# 417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow
Problem Link (opens new window)
There is an m x n rectangular island, bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the left and top edges and the Atlantic Ocean to the right and bottom edges.
The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. Given an m x n integer matrix heights, where heights[r][c] represents the height above sea level at coordinates (r, c).
Rainwater can flow from one cell to another 4-directionally (north, south, east, west) if the neighboring cell's height is less than or equal to the current cell's height.
Water can flow into either ocean from the cells connected to each ocean.
Return a 2D list of grid coordinates result where result[i] = [ri, ci] indicates that the rainwater from cell (ri, ci) can flow to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 1:
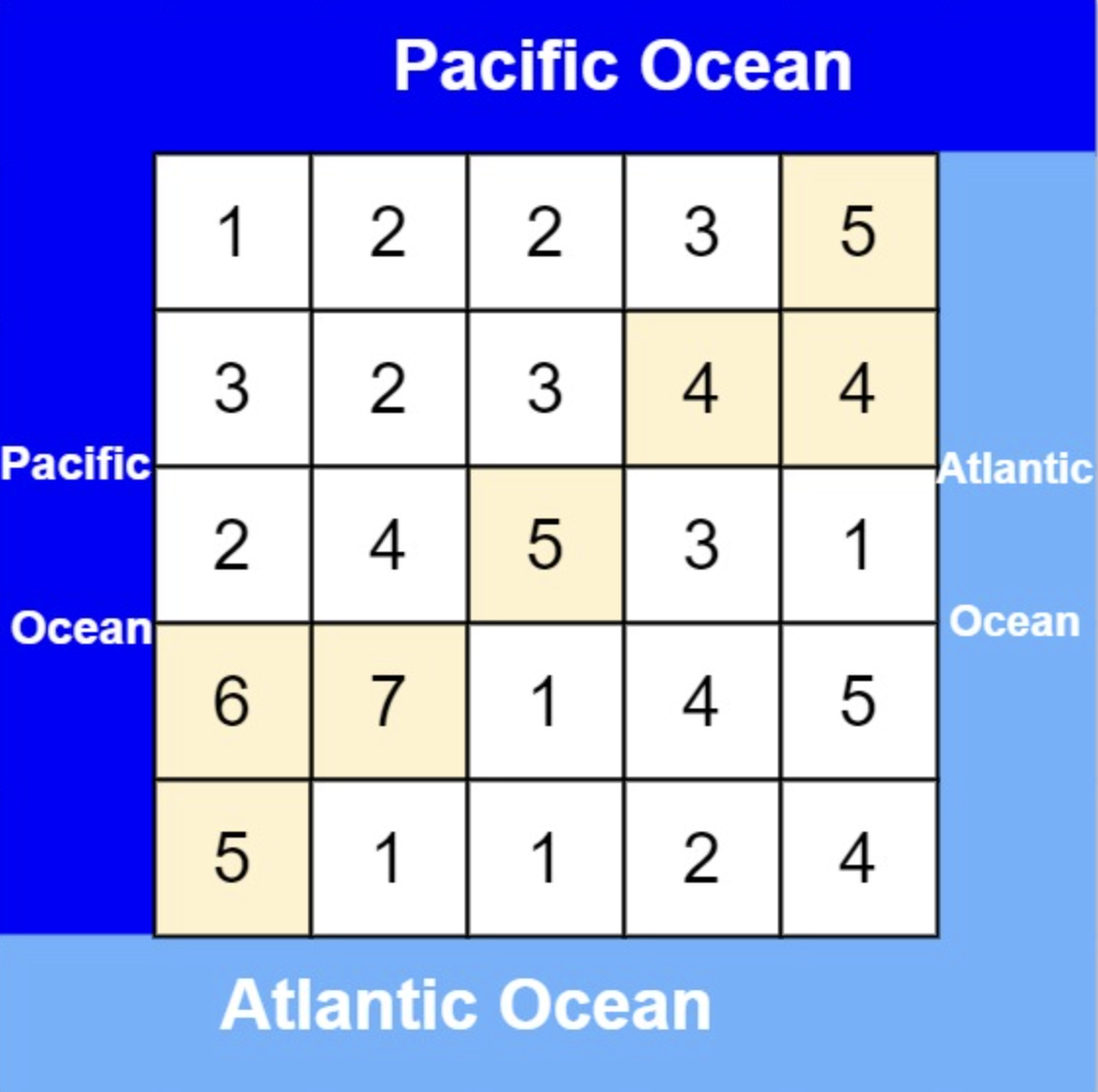
- Input:
heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]] - Output:
[[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
Example 2:
- Input:
heights = [[2,1],[1,2]] - Output:
[[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
Constraints:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[r].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heights[r][c] <= 10^5
# Approach
Some may be confused by the problem description, but essentially it's about finding which points can simultaneously reach the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The flow can only go from high to low.
