# 787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
There are n cities connected by some flights. You are given an array flights, where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei], representing a flight from city fromi to city toi with a price of pricei.
Now given all the cities and flights, as well as a starting city src and a destination city dst, your task is to find the route with at most k stops that results in the cheapest price from src to dst, and return that price. If no such route exists, return -1.
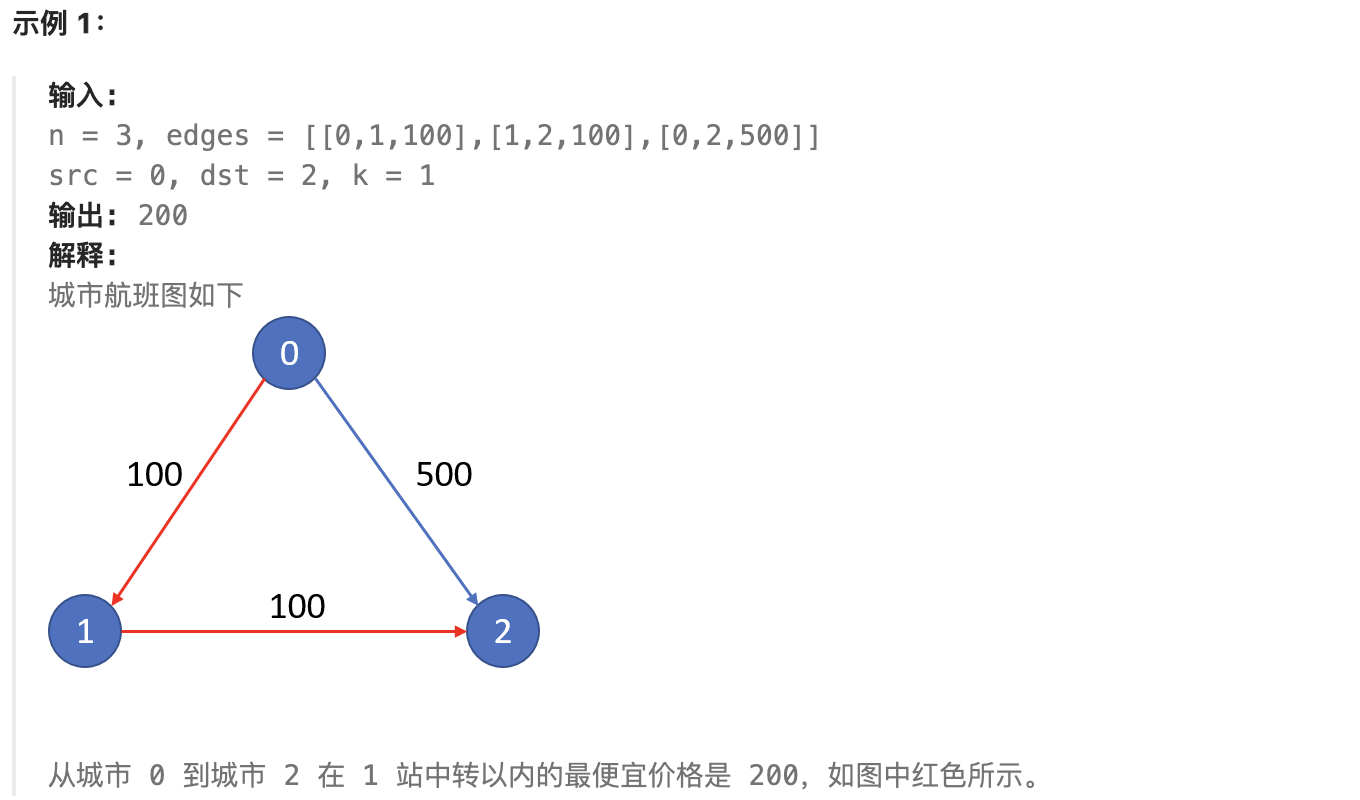
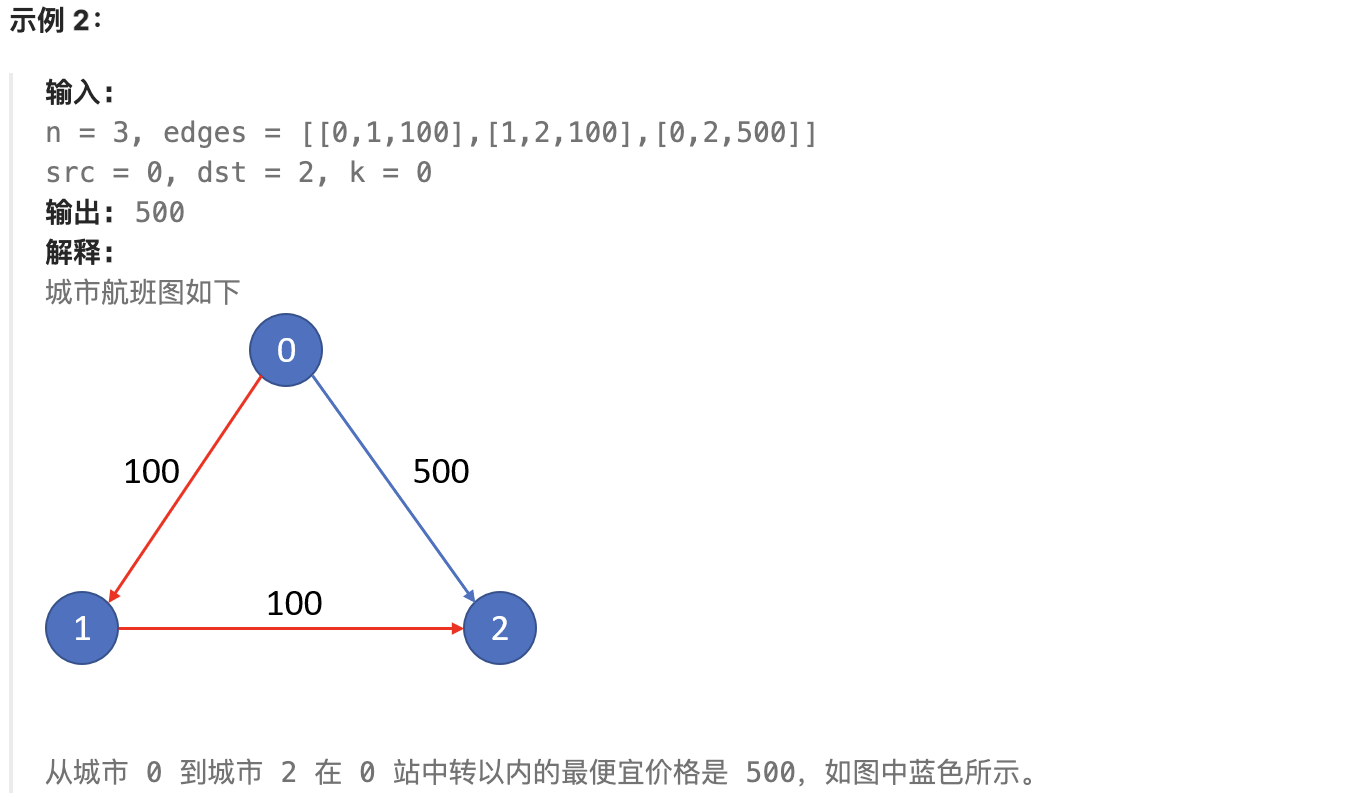

# Approach
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector<int> minDist(n, INT_MAX/2);
minDist[src] = 0;
vector<int> minDist_copy(n); // Used to record the result of each iteration
for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
minDist_copy = minDist; // Get the results of the previous calculation
for (auto &f : flights) {
int from = f[0];
int to = f[1];
int price = f[2];
minDist[to] = min(minDist_copy[from] + price, minDist[to]);
// if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
}
}
int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
return result;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Below is a common wrong approach
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector<int> minDist(n, INT_MAX/2);
minDist[src] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
for (auto &f : flights) {
int from = f[0];
int to = f[1];
int price = f[2];
if (minDist[to] > minDist[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist[from] + price;
}
}
int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
return result;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
SPFA
class Solution {
struct Edge {
int to; // Connected node
int val; // Weight of the edge
Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // Constructor
};
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector<int> minDist(n, INT_MAX/2);
vector<list<Edge>> grid(n + 1); // Adjacency list
for (auto &f : flights) {
int from = f[0];
int to = f[1];
int price = f[2];
grid[from].push_back(Edge(to, price));
}
minDist[src] = 0;
vector<int> minDist_copy(n); // Used to record the result of each iteration
