# Interview Question 02.07: Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Same as: 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given the heads of two singly linked lists, headA and headB, find and return the node at which the two linked lists intersect. If they do not intersect, return null.
The example below shows two linked lists intersecting at node c1:
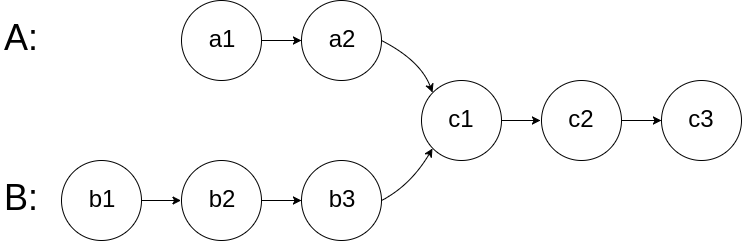
The problem data ensures no loops exist in the entire linked structure.
Note that after the function returns, the linked lists must retain their original structure.
Example 1:
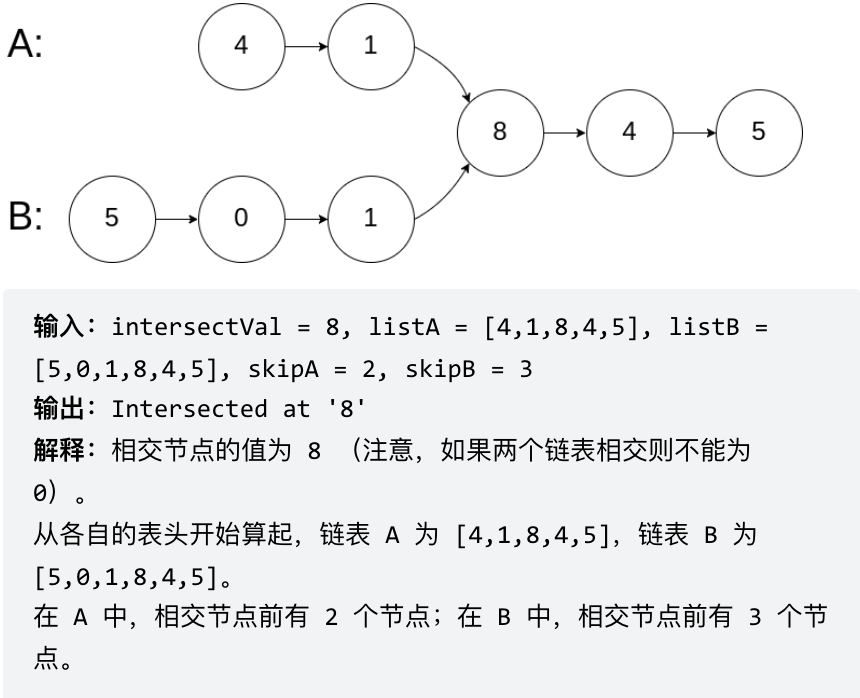
Example 2:
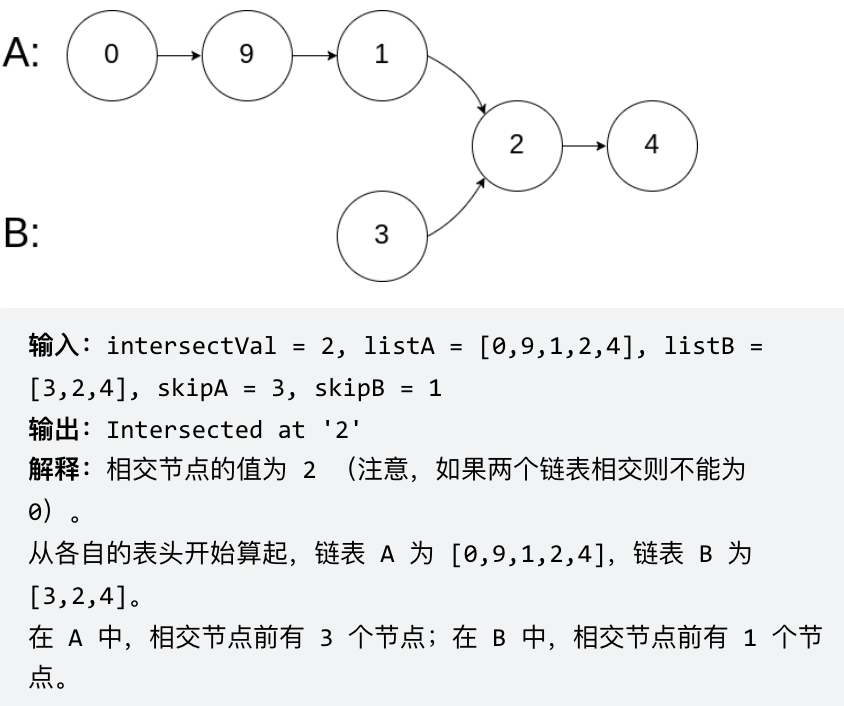
Example 3:
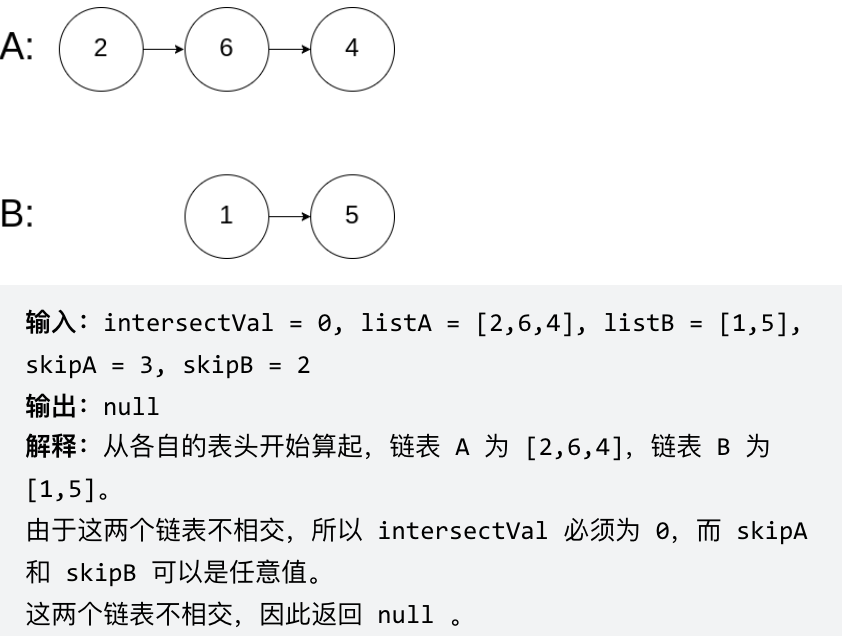
# Approach
In simple terms, we need to find the pointer of the intersecting node of the two linked lists. Note that the intersection is determined by pointer equality, not value equality.
To simplify, assume that the nodes have equal values if the pointers are equal.
