
Each row starts searching from its initial position, thus always beginning from 0.
Code:
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // Place a queen if placement is valid
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // Place queen
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // Backtrack to remove the queen
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
- Verify Validity of the Board
Apply the following standard for elimination:
- No two queens in the same row
- No two queens in the same column
- No two queens on the same diagonal (45-degree and 135-degree angles)
Code:
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
// Check column
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // Employ branch-cutting
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// Check 45-degree diagonal
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// Check 135-degree diagonal
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
The key realization is that, within each layer of search, selection from the same row is inherently avoided due to how recursion and looping are structured, hence there's no need to check for same-row repetitions.
It's then straightforward to write the following C++ code:
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> result;
// n denotes board size
// row denotes the current recursion depth
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // If valid, then place the queen
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // Place queen
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // Backtrack to remove the queen
}
}
}
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
// Column check
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // This acts as a branch cut
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 45-degree angle check
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 135-degree angle check
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
result.clear();
std::vector<std::string> chessboard(n, std::string(n, '.'));
backtracking(n, 0, chessboard);
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
- Time Complexity: O(n!)
- Space Complexity: O(n)
Notice that aside from verifying the validity of the chessboard, the remaining structure is fashioned in accordance with the backtracking template.
# Summary
This problem is our first exposure to a chessboard-related task.
For those encountering the N-Queens problem for the first time, there might be an initial lack of direction, possibly understanding that backtracking is involved but unsure how to proceed with the search.
Here, I explicitly illustrate that the chessboard's width essentially equals the length of the for loop, and the depth of recursion corresponds to the chessboard's height, which then can seamlessly fit into the backtracking template.
Feel free to further explore and digest these concepts!
# Additional Languages
# Java
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n];
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
}
backTrack(n, 0, chessboard);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(int n, int row, char[][] chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
res.add(Array2List(chessboard));
return;
}
for (int col = 0;col < n; ++col) {
if (isValid (row, col, n, chessboard)) {
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
backTrack(n, row+1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
public List Array2List(char[][] chessboard) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
list.add(String.copyValueOf(c));
}
return list;
}
public boolean isValid(int row, int col, int n, char[][] chessboard) {
// Check column
for (int i=0; i<row; ++i) { // Prunes the search space
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// Check 45 degree diagonal
for (int i=row-1, j=col-1; i>=0 && j>=0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// Check 135 degree diagonal
for (int i=row-1, j=col+1; i>=0 && j<=n-1; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
// Method 2: Using boolean arrays to represent occupied lines (diagonals included)
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] usedCol, usedDiag45, usedDiag135; // Each element in the boolean array represents a line
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
usedCol = new boolean[n]; // Number of columns
usedDiag45 = new boolean[2 * n - 1]; // Number of 45-degree lines
usedDiag135 = new boolean[2 * n - 1]; // Number of 135-degree lines
// Track results. Element index denotes the row, value indicates the column
int[] board = new int[n];
backTracking(board, n, 0);
return res;
}
private void backTracking(int[] board, int n, int row) {
if (row == n) {
// Collect results
List<String> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i : board) {
char[] str = new char[n];
Arrays.fill(str, '.');
str[i] = 'Q';
temp.add(new String(str));
}
res.add(temp);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (usedCol[col] | usedDiag45[row + col] | usedDiag135[row - col + n - 1]) {
continue;
}
board[row] = col;
// Mark the column as occupied
usedCol[col] = true;
// Elements on the 45-degree diagonal have a constant row + col
usedDiag45[row + col] = true;
// Elements on the 135-degree diagonal have a constant row - col
usedDiag135[row - col + n - 1] = true;
// Recur
backTracking(board, n, row + 1);
usedCol[col] = false;
usedDiag45[row + col] = false;
usedDiag135[row - col + n - 1] = false;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# Python
class Solution:
def solveNQueens(self, n: int) -> List[List[str]]:
result = [] # 2D string array to store the final result
chessboard = ['.' * n for _ in range(n)] # Initialize the board
self.backtracking(n, 0, chessboard, result) # Backtrack to solve
return [[''.join(row) for row in solution] for solution in result] # Return the result set
def backtracking(self, n: int, row: int, chessboard: List[str], result: List[List[str]]) -> None:
if row == n:
result.append(chessboard[:]) # Once the board is filled, add the current solution to the result.