k++;
queue<int> que;
que.push(src);
std::vector<bool> visited(n + 1, false); // Optional, improves efficiency by preventing repeated visits
int que_size;
while (k-- && !que.empty()) {
minDist_copy = minDist; // Get the results of the previous calculation
que_size = que.size();
while (que_size--) { // This while loop design is really ingenious
int node = que.front(); que.pop();
for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
int from = node;
int to = edge.to;
int price = edge.val;
if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) {
minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
que.push(to);
}
}
}
}
int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
return result;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
Queue with visited to prevent repeated visits
class Solution {
struct Edge {
int to; // Connected node
int val; // Weight of the edge
Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // Constructor
};
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector<int> minDist(n, INT_MAX/2);
vector<list<Edge>> grid(n + 1); // Adjacency list
for (auto &f : flights) {
int from = f[0];
int to = f[1];
int price = f[2];
grid[from].push_back(Edge(to, price));
}
minDist[src] = 0;
vector<int> minDist_copy(n); // Used to record the result of each iteration
k++;
queue<int> que;
que.push(src);
int que_size;
while (k-- && !que.empty()) {
// Note the position of this array
vector<bool> visited(n + 1, false); // Optional, improves efficiency by preventing repeated access if the value is already calculated
minDist_copy = minDist; // Get the results of the previous calculation
que_size = que.size();
while (que_size--) {
int node = que.front(); que.pop();
for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
int from = node;
int to = edge.to;
int price = edge.val;
if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) {
minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
if(visited[to]) continue; // No need to enqueue again, but need to calculate repeatedly, so placed here
visited[to] = true;
que.push(to);
}
}
}
}
int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
return result;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
Copyright © 2025 keetcoder
