# 100. Same Tree
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same values.
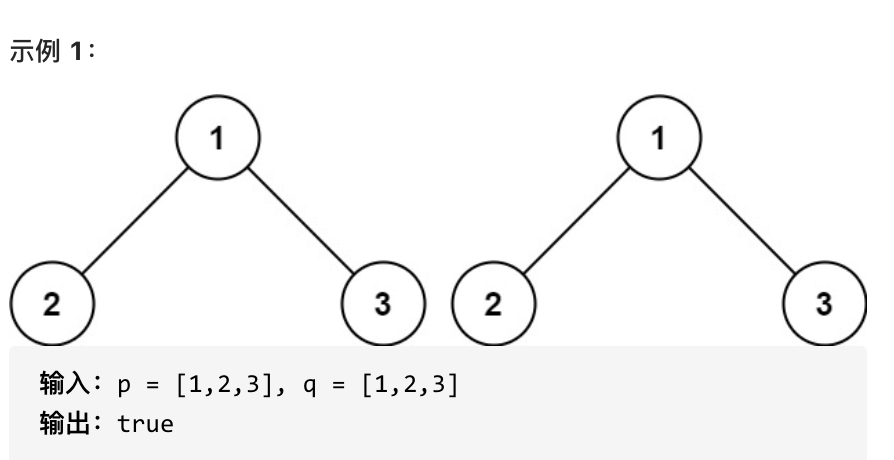
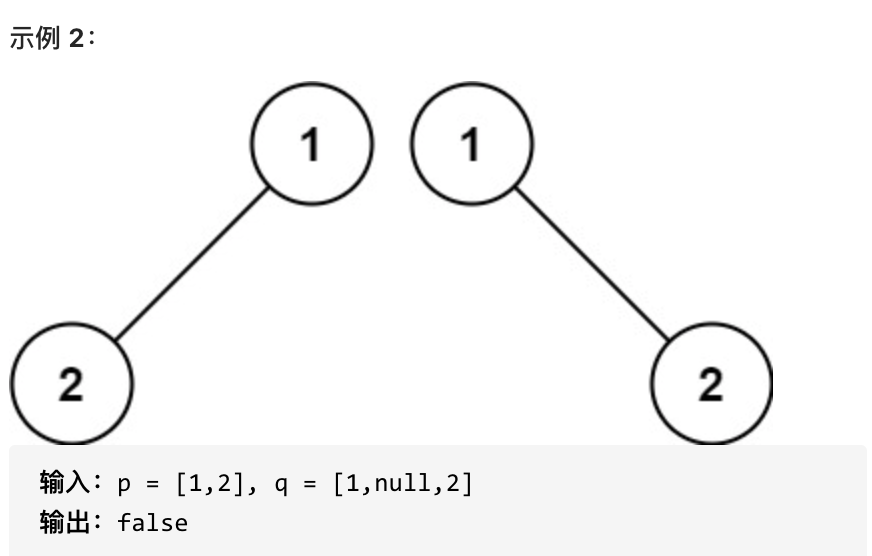
# Thought Process
In 0101.Symmetric Tree (opens new window), we discussed that to check if a binary tree is symmetric, we must compare if the left subtree and right subtree of the root node are mirrors of each other. Understanding this means that we actually need to compare two trees (the left and right subtrees of the root node), allowing us to grasp that the recursion involves traversing both trees simultaneously.
With this understanding, you'll find that determining if two binary trees are symmetric and determining if they are identical are almost the same problem.
If you haven't read 0101.Symmetric Tree (opens new window) yet, please read it carefully before attempting this problem for a better understanding.
In the context of recursion, we follow a three-step process:
- Determine the parameters and return value of the recursive function
We need to compare if two trees are identical, so the parameters are the root nodes of the two trees.
The return type is bool.
The code is as follows:
bool compare(TreeNode* tree1, TreeNode* tree2)
The analysis is similar to 0101.Symmetric Tree (opens new window).
- Determine the termination condition
To compare the values of two nodes, we first need to handle the cases where one or both nodes are null to avoid operating on a null pointer.
Cases where nodes are null include:
tree1is null andtree2is not, not symmetric, returnfalsetree1is not null andtree2is, not symmetric, returnfalse- Both
tree1andtree2are null, symmetric, returntrue
Now, we exclude cases where nodes are null, leaving cases where neither tree1 nor tree2 is null:
- Both
tree1andtree2are not null, compare node values, if not equal returnfalse
Now, we've handled situations where the nodes are not null and their values are not the same.
The code is as follows:
if (tree1 == NULL && tree2 != NULL) return false;
else if (tree1 != NULL && tree2 == NULL) return false;
else if (tree1 == NULL && tree2 == NULL) return true;
else if (tree1->val != tree2->val) return false; // Note I didn't use else here
2
3
4
The analysis is similar to 0101.Symmetric Tree (opens new window).
- Determine the logic for a single level of recursion
- To compare if two binary trees are identical: pass in the left child of
tree1and the left child oftree2. - If both sides are identical return
true, if one side isn't returnfalse.