A straightforward idea is to traverse each point and check if this point can reach both oceans.
For traversal, we can use either DFS or BFS. Here is an example using DFS.
The implementation code based on this idea is as follows:
class Solution {
private:
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1};
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
if (visited[x][y]) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= heights.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= heights[0].size()) continue;
if (heights[x][y] < heights[nextx][nexty]) continue;
dfs(heights, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
return;
}
bool isResult(vector<vector<int>>& heights, int x, int y) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(heights.size(), vector<bool>(heights[0].size(), false));
dfs(heights, visited, x, y);
bool isPacific = false;
bool isAtlantic = false;
for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) {
if (visited[0][j]) {
isPacific = true;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i][0]) {
isPacific = true;
break;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) {
if (visited[heights.size() - 1][j]) {
isAtlantic = true;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i][heights[0].size() - 1]) {
isAtlantic = true;
break;
}
}
if (isAtlantic && isPacific) return true;
return false;
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < heights[0].size(); j++) {
if (isResult(heights, i, j)) result.push_back({i, j});
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
This approach is straightforward, but clearly, the above code times out. Let's analyze the time complexity.
Traversing each node is m * n, and during each traversal, a deep search (DFS) is conducted. The time complexity of DFS is m * n.
Thus, the overall time complexity is O(m^2 * n^2), which is a fourth-degree polynomial time complexity.
# Optimization
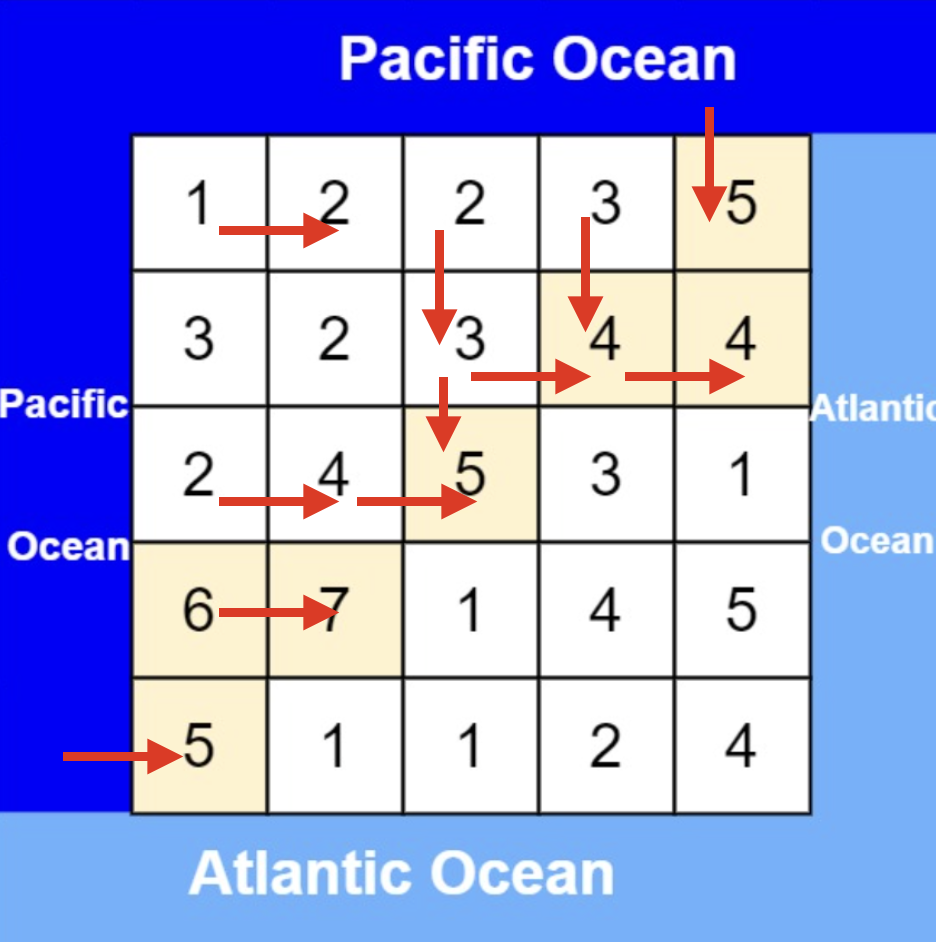
We can think in reverse: starting from the nodes on the edge of the Pacific Ocean and moving upwards, marking visited nodes. Similarly, start from the edge of the Atlantic Ocean and move upwards, marking visited nodes as well. Then, nodes visited from both sides are those where water can flow to both oceans.