return
for col in range(n):
if self.isValid(row, col, chessboard):
chessboard[row] = chessboard[row][:col] + 'Q' + chessboard[row][col+1:] # Place the queen
self.backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard, result) # Recur to the next row
chessboard[row] = chessboard[row][:col] + '.' + chessboard[row][col+1:] # Backtrack to remove the queen
def isValid(self, row: int, col: int, chessboard: List[str]) -> bool:
# Check the column
for i in range(row):
if chessboard[i][col] == 'Q':
return False # A queen already exists in the column, invalid placement
# Check the 45-degree diagonal for queens
i, j = row - 1, col - 1
while i >= 0 and j >= 0:
if chessboard[i][j] == 'Q':
return False # A queen is found in the upper-left direction, invalid placement
i -= 1
j -= 1
# Check the 135-degree diagonal for queens
i, j = row - 1, col + 1
while i >= 0 and j < len(chessboard):
if chessboard[i][j] == 'Q':
return False # A queen is found in the upper-right direction, invalid placement
i -= 1
j += 1
return True # Valid position for a queen
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# Go
func solveNQueens(n int) [][]string {
var res [][]string
chessboard := make([][]string, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
chessboard[i] = make([]string, n)
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
chessboard[i][j] = "."
}
}
var backtrack func(int)
backtrack = func(row int) {
if row == n {
temp := make([]string, n)
for i, rowStr := range chessboard {
temp[i] = strings.Join(rowStr, "")
}
res = append(res, temp)
return
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if isValid(n, row, i, chessboard) {
chessboard[row][i] = "Q"
backtrack(row + 1)
chessboard[row][i] = "."
}
}
}
backtrack(0)
return res
}
func isValid(n, row, col int, chessboard [][]string) bool {
for i := 0; i < row; i++ {
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q" {
return false
}
}
for i, j := row-1, col-1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i, j = i-1, j-1 {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" {
return false
}
}
for i, j := row-1, col+1; i >= 0 && j < n; i, j = i-1, j+1 {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" {
return false
}
}
return true
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# JavaScript
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {string[][]}
*/
var solveNQueens = function (n) {
const ans = [];
const path = [];
const matrix = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill("."));
// Determine if the queens can attack each other
const canAttack = (matrix, row, col) => {
let i;
let j;
// Check the column
for (i = 0, j = col; i < n; i++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
// Check the left and right sides
for (i = row, j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
// Check the upper left
for (i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
// Check the upper right
for (i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
const backtrack = (matrix, row, col) => {
if (path.length === matrix.length) {
ans.push(path.slice());
return;
}
for (let i = row; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (let j = col; j < matrix.length; j++) {
// If the current position causes mutual attack, continue to the next search
if (canAttack(matrix, i, j)) {
continue;
}
matrix[i][j] = "Q";
path.push(matrix[i].join(""));
// Start a new row search, only one queen can be placed per row
backtrack(matrix, i + 1, 0);
matrix[i][j] = ".";
path.pop();
}
}
};
backtrack(matrix, 0, 0);
return ans;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# TypeScript
function solveNQueens(n: number): string[][] {
const board: string[][] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(_ => new Array(n).fill('.'));
const resArr: string[][] = [];
backTracking(n, 0, board);
return resArr;
function backTracking(n: number, rowNum: number, board: string[][]): void {
if (rowNum === n) {
resArr.push(transformBoard(board));
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isValid(i, rowNum, board) === true) {
board[rowNum][i] = 'Q';
backTracking(n, rowNum + 1, board);
board[rowNum][i] = '.';
}
}
}
};
function isValid(col: number, row: number, board: string[][]): boolean {
const n: number = board.length;
if (col < 0 || col >= n || row < 0 || row >= n) return false;
// Check column
for (let row of board) {
if (row[col] === 'Q') return false;
}
// Check 45-degree diagonal
let x: number = col,
y: number = row;
while (y >= 0 && x < n) {
if (board[y--][x++] === 'Q') return false;
}
// Check 135-degree diagonal
x = col;
y = row;
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0) {
if (board[y--][x--] === 'Q') return false;
}