Consider these two linked lists: currently, curA points to the head of list A, and curB points to the head of list B:
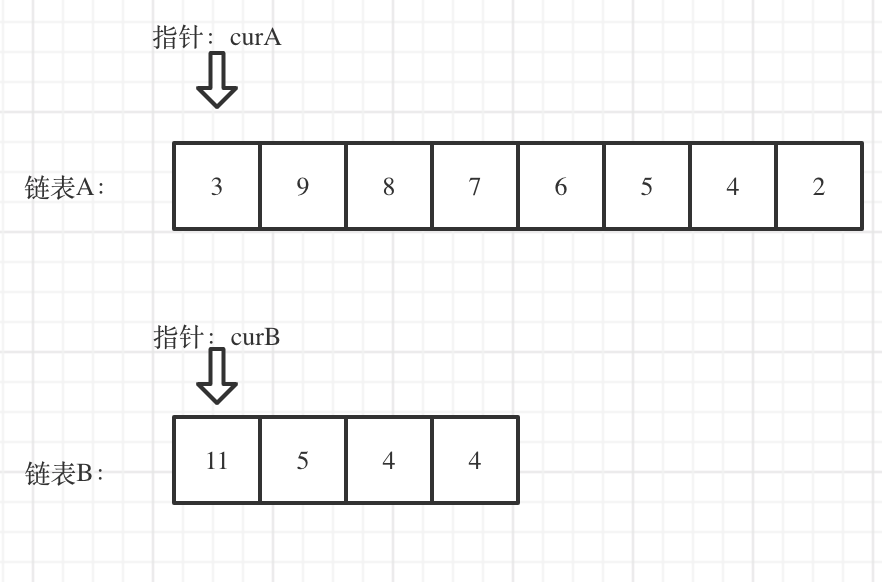
Calculate the lengths of both linked lists and the difference between them. Move curA to the position aligning with the end of curB, as shown below:
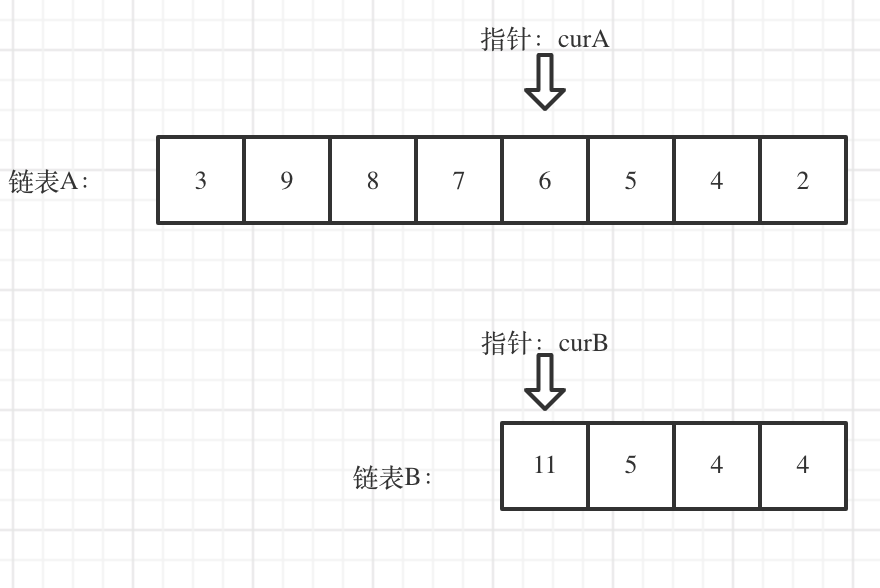
Now you can compare curA and curB. If they are not equal, move them forward simultaneously, and if curA == curB, you have found the intersection node.
Otherwise, exit the loop and return a null pointer.
C++ code is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != NULL) { // Calculate the length of linked list A
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while (curB != NULL) { // Calculate the length of linked list B
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// Make curA point to the longer list's head, with lenA being its length
if (lenB > lenA) {
swap (lenA, lenB);
swap (curA, curB);
}
// Calculate the length difference
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// Align curA and curB to the same starting point (end position aligned)
while (gap--) {
curA = curA->next;
}
// Traverse curA and curB; return immediately upon finding the same node
while (curA != NULL) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
- Time complexity: O(n + m)
- Space complexity: O(1)
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
(Version 1) Advance the longer linked list to achieve synchronized movement
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != null) { // Calculate the length of linked list A
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curB != null) { // Calculate the length of linked list B
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// Make curA point to the longer list's head, with lenA being its length
if (lenB > lenA) {
//1. swap (lenA, lenB);
int tmpLen = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmpLen;
//2. swap (curA, curB);
ListNode tmpNode = curA;
curA = curB;
curB = tmpNode;
}
// Calculate the length difference
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// Align curA and curB to the same starting point (end position aligned)
while (gap-- > 0) {
curA = curA.next;
}
// Traverse curA and curB; return immediately upon finding the same node
while (curA != null) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
(Version 2) Merge linked lists for synchronized movement
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// p1 points to head of A, p2 points to head of B
ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB;
while (p1 != p2) {
// Move p1 one step; if it reaches end of A, switch to B
if (p1 == null) p1 = headB;
else p1 = p1.next;
// Move p2 one step; if it reaches end of B, switch to A
if (p2 == null) p2 = headA;
else p2 = p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# Python:
(Version 1) Calculate length, start simultaneously
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
lenA, lenB = 0, 0
cur = headA
while cur: # Calculate the length of linked list A
cur = cur.next
lenA += 1
cur = headB
while cur: # Calculate the length of linked list B
cur = cur.next
lenB += 1
curA, curB = headA, headB
if lenA > lenB: # Make curB point to the longer list's head, with lenB being its length
curA, curB = curB, curA
lenA, lenB = lenB, lenA
for _ in range(lenB - lenA): # Align curA and curB to the same starting point (end position aligned)
curB = curB.next
while curA: # Traverse curA and curB; return immediately upon finding the same node
if curA == curB:
return curA
else:
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
return None
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
(Version 2) Calculate length, start simultaneously (Code reuse)
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
lenA = self.getLength(headA)
lenB = self.getLength(headB)
