# 827. Making A Large Island
LeetCode Link (opens new window)
You are given an n x n binary matrix grid. You can at most change one 0 to 1.
Return the largest island area in grid after you make that change.
An island is a group of 1s connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical).
Example 1:
- Input:
grid = [[1, 0], [0, 1]] - Output: 3
- Explanation: Change one
0to1, connecting two small islands to form an island of area 3.
Example 2:
- Input:
grid = [[1, 1], [1, 0]] - Output: 4
- Explanation: Change the
0to1to expand the island area to 4.
Example 3:
- Input:
grid = [[1, 1], [1, 1]] - Output: 4
- Explanation: There is no
0to change to1, and the area remains 4.
# Approach
One brute-force approach to this problem is to try changing every 0 on the map to 1, then search for the largest island area on the map.
To calculate the maximum area of an island: traverse the map and perform a depth-first search (DFS) on the island, with a time complexity of n * n.
(Actually, you can use either DFS or breadth-first search (BFS); both aim to traverse the island and make a mark, essentially "coloring" it, so any traversal method works. I'll explain using DFS below.)
By changing each 0, we need to re-calculate the maximum map area, resulting in an overall time complexity of n^4.
If you're not familiar with depth-first search, you can check it out here: Depth-first Search Theory (opens new window).
# Optimization Approach
We actually do a lot of redundant work when using DFS iteratively to calculate the maximum island area.
We only need to record the area of each island once using DFS.
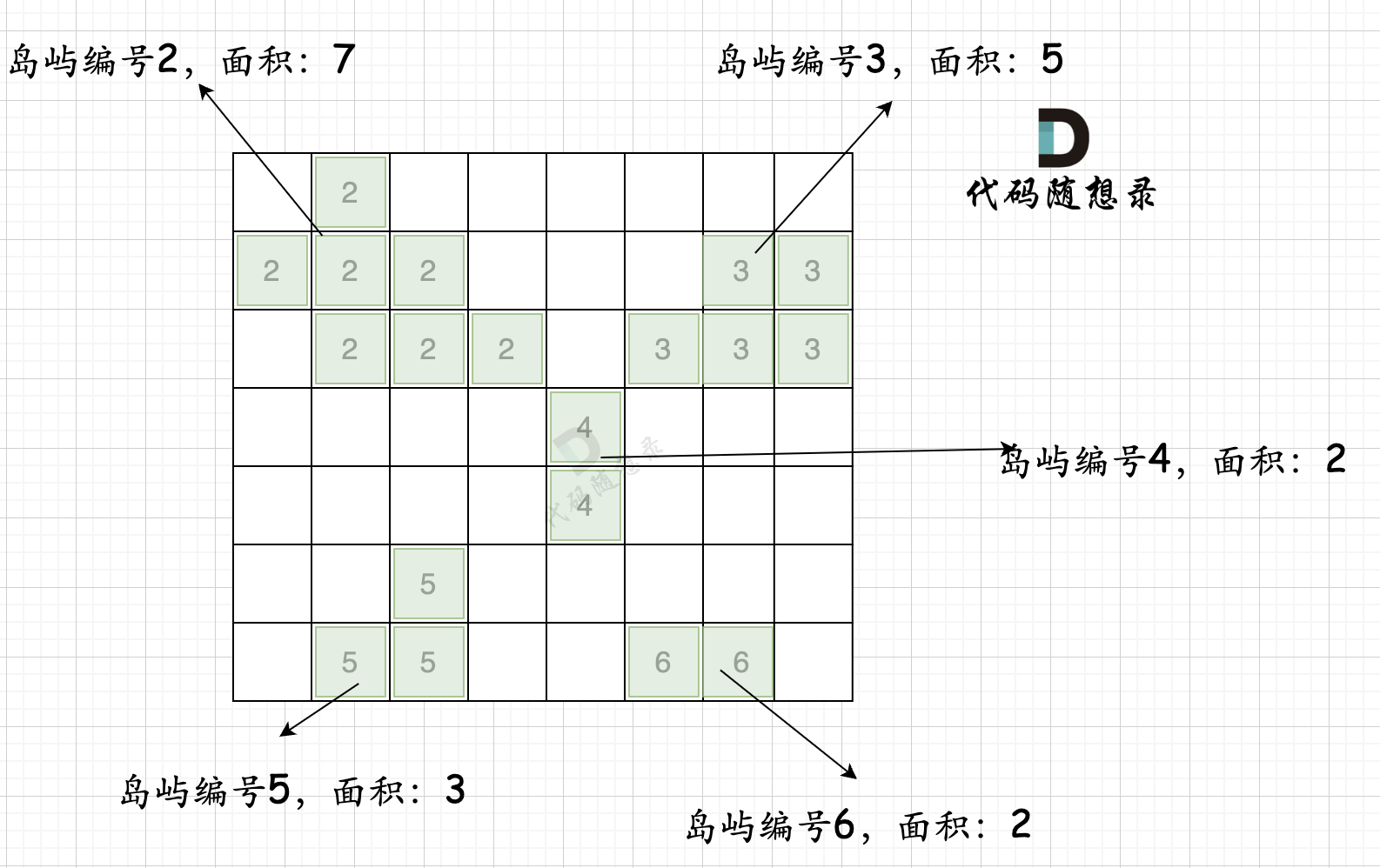
Step 1: Traverse the map once to find and record the size of each island with a unique identifier. We can use a map where the key is the island number and the value is the island area.