return true;
}
function transformBoard(board: string[][]): string[] {
const resArr = [];
for (let row of board) {
resArr.push(row.join(''));
}
return resArr;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Swift
func solveNQueens(_ n: Int) -> [[String]] {
var result = [[String]]()
// Chessboard, using a 2D array of Character for easier updates
var chessboard = [[Character]](repeating: [Character](repeating: ".", count: n), count: n)
// Check if the chessboard configuration is a valid N-Queens arrangement
func isVaild(row: Int, col: Int) -> Bool {
// Check the column
for i in 0 ..< row {
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q" { return false }
}
var i, j: Int
// Check 45-degree
i = row - 1
j = col - 1
while i >= 0 && j >= 0 {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" { return false }
i -= 1
j -= 1
}
// Check 135-degree
i = row - 1
j = col + 1
while i >= 0 && j < n {
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" { return false }
i -= 1
j += 1
}
return true
}
func backtracking(row: Int) {
if row == n {
result.append(chessboard.map { String($0) })
}
for col in 0 ..< n {
guard isVaild(row: row, col: col) else { continue }
chessboard[row][col] = "Q" // Place the queen
backtracking(row: row + 1)
chessboard[row][col] = "." // Backtrack
}
}
backtracking(row: 0)
return result
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# Rust
impl Solution {
fn is_valid(row: usize, col: usize, chessboard: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>, n: usize) -> bool {
let mut i = 0 as usize;
while i < row {
if chessboard[i][col] == 'Q' { return false; }
i += 1;
}
let (mut i, mut j) = (row as i32 - 1, col as i32 - 1);
while i >= 0 && j >= 0 {
if chessboard[i as usize][j as usize] == 'Q' { return false; }
i -= 1;
j -= 1;
}
let (mut i, mut j) = (row as i32 - 1, col as i32 + 1);
while i >= 0 && j < n as i32 {
if chessboard[i as usize][j as usize] == 'Q' { return false; }
i -= 1;
j += 1;
}
return true;
}
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<String>>, n: usize, row: usize, chessboard: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) {
if row == n {
let mut chessboard_clone: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
for i in chessboard {
chessboard_clone.push(i.iter().collect::<String>());
}
result.push(chessboard_clone);
return;
}
for col in 0..n {
if Self::is_valid(row, col, chessboard, n) {
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
Self::backtracking(result, n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
pub fn solve_n_queens(n: i32) -> Vec<Vec<String>> {
let mut result: Vec<Vec<String>> = Vec::new();
let mut chessboard: Vec<Vec<char>> = vec![vec!['.'; n as usize]; n as usize];
Self::backtracking(&mut result, n as usize, 0, &mut chessboard);
result
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# C
char ***ans;
char **path;
int ansTop, pathTop;
// Copy the path into ans
void copyPath(int n) {
char **tempPath = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * pathTop);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < pathTop; ++i) {
tempPath[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * n + 1);
int j;
for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
tempPath[i][j] = path[i][j];
tempPath[i][j] = '\0';
}
ans[ansTop++] = tempPath;
}
// Check if the current position can be attacked by any other queens
int isValid(int x, int y, int n) {
int i, j;
// Check the same row and column for validity
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(path[y][i] == 'Q' || path[i][x] == 'Q')
return 0;
}
// Check the 45-degree diagonal for validity
i = y - 1;
j = x - 1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
--i, --j;
}
i = y + 1;
j = x + 1;
while(i < n && j < n) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
++i, ++j;
}
// Check the 135-degree diagonal for validity
i = y - 1;
j = x + 1;
while(i >= 0 && j < n) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
--i, ++j;
}
i = y + 1;
j = x -1;
while(j >= 0 && i < n) {
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
return 0;
++i, --j;
}
return 1;
}
void backTracking(int n, int depth) {
// If path contains n elements, copy them to ans and return
if(pathTop == n) {
copyPath(n);
return;
}
// Loop through horizontal board positions
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// Check if the current position is valid
if(isValid(i, depth, n)) {
// Place queen at current position
path[depth][i] = 'Q';
// Increment path element count
++pathTop;
backTracking(n, depth + 1);
// Perform backtracking
path[depth][i] = '.';
// Decrement path element count
--pathTop;
}
}
}
// Initialize path stored as a char* array, set every element to '.'