# Move the longer list to make lengths equal
if lenA > lenB:
headA = self.moveForward(headA, lenA - lenB)
else:
headB = self.moveForward(headB, lenB - lenA)
# Move both heads forward until they intersect
while headA and headB:
if headA == headB:
return headA
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return None
def getLength(self, head: ListNode) -> int:
length = 0
while head:
length += 1
head = head.next
return length
def moveForward(self, head: ListNode, steps: int) -> ListNode:
while steps > 0:
head = head.next
steps -= 1
return head
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
(Version 3) Calculate length, start simultaneously (Code reuse + Simplification)
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dis = self.getLength(headA) - self.getLength(headB)
# Move the longer list to make lengths equal
if dis > 0:
headA = self.moveForward(headA, dis)
else:
headB = self.moveForward(headB, abs(dis))
# Move both heads forward until they intersect
while headA and headB:
if headA == headB:
return headA
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return None
def getLength(self, head: ListNode) -> int:
length = 0
while head:
length += 1
head = head.next
return length
def moveForward(self, head: ListNode, steps: int) -> ListNode:
while steps > 0:
head = head.next
steps -= 1
return head
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
(Version 4) Equal method
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# Deal with edge cases
if not headA or not headB:
return None
# Initialize two pointers at the heads of each linked list
pointerA = headA
pointerB = headB
# Traverse both linked lists until the pointers meet
while pointerA != pointerB:
# Move pointers forward one node
pointerA = pointerA.next if pointerA else headB
pointerB = pointerB.next if pointerB else headA
# Upon intersection, pointers will reside at the intersecting node; if not, the value is None
return pointerA
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# Go:
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
curA := headA
curB := headB
lenA, lenB := 0, 0
// Calculate the lengths of A and B
for curA != nil {
curA = curA.Next
lenA++
}
for curB != nil {
curB = curB.Next
lenB++
}
var step int
var fast, slow *ListNode
// Find length difference and move the longer list ahead
if lenA > lenB {
step = lenA - lenB
fast, slow = headA, headB
} else {
step = lenB - lenA
fast, slow = headB, headA
}
for i:=0; i < step; i++ {
fast = fast.Next
}
// Traverse both lists, stop upon finding the same node
for fast != slow {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return fast
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
Two-pointer method
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
l1,l2 := headA, headB
for l1 != l2 {
if l1 != nil {
l1 = l1.Next
} else {
l1 = headB
}
if l2 != nil {
l2 = l2.Next
} else {
l2 = headA
}
}
return l1
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# JavaScript:
var getListLen = function(head) {
let len = 0, cur = head;
while(cur) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return len;
}
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
let curA = headA,curB = headB,
lenA = getListLen(headA), // Calculate the length of linked list A
lenB = getListLen(headB);
if(lenA < lenB) { // Make curA point to the longer list's head, with lenA being its length
// Note to add semicolons when swapping variables; when swapping two arrays under the same scope,
// without semicolons, the following two statements are equivalent to one: [curA, curB] = [lenB, lenA]
[curA, curB] = [curB, curA];
[lenA, lenB] = [lenB, lenA];
}
let i = lenA - lenB; // Calculate the length difference
while(i-- > 0) { // Align curA and curB to the same starting point (end position aligned)
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curA && curA !== curB) { // Traverse curA and curB; return immediately upon finding the same node