Starting from the edges next to the Pacific Ocean, as shown below:
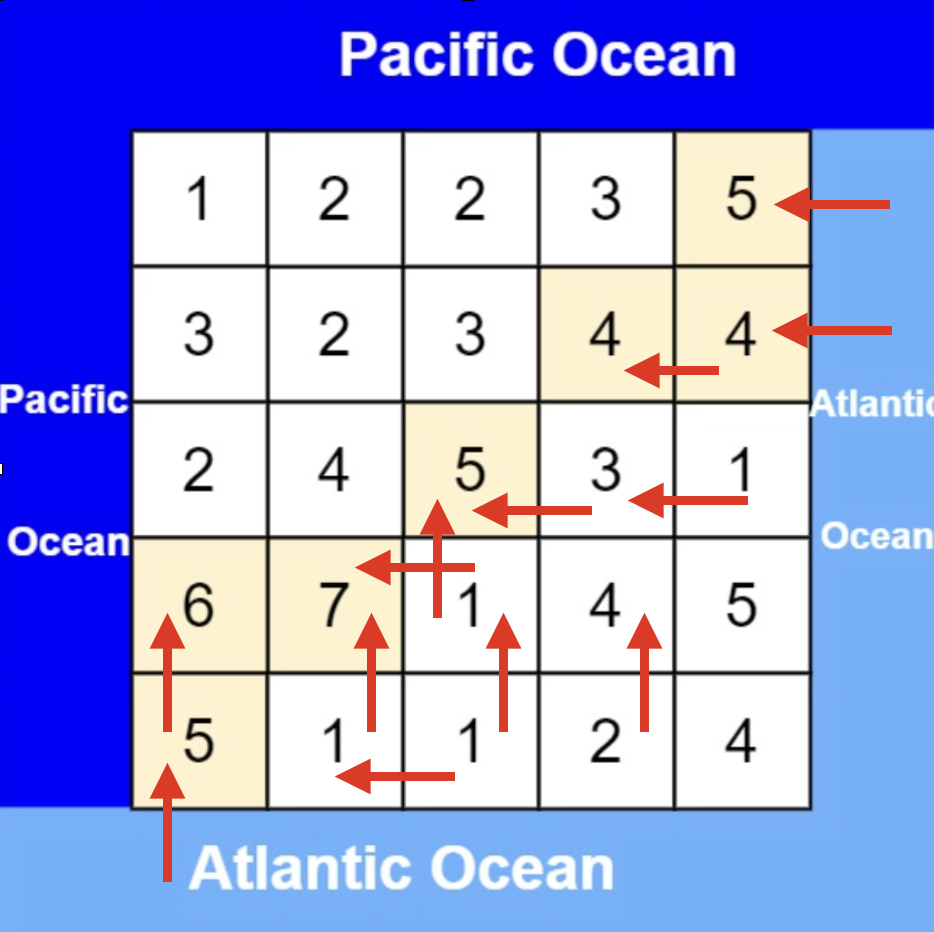
Starting from the edges next to the Atlantic Ocean, as shown below:
Based on this logic, we can write the following traversal code:
(If you are not familiar with the basics of DFS, I recommend watching "DFS Algorithm Explanation" (opens new window). You can also solve 797. All Paths From Source to Target (opens new window) along the way.)
class Solution {
private:
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1];
// Traverse from low to high, note that visited is passed by reference to modify the values of pacific and atlantic
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
if (visited[x][y]) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= heights.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= heights[0].size()) continue;
if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextx][nexty]) continue;
dfs(heights, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
return;
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int n = heights.size();
int m = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, m - 1);
}
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, n - 1, j);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) result.push_back({i, j});
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
To analyze the time complexity, note that the DFS search process can be easily thought of as having a time complexity of O(n * m).