Step 2: Traverse the map again, inspecting 0s (as we want to change 0 to 1), summing the areas of adjacent islands, and then determine the maximum area after considering each 0.
Taking the island scenario on the map below as an example: (where 1 represents land)
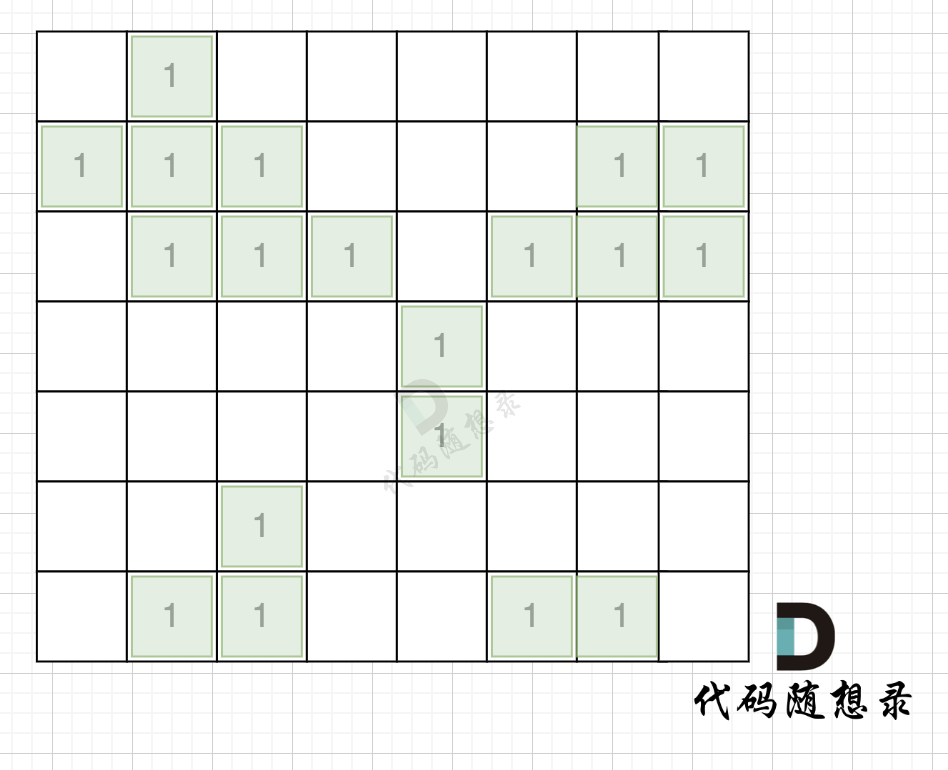
In the first step, traverse the map and collect statistics on island numbers and sizes as shown in the diagram below:
The code for this process is as follows:
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // Four directions
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y, int mark) {
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // Termination condition: node already visited or encounter water
visited[x][y] = true; // Mark as visited
grid[x][y] = mark; // Assign a new label to the land
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // Out of bounds, skip
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty, mark);
}
}
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false)); // Mark visited points
unordered_map<int, int> gridNum;
int mark = 2; // Record each island's identifier
bool isAllGrid = true; // Flag to check if the entire map is land
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark); // Mark all connected lands as true
gridNum[mark] = count; // Record each island's area
mark++; // Record the next island identifier
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
This process has a time complexity of n * n. Some may wonder: it clearly seems like two nested loops with a dfs below; how does it end up as n * n?
If you look at the code closely, each node in the n * n grid is traversed only once and not repeatedly.