void initPath(int n) {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Allocate space for each char* in path
path[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * n + 1);
// Set all characters in path to '.'
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
path[i][j] = '.';
// Append '\0' to each string
path[i][j] = '\0';
}
}
char *** solveNQueens(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
// Initialize auxiliary variables
ans = (char***)malloc(sizeof(char**) * 400);
path = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * n);
ansTop = pathTop = 0;
// Initialize the path array
initPath(n);
backTracking(n, 0);
// Set return array size
*returnSize = ansTop;
int i;
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * ansTop);
for(i = 0; i < ansTop; ++i) {
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = n;
}
return ans;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
# Scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def solveNQueens(n: Int): List[List[String]] = {
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[String]]()
def judge(x: Int, y: Int, maze: Array[Array[Boolean]]): Boolean = {
// Direct top
var xx = x
while (xx >= 0) {
if (maze(xx)(y)) return false
xx -= 1
}
// Direct left
var yy = y
while (yy >= 0) {
if (maze(x)(yy)) return false
yy -= 1
}
// Top left
xx = x
yy = y
while (xx >= 0 && yy >= 0) {
if (maze(xx)(yy)) return false
xx -= 1
yy -= 1
}
xx = x
yy = y
// Top right
while (xx >= 0 && yy < n) {
if (maze(xx)(yy)) return false
xx -= 1
yy += 1
}
true
}
def backtracking(row: Int, maze: Array[Array[Boolean]]): Unit = {
if (row == n) {
// Transform result into required form
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
for (x <- maze) {
var tmp = mutable.ListBuffer[String]()
for (y <- x) {
if (y == true) tmp.append("Q")
else tmp.append(".")
}
path.append(tmp.mkString)
}
result.append(path.toList)
return
}
for (j <- 0 until n) {
// Determine if the position is suitable for placing a queen
if (judge(row, j, maze)) {
maze(row)(j) = true
backtracking(row + 1, maze)
maze(row)(j) = false
}
}
}
backtracking(0, Array.ofDim[Boolean](n, n))
result.toList
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
# C#
public class Solution
{
public List<IList<string>> res = new();
public IList<IList<string>> SolveNQueens(int n)
{
char[][] chessBoard = new char[n][];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
chessBoard[i] = new char[n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
chessBoard[i][j] = '.';
}
}
BackTracking(n, 0, chessBoard);
return res;
}
public void BackTracking(int n, int row, char[][] chessBoard)
{
if (row == n)
{
res.Add(chessBoard.Select(x => new string(x)).ToList());
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
if (IsValid(row, col, chessBoard, n))
{
chessBoard[row][col] = 'Q';
BackTracking(n, row + 1, chessBoard);
chessBoard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
public bool IsValid(int row, int col, char[][] chessBoard, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if (chessBoard[i][col] == 'Q') return false;
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
{
if (chessBoard[i][j] == 'Q') return false;
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++)
{
if (chessBoard[i][j] == 'Q') return false;
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