The crucial part is the main function. When DFS is conducted, there are also for-loops on top.
The first for-loop has a time complexity of n * (n * m).
The second for-loop has a time complexity of m * (n * m).
So this problem seems to have a time complexity of (m * n) * (m + n).
However, this is a misunderstanding. Review the implementation of the DFS function. In fact, there is a visited function recording the paths taken, and paths walked are not repeated.
Therefore, calling the DFS function, as long as the parameter is the array pacific, each node in the map is actually traversed once, no matter how many times it is called.
Similarly, calling the DFS function, as long as the parameter is the array atlantic, each node in the map is also traversed once.
So, the time complexity of the following code block is 2 * n * m. Each node in the map is traversed twice: once when the parameter is pacific, and once when it is atlantic.
// Starting from the top and bottom rows, traverse upwards
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, m - 1);
}
// Starting from the leftmost and rightmost columns, traverse upwards
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, n - 1, j);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Therefore, the overall time complexity of this problem is 2 * n * m + n * m, which is O(n * m).
The space complexity is O(n * m), which is straightforward to understand since several n * m arrays are created.
# Other Language Versions
# Java
Depth First Search:
class Solution {
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public void dfs(int[][] heights, int row, int col, int sign, boolean[][][] visited) {
for (int[] current: position) {
int curRow = row + current[0], curCol = col + current[1];
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= heights.length || curCol < 0 || curCol >= heights[0].length)
continue;
if (heights[curRow][curCol] < heights[row][col] || visited[curRow][curCol][sign]) continue;
visited[curRow][curCol][sign] = true;
dfs(heights, curRow, curCol, sign, visited);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int rowSize = heights.length, colSize = heights[0].length;
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize][2];
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = true;
visited[row][0][1] = true;
dfs(heights, row, colSize - 1, 0, visited);
dfs(heights, row, 0, 1, visited);
}
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = true;
visited[0][col][1] = true;
dfs(heights, rowSize - 1, col, 0, visited);
dfs(heights, 0, col, 1, visited);
}
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
if (visited[row][col][0] && visited[row][col][1])
ans.add(List.of(row, col));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
class Solution {
private int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
public void dfs(int[][] heights, boolean[][] visited, int m, int n){
if(visited[m][n]) return;
visited[m][n] = true;
for(int[] dir: directions){
int nextm = m + dir[0];
int nextn = n + dir[1];
if(nextm < 0||nextm == heights.length||nextn <0||nextn== heights[0].length) continue;
if(heights[m][n] > heights[nextm][nextn]) continue;
dfs(heights, visited, nextm, nextn);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i<m; i++){
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, n-1);
}
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, m-1, j);
}
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(int a = 0; a<m; a++){
for(int b = 0; b<n; b++){
if(pacific[a][b] && atlantic[a][b]){
List<Integer> pair = new ArrayList<>();
pair.add(a);
pair.add(b);
result.add(pair);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Breadth-First Search:
class Solution {
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public void bfs(int[][] heights, Queue<int[]> queue, boolean[][][] visited) {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] curPos = queue.poll();
for (int[] current: position) {
int row = curPos[0] + current[0], col = curPos[1] + current[1], sign = curPos[2];
if (row < 0 || row >= heights.length || col < 0 || col >= heights[0].length) continue;
if (heights[row][col] < heights[curPos[0]][curPos[1]] || visited[row][col][sign]) continue;
visited[row][col][sign] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, col, sign});
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int rowSize = heights.length, colSize = heights[0].length;
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize][2];
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = true;
visited[row][0][1] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1, 0});
queue.add(new int[]{row, 0, 1});
}
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = true;
visited[0][col][1] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col, 0});
queue.add(new int[]{0, col, 1});
}
bfs(heights, queue, visited);
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
if (visited[row][col][0] && visited[row][col][1])
ans.add(List.of(row, col));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# Python
Depth-First Search
