# 1382. Balance a Binary Search Tree
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given a binary search tree, return a balanced binary search tree with the same node values. If there are multiple ways to achieve this, return any one of them.
A binary search tree is considered balanced if the height difference between the left and right subtrees for every node is no more than 1.
Example:
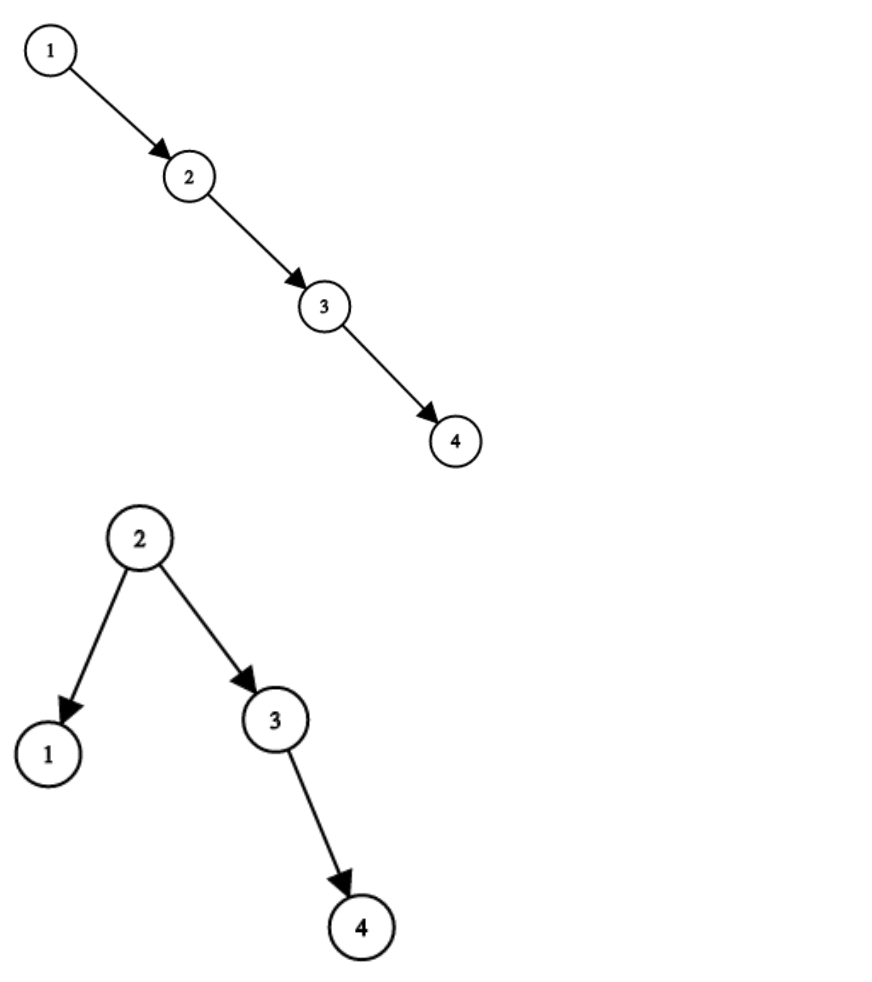
- Input:
root = [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,null] - Output:
[2,1,3,null,null,null,4] - Explanation: This is not the only correct answer;
[3,1,4,null,2,null,null]is also a valid solution.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is between 1 and 10^4.
- Node values are unique and between 1 and 10^5.
# Solution
To solve this problem, we can perform an inorder traversal to convert the binary tree into a sorted array and then construct a balanced binary search tree from the sorted array.
Before attempting this problem, it's recommended to review the following two explanations:
- 0098.Validate Binary Search Tree (opens new window) to understand the properties of a binary search tree.
- 0108.Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (opens new window) to learn how to construct a balanced binary search tree from a sorted array.
After understanding these, this problem will be straightforward.
Here is the code:
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> vec;
// Convert binary tree to sorted array
void traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == nullptr) {
return;
}
traversal(cur->left);
vec.push_back(cur->val);
traversal(cur->right);
}
// Convert sorted array to balanced binary search tree
TreeNode* getTree(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) return nullptr;
int mid = left + ((right - left) / 2);
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = getTree(nums, left, mid - 1);
root->right = getTree(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* balanceBST(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root);
return getTree(vec, 0, vec.size() - 1);
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
class Solution {
ArrayList <Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Convert binary tree to sorted array
private void travesal(TreeNode cur) {
if (cur == null) return;
travesal(cur.left);
res.add(cur.val);
travesal(cur.right);
}
// Convert sorted array to balanced binary search tree
private TreeNode getTree(ArrayList <Integer> nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) return null;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums.get(mid));
root.left = getTree(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = getTree(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
public TreeNode balanceBST(TreeNode root) {
travesal(root);
return getTree(res, 0, res.size() - 1);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Python:
class Solution:
def balanceBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
res = []
# Convert binary tree to sorted array
def traversal(cur: TreeNode):
if not cur: return
traversal(cur.left)
res.append(cur.val)
traversal(cur.right)
# Convert sorted array to balanced binary search tree
def getTree(nums: List, left, right):
if left > right: return
mid = left + (right -left) // 2
root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
root.left = getTree(nums, left, mid - 1)
root.right = getTree(nums, mid + 1, right)
return root
traversal(root)
return getTree(res, 0, len(res) - 1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# Go:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func balanceBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// Convert binary tree to sorted array
nums := []int{}
// Inorder traversal
var travel func(node *TreeNode)
travel = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
travel(node.Left)
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
travel(node.Right)
}
// Construct balanced binary search tree using binary search
var buildTree func(nums []int, left, right int) *TreeNode
buildTree = func(nums []int, left, right int) *TreeNode {
if left > right {
return nil
}
mid := left + (right-left) >> 1
root := &TreeNode{Val: nums[mid]}
root.Left = buildTree(nums, left, mid-1)
root.Right = buildTree(nums, mid+1, right)
return root
}
travel(root)
return buildTree(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# JavaScript:
var balanceBST = function(root) {
const res = [];
// Inorder traversal to convert to a sorted array
const travesal = cur => {
if(!cur) return;
travesal(cur.left);
res.push(cur.val);
travesal(cur.right);
}
// Construct a balanced binary search tree from the sorted array
const getTree = (nums, left, right) => {
if(left > right) return null;
let mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
let root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);// Use the middle element as the current node value
root.left = getTree(nums, left, mid - 1);// Recursively create the left subtree
root.right = getTree(nums, mid + 1, right);// Recursively create the right subtree
return root;
}
travesal(root);
return getTree(res, 0, res.length - 1);
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# TypeScript:
function balanceBST(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
const inorderArr: number[] = [];
inorderTraverse(root, inorderArr);
return buildTree(inorderArr, 0, inorderArr.length - 1);
};
function inorderTraverse(node: TreeNode | null, arr: number[]): void {
if (node === null) return;
inorderTraverse(node.left, arr);
arr.push(node.val);
inorderTraverse(node.right, arr);
}
function buildTree(arr: number[], left: number, right: number): TreeNode | null {
if (left > right) return null;
const mid = (left + right) >> 1;
const resNode: TreeNode = new TreeNode(arr[mid]);
resNode.left = buildTree(arr, left, mid - 1);
resNode.right = buildTree(arr, mid + 1, right);
return resNode;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Copyright © 2025 keetcoder