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return curA;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# TypeScript:
function getIntersectionNode(headA: ListNode | null, headB: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let sizeA: number = 0,
sizeB: number = 0;
let curA: ListNode | null = headA,
curB: ListNode | null = headB;
while (curA) {
sizeA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curB) {
sizeB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if (sizeA < sizeB) {
[sizeA, sizeB] = [sizeB, sizeA];
[curA, curB] = [curB, curA];
}
let gap = sizeA - sizeB;
while (gap-- && curA) {
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curA && curB) {
if (curA === curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# C:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *l = NULL, *s = NULL;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0, gap = 0;
// Calculate the lengths of both linked lists
s = headA;
while (s) {
lenA ++;
s = s->next;
}
s = headB;
while (s) {
lenB ++;
s = s->next;
}
// Calculate the length difference
if (lenA > lenB) {
l = headA, s = headB;
gap = lenA - lenB;
} else {
l = headB, s = headA;
gap = lenB - lenA;
}
// Align the tails
while (gap--) l = l->next;
// Move and check for a matching node
while (l) {
if (l == s) return l;
l = l->next, s = s->next;
}
return NULL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# Scala:
object Solution {
def getIntersectionNode(headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode): ListNode = {
var lenA = 0 // Length of headA
var lenB = 0 // Length of headB
var tmp = headA // Temporary variable
// Calculate the length of headA
while (tmp != null) {
lenA += 1;
tmp = tmp.next
}
// Calculate the length of headB
tmp = headB // Assign temporary variable to headB
while (tmp != null) {
lenB += 1
tmp = tmp.next
}
// Redefine as the passed parameters are immutable
var listA = headA
var listB = headB
// Length difference between two lists
// If gap>0, lenA>lenB, move headA(listA) forward gap steps
// If gap<0, lenA<lenB, move headB(listB) forward -gap steps
var gap = lenA - lenB
if (gap > 0) {
// Use for instead of i-=1, since it's not possible
for (i <- 0 until gap) {
listA = listA.next // Move headA(listA)
}
} else {
gap = math.abs(gap) // Currently gap is negative, take absolute value
for (i <- 0 until gap) {
listB = listB.next
}
}
// Now move both lists at the same time, return upon finding a match
while (listA != null && listB != null) {
if (listA == listB) {
return listA
}
listA = listA.next
listB = listB.next
}
// If no intersection, return null, return can be omitted
null
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# C#
public ListNode GetIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
{
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode cur1 = headA, cur2 = headB;
while (cur1 != cur2)
{
cur1 = cur1 == null ? headB : cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2 == null ? headA : cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Swift:
func getIntersectionNode(_ headA: ListNode?, _ headB: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var lenA = 0
var lenB = 0
var nodeA = headA
var nodeB = headB
// Calculate length of A and B
while nodeA != nil {
lenA += 1
nodeA = nodeA?.next
}
while nodeB != nil {
lenB += 1
nodeB = nodeB?.next
}
// Reset pointers
nodeA = headA
nodeB = headB
// If A is longer, move it forward lenA-lenB steps
if lenA > lenB {
for _ in 0..<(lenA - lenB) {
nodeA = nodeA?.next
}
} else if lenB > lenA {
// If B is longer, move it forward lenB-lenA steps
for _ in 0..<(lenB - lenA) {
nodeB = nodeB?.next
}
}
// Traverse both lists, looking for intersection
while nodeA !== nodeB {
nodeA = nodeA?.next
nodeB = nodeB?.next
}
return nodeA
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