The second step process is illustrated in the diagram below:
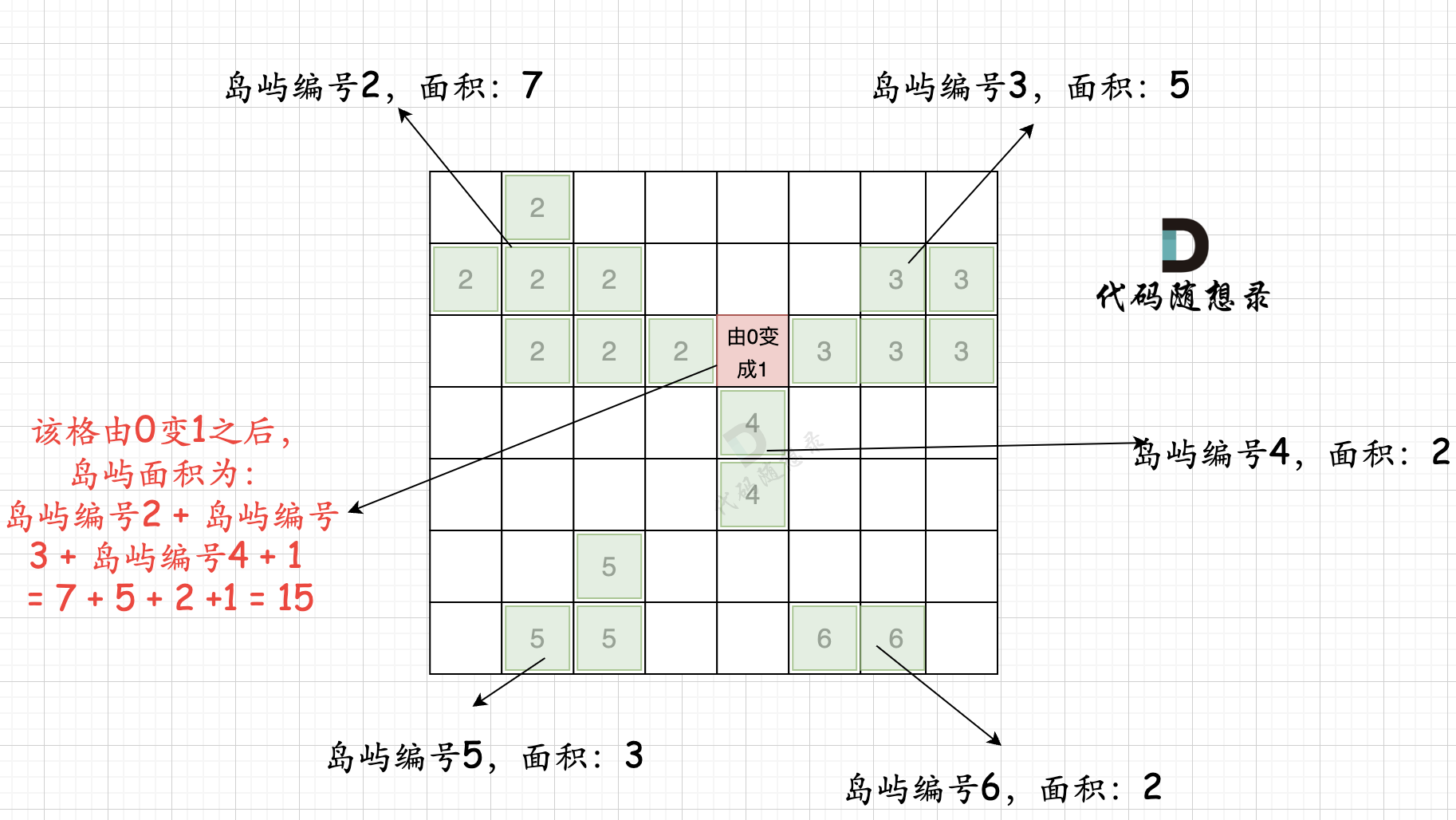
That is, for every 0 block, calculate the areas of its adjacent islands, sum them up, and finally get the maximum area after iterating through all 0s.
The process also has a time complexity of n * n.
So the overall solution has a time complexity of n * n + n * n, which is n^2.
Of course, there is another point for optimization: you don't need a visited array since you have mark for marking, so grid[i][j] that has been traversed will not be equal to 1.
The code is as follows:
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // Four directions
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y, int mark) {
if (grid[x][y] != 1 || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // Termination condition: node already visited or encounter water
grid[x][y] = mark; // Assign a new label to the land
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // Out of bounds, skip
dfs(grid, nextx, nexty, mark);
}
}
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
unordered_map<int ,int> gridNum;
int mark = 2; // Record each island's identifier
bool isAllGrid = true; // Flag to check if the entire map is land
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
dfs(grid, i, j, mark); // Mark all connected lands as true
gridNum[mark] = count; // Record each island's area
mark++; // Record the next island identifier
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
To maintain clarity among variables and ensure clean code, the complete code still uses a visited array for marking.