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.position = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]]
def dfs(self, heights: List[List[int]], row: int, col: int, sign: int, visited: List[List[List[int]]]):
for current in self.position:
curRow, curCol = row + current[0], col + current[1]
if curRow < 0 or curRow >= len(heights) or curCol < 0 or curCol >= len(heights[0]): continue
if heights[curRow][curCol] < heights[row][col] or visited[curRow][curCol][sign]: continue
visited[curRow][curCol][sign] = True
self.dfs(heights, curRow, curCol, sign, visited)
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
rowSize, colSize = len(heights), len(heights[0])
ans, visited = [], [[[False for _ in range(2)] for _ in range(colSize)] for _ in range(rowSize)]
for row in range(rowSize):
visited[row][0][1] = True
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = True
self.dfs(heights, row, 0, 1, visited)
self.dfs(heights, row, colSize - 1, 0, visited)
for col in range(0, colSize):
visited[0][col][1] = True
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = True
self.dfs(heights, 0, col, 1, visited)
self.dfs(heights, rowSize - 1, col, 0, visited)
for row in range(rowSize):
for col in range(colSize):
if visited[row][col][0] and visited[row][col][1]:
ans.append([row, col])
return ans
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Breadth-First Search
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.position = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]]
def bfs(self, heights: List[List[int]], queue: deque, visited: List[List[List[int]]]):
while queue:
curPos = queue.popleft()
for current in self.position:
row, col, sign = curPos[0] + current[0], curPos[1] + current[1], curPos[2]
if row < 0 or row >= len(heights) or col < 0 or col >= len(heights[0]): continue
if heights[row][col] < heights[curPos[0]][curPos[1]] or visited[row][col][sign]: continue
visited[row][col][sign] = True
queue.append([row, col, sign])
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
rowSize, colSize = len(heights), len(heights[0])
ans, visited = [], [[[False for _ in range(2)] for _ in range(colSize)] for _ in range(rowSize)]
queue = deque()
for row in range(rowSize):
visited[row][0][1] = True
visited[row][colSize - 1][0] = True
queue.append([row, 0, 1])
queue.append([row, colSize - 1, 0])
for col in range(0, colSize):
visited[0][col][1] = True
visited[rowSize - 1][col][0] = True
queue.append([0, col, 1])
queue.append([rowSize - 1, col, 0])
self.bfs(heights, queue, visited)
for row in range(rowSize):
for col in range(colSize):
if visited[row][col][0] and visited[row][col][1]:
ans.append([row, col])
return ans
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# JavaScript
/**
* @description Depth First Search
* @param {number[][]} heights
* @return {number[][]}
*/
function pacificAtlantic(heights) {
const dir = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]];
const [rowSize, colSize] = [heights.length, heights[0].length];
const visited = Array.from({ length: rowSize }, _ =>
Array.from({ length: colSize }, _ => new Array(2).fill(false))
);
const result = [];
function dfs(heights, visited, x, y, sign) {
if (visited[x][y][sign]) {
return;
}
visited[x][y][sign] = true;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nextX = x + dir[i][0];
const nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
continue;
}
if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextX][nextY]) {
continue;
}
dfs(heights, visited, nextX, nextY, sign);
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
dfs(heights, visited, i, 0, 0);
dfs(heights, visited, i, colSize - 1, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < colSize; i++) {
dfs(heights, visited, 0, i, 0);
dfs(heights, visited, rowSize - 1, i, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
if (visited[i][k][0] && visited[i][k][1]) {
result.push([i, k]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* @description Breadth First Search
* @param {number[][]} heights
* @return {number[][]}
*/
function pacificAtlantic(heights) {
const dir = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]];
const [rowSize, colSize] = [heights.length, heights[0].length];
const visited = Array.from({ length: rowSize }, _ =>
Array.from({ length: colSize }, _ => new Array(2).fill(false))
);
const result = [];
function bfs(heights, visited, x, y, sign) {
if (visited[x][y][sign]) {
return;
}
visited[x][y][sign] = true;
const stack = [y, x];
while (stack.length !== 0) {
[x, y] = [stack.pop(), stack.pop()];
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nextX = x + dir[i][0];
const nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
continue;
}
if (heights[x][y] > heights[nextX][nextY] || visited[nextX][nextY][sign]) {
continue;
}
visited[nextX][nextY][sign] = true;
stack.push(nextY, nextX);
}
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
bfs(heights, visited, i, 0, 0);
bfs(heights, visited, i, colSize - 1, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < colSize; i++) {
bfs(heights, visited, 0, i, 0);
bfs(heights, visited, rowSize - 1, i, 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