The code is as follows:
bool left = compare(tree1->left, tree2->left); // Left subtree: left, right subtree: left
bool right = compare(tree1->right, tree2->right); // Left subtree: right, right subtree: right
bool isSame = left && right; // Left subtree: center, right subtree: center (logical processing)
return isSame;
2
3
4
The complete C++ code for the recursive solution is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* tree1, TreeNode* tree2) {
if (tree1 == NULL && tree2 != NULL) return false;
else if (tree1 != NULL && tree2 == NULL) return false;
else if (tree1 == NULL && tree2 == NULL) return true;
else if (tree1->val != tree2->val) return false; // Note I didn't use else here
// Now: both nodes are not null and values are equal
// Proceed to recursion for next-level comparisons
bool left = compare(tree1->left, tree2->left); // Left: left, right: left
bool right = compare(tree1->right, tree2->right); // Left: right, right: right
bool isSame = left && right; // Left: center, right: center
return isSame;
}
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
return compare(p, q);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
The code provided may not be the most concise, but it clearly outlines each step of the logical process.
If you jump straight to online concise code, it may seem straightforward; however, many logical details may be omitted and possibly not explained in depth in the solutions.
Blindly copying without understanding results in "solving a simple problem" without fully appreciating each logical decision.
Of course, I can organize the code in a more concise manner as follows:
# Recursive Approach
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
else return compare(left->left, right->left) && compare(left->right, right->right);
}
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
return compare(p, q);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Iterative Approach
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;
if (p == NULL || q == NULL) return false;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(p); // Add root node p
que.push(q); // Add root node q
while (!que.empty()) {
TreeNode* leftNode = que.front(); que.pop();
TreeNode* rightNode = que.front(); que.pop();
if (!leftNode && !rightNode) { // If both nodes are null
continue;
}
// If one node is null or values differ
if (!leftNode || !rightNode || (leftNode->val != rightNode->val)) {
return false;
}
que.push(leftNode->left); // Add left subtree node of p
que.push(rightNode->left); // Add left subtree node of q
que.push(leftNode->right); // Add right subtree node of p
que.push(rightNode->right); // Add right subtree node of q
}
return true;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# Versions in Other Languages
# Java:
// Recursive Approach
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) return true;
else if (q == null || p == null) return false;
else if (q.val != p.val) return false;
return isSameTree(q.left, p.left) && isSameTree(q.right, p.right);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// Iterative Approach
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
if(p == null || q == null) return false;
Queue<TreeNode> que= new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
que.offer(p);
que.offer(q);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
TreeNode leftNode = que.poll();
TreeNode rightNode = que.poll();
if(leftNode == null && rightNode == null) continue;
if(leftNode == null || rightNode== null || leftNode.val != rightNode.val) return false;
que.offer(leftNode.left);
que.offer(rightNode.left);
que.offer(leftNode.right);
que.offer(rightNode.right);
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Python:
# Recursive Approach
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not p and not q: return True
elif not p or not q: return False
elif p.val != q.val: return False
return self.isSameTree(p.left, q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right, q.right)
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Iterative Approach
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not p and not q: return True
if not p or not q: return False
que = collections.deque()
que.append(p)
que.append(q)
while que:
leftNode = que.popleft()
rightNode = que.popleft()
if not leftNode and not rightNode: continue
if not leftNode or not rightNode or leftNode.val != rightNode.val: return False
que.append(leftNode.left)
que.append(rightNode.left)
que.append(leftNode.right)
que.append(rightNode.right)
return True
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Go:
Recursive Approach
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
if p != nil && q == nil {
return false
}
if p == nil && q != nil {
return false
}
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
}
if p.Val != q.Val {
return false
}
Left := isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left)
Right := isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
return Left && Right
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# JavaScript:
Recursive Approach
var isSameTree = function (p, q) {
if (p == null && q == null)
return true;
if (p == null || q == null)
return false;
if (p.val != q.val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Iterative Approach
var isSameTree = (p, q) => {
const queue = [{ p, q }];
// Using { } to handle null instances
while (queue.length) {
const cur = queue.shift();
if (cur.p == null && cur.q == null) continue;
if (cur.p == null || cur.q == null) return false;
if (cur.p.val != cur.q.val) return false;
queue.push({
p: cur.p.left,
q: cur.q.left
}, {
p: cur.p.right,
q: cur.q.right
});
}
return true;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# TypeScript:
Recursive Approach - Preorder Traversal
function isSameTree(p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean {
if (p === null && q === null) return true;
if (p === null || q === null) return false;
if (p.val !== q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
};
2
3
4
5
6
Iterative Approach - Level Order Traversal
function isSameTree(p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean {
const queue1: (TreeNode | null)[] = [],
queue2: (TreeNode | null)[] = [];
queue1.push(p);
queue2.push(q);
while (queue1.length > 0 && queue2.length > 0) {
const node1 = queue1.shift(),
node2 = queue2.shift();
if (node1 === null && node2 === null) continue;
if (
(node1 === null || node2 === null) ||
node1!.val !== node2!.val
) return false;
queue1.push(node1!.left);
queue1.push(node2!.left);
queue1.push(node1!.right);
queue2.push(node2!.right);
}
return true;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