Finally, the complete code is as follows:
class Solution {
private:
int count;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // Four directions
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y, int mark) {
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // Termination condition: node already visited or encounter water
visited[x][y] = true; // Mark as visited
grid[x][y] = mark; // Assign a new label to the land
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // Out of bounds, skip
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty, mark);
}
}
public:
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false)); // Mark visited points
unordered_map<int, int> gridNum;
int mark = 2; // Record each island's identifier
bool isAllGrid = true; // Flag to check if the entire map is land
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark); // Mark all connected lands as true
gridNum[mark] = count; // Record each island's area
mark++; // Record the next island identifier
}
}
}
if (isAllGrid) return n * m; // If all cells are land, return full area
// The following logic calculates the sum of areas of adjacent islands based on the position of the added land
int result = 0; // Record the final result
unordered_set<int> visitedGrid; // Mark visited islands
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int count = 1; // Record the island count after the linkage
visitedGrid.clear(); // Clear before each use
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int neari = i + dir[k][1]; // Calculate adjacent coordinates
int nearj = j + dir[k][0];
if (neari < 0 || neari >= grid.size() || nearj < 0 || nearj >= grid[0].size()) continue;
if (visitedGrid.count(grid[neari][nearj])) continue; // Avoid adding the same island multiple times
// Sum up the size of adjacent islands
count += gridNum[grid[neari][nearj]];
visitedGrid.insert(grid[neari][nearj]); // Mark island as added
}
}
result = max(result, count);
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# Other Language Versions
# Java
class Solution {
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // Four directions
/**
* @param grid The grid array
* @param row The current row of the node being traversed
* @param col The current column of the node being traversed
* @param mark The current region's mark
* @return The number of 1s in the current region
*/
public int dfs(int[][] grid, int row, int col, int mark) {
int ans = 0;
grid[row][col] = mark;
for (int[] current: position) {
int curRow = row + current[0], curCol = col + current[1];
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= grid.length || curCol < 0 || curCol >= grid.length) continue; // Out of bounds
if (grid[curRow][curCol] == 1)
ans += 1 + dfs(grid, curRow, curCol, mark);
}
return ans;
}
public int largestIsland(int[][] grid) {
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE, size = grid.length, mark = 2;
Map<Integer, Integer> getSize = new HashMap<>();
for (int row = 0; row < size; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < size; col++) {
if (grid[row][col] == 1) {
int areaSize = 1 + dfs(grid, row, col, mark);
getSize.put(mark++, areaSize);
}
}
}
for (int row = 0; row < size; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < size; col++) {
// Skip the current position if it's not 0 since we can only change 0 to 1
if (grid[row][col] != 0) continue;
Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); // Prevent the same region from being counted multiple times
// Calculate the number of 1s from the current position by default
// because the 0 is turned into a 1
int curSize = 1;
for (int[] current: position) {
int curRow = row + current[0], curCol = col + current[1];
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= grid.length || curCol < 0 || curCol >= grid.length) continue;
int curMark = grid[curRow][curCol]; // Get the mark of the corresponding position
// If the mark is already in hashSet, it means the mark has been recorded once
// If it doesn't exist in getSize, it means the mark is invalid (at this point curMark = 0)
if (hashSet.contains(curMark) || !getSize.containsKey(curMark)) continue;
hashSet.add(curMark);
curSize += getSize.get(curMark);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, curSize);
}
}
// When ans == Integer.MIN_VALUE, it means there are no 0s in the grid, all are valid regions, return the size of the grid
return ans == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? size * size : ans;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# Python
class Solution:
def largestIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
visited = set() # Mark visited positions
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
res = 0
island_size = 0 # Used to store the current island size
directions = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]] # Four directions
islands_size = defaultdict(int) # Save the size of each island
def dfs(island_num, r, c):
visited.add((r, c))
grid[r][c] = island_num # Mark visited positions with island number
nonlocal island_size
island_size += 1
for i in range(4):
nextR = r + directions[i][0]
nextC = c + directions[i][1]
if (nextR not in range(m) or # Row index out of bounds
nextC not in range(n) or # Column index out of bounds
(nextR, nextC) in visited): # Coordinate already visited
continue
if grid[nextR][nextC] == 1: # Encounter valid coordinate, go to the next level search
dfs(island_num, nextR, nextC)
island_num = 2 # Initial island number set to 2, because grid data contains 0 and 1, so start numbering with 2
all_land = True # Flag to check if the entire map is land
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == 0:
all_land = False # The map is not all land
if (r, c) not in visited and grid[r][c] == 1:
island_size = 0 # Reset island size to 0 before traversing each position
dfs(island_num, r, c)
islands_size[island_num] = island_size # Save current island size
island_num += 1 # Move to the next island number
if all_land:
return m * n # If all are land cells, return the map area
count = 0 # Size of the current island after changing any 0 to 1
# Since calculating island area needs to traverse in four directions, it's possible that the position in two or three directions may belong to the same island,
# to avoid duplicate addition, add the already visited island number into this set.
visited_island = set() # Save visited islands
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == 0:
count = 1 # Include the position where 0 is converted to 1 into the area
visited_island.clear() # Clear set before traversing each position
for i in range(4):
nearR = r + directions[i][0]
nearC = c + directions[i][1]
if nearR not in range(m) or nearC not in range(n): # Surrounding positions out of bounds
continue
if grid[nearR][nearC] in visited_island: # Island already visited
continue
count += islands_size[grid[nearR][nearC]] # Accumulate the area of adjacent islands
visited_island.add(grid[nearR][nearC]) # Mark current island as visited
res = max(res, count)
return res
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# Go
func largestIsland(grid [][]int) int {
dir := [][]int{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}}
n := len(grid)
m := len(grid[0])
area := 0
visited := make([][]bool, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, m)
}
gridNum := make(map[int]int, 0) // Record the area of each island
mark := 2 // Record each island's identifier
isAllGrid := true
res := 0 // Flag to check if the entire map is land
var dfs func(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y, mark int)
dfs = func(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y, mark int) {
// Termination condition: node already visited or encounter water
if visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0 {
return
}
visited[x][y] = true // Mark as visited
grid[x][y] = mark // Assign a new label to the land
area++
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
nextX := x + dir[i][0]
nextY := y + dir[i][1]
if nextX < 0 || nextX >= len(grid) || nextY < 0 || nextY >= len(grid[0]) {
continue
}
dfs(grid, visited, nextX, nextY, mark)
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 0 {
isAllGrid = false
}
if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
area = 0
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark) // Mark all connected lands as true
gridNum[mark] = area // Record each island's area
mark++ // Update to the next island identifier
}
}
}
if isAllGrid {
return n * m
}
// Based on the position of the added land, calculate the sum of adjacent island areas
visitedGrid := make(map[int]struct{}) // Mark visited islands
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
count := 1 // Record the island count after linkage
visitedGrid = make(map[int]struct{}) // Clear before each use
if grid[i][j] == 0 {
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
// Calculate adjacent coordinates
nearI := i + dir[k][0]
nearJ := j + dir[k][1]
if nearI < 0 || nearI >= len(grid) || nearJ < 0 || nearJ >= len(grid[0]) {
continue
}
// Skip already added islands
if _, ok := visitedGrid[grid[nearI][nearJ]]; ok {
continue
}
// Add up the size of adjacent islands
count += gridNum[grid[nearI][nearJ]]
// Mark the island as added
visitedGrid[grid[nearI][nearJ]] = struct{}{}
}
}
res = max827(res, count)
}
}
return res
}
// Helper function to find max between two numbers
func max827(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
# JavaScript
var largestIsland = function(grid) {
let res = 0;
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
const tag = new Array(n).fill().map(_ => new Array(m).fill(0));
const area = new Map();
const dir = [[0,1],[0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0]];
const dfs = (grid, tag, x, y, mark) => {
let res = 1;
tag[x][y] = mark;
for(let i = 0; i < dir.length; i++) {
let nextX = x + dir[i][0];
let nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextX >= m || nextY < 0 || nextY >= n) {
continue;
}
if(grid[nextX][nextY] === 1 && tag[nextX][nextY] === 0) {
res += dfs(grid, tag, nextX, nextY, mark);
}
}
return res;
}
let mark = 2;
// Assign mark to islands
for(let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] === 1 && tag[i][j] === 0) {
area.set(mark, dfs(grid, tag, i, j, mark));
res = Math.max(res, area.get(mark));
mark++;
}
}
}
// Change a non-island cell to land
for(let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] === 0) {
let z = 1;
const connected = new Set();
for(let k = 0; k < dir.length; k++) {
let nextX = i + dir[k][0];
let nextY = j + dir[k][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextX >= m || nextY < 0 || nextY >= n || tag[nextX][nextY] === 0 || connected.has(tag[nextX][nextY])) {
continue;
}
z += area.get(tag[nextX][nextY]);
connected.add(tag[nextX][nextY]);
}
res = Math.max(res, z);
}
}
}
return res;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