if (visited[i][k][0] && visited[i][k][1]) {
result.push([i, k]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
# Go
DFS:
var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}
func pacificAtlantic(heights [][]int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
pacific := make([][]bool, len(heights))
atlantic := make([][]bool, len(heights))
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
pacific[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
atlantic[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
}
// Columns
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0)
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, len(heights[0])-1)
}
// Rows
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j)
dfs(heights, atlantic, len(heights)-1, j)
}
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res = append(res, []int{i, j})
}
}
}
return res
}
func dfs(heights [][]int, visited [][]bool, i, j int) {
visited[i][j] = true
for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
x, y := i+d[0], j+d[1]
if x < 0 || x >= len(heights) || y < 0 || y >= len(heights[0]) || heights[i][j] > heights[x][y] || visited[x][y] {
continue
}
dfs(heights, visited, x, y)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
BFS:
var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}
func pacificAtlantic(heights [][]int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
pacific := make([][]bool, len(heights))
atlantic := make([][]bool, len(heights))
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
pacific[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
atlantic[i] = make([]bool, len(heights[0]))
}
// Columns
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
bfs(heights, pacific, i, 0)
bfs(heights, atlantic, i, len(heights[0])-1)
}
// Rows
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
bfs(heights, pacific, 0, j)
bfs(heights, atlantic, len(heights)-1, j)
}
for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(heights[0]); j++ {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res = append(res, []int{i, j})
}
}
}
return res
}
func bfs(heights [][]int, visited [][]bool, i, j int) {
queue := make([][]int, 0)
queue = append(queue, []int{i, j})
visited[i][j] = true
for len(queue) > 0 {
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
x, y := cur[0]+d[0], cur[1]+d[1]
if x < 0 || x >= len(heights) || y < 0 || y >= len(heights[0]) || heights[cur[0]][cur[1]] > heights[x][y] || visited[x][y] {
continue
}
queue = append(queue, []int{x, y})
visited[x][y] = true
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# Rust
DFS:
impl Solution {
const DIRECTIONS: [(isize, isize); 4] = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)];
pub fn pacific_atlantic(heights: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let (m, n) = (heights.len(), heights[0].len());
let mut res = vec![];
let (mut pacific, mut atlantic) = (vec![vec![false; n]; m], vec![vec![false; n]; m]);
// Columns
for i in 0..m {
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut pacific, i, 0);
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, i, n - 1);
}
for j in 0..n {
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut pacific, 0, j);
Self::dfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, m - 1, j);
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
}
}
}
res
}
pub fn dfs(heights: &[Vec<i32>], visited: &mut [Vec<bool>], i: usize, j: usize) {
visited[i][j] = true;
for (dx, dy) in Self::DIRECTIONS {
let (x, y) = (i as isize + dx, j as isize + dy);
if x < 0 || x >= heights.len() as isize || y < 0 || y >= heights[0].len() as isize {
continue;
}
let (x, y) = (x as usize, y as usize);
if !visited[x][y] && heights[x][y] >= heights[i][j] {
Self::dfs(heights, visited, x, y);
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
BFS:
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
const DIRECTIONS: [(isize, isize); 4] = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)];
pub fn pacific_atlantic(heights: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let (m, n) = (heights.len(), heights[0].len());
let mut res = vec![];
let (mut pacific, mut atlantic) = (vec![vec![false; n]; m], vec![vec![false; n]; m]);
// Columns
for i in 0..m {
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut pacific, i, 0);
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, i, n - 1);
}
for j in 0..n {
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut pacific, 0, j);
Self::bfs(&heights, &mut atlantic, m - 1, j);
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j] {
res.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
}
}
}
res
}
pub fn bfs(heights: &[Vec<i32>], visited: &mut [Vec<bool>], i: usize, j: usize) {
let mut queue = VecDeque::from([(i, j)]);
visited[i][j] = true;
while let Some((i, j)) = queue.pop_front() {
for (dx, dy) in Self::DIRECTIONS {
let (x, y) = (i as isize + dx, j as isize + dy);
if x < 0 || x >= heights.len() as isize || y < 0 || y >= heights[0].len() as isize {
continue;
}
let (x, y) = (x as usize, y as usize);
if !visited[x][y] && heights[x][y] >= heights[i][j] {
queue.push_back((x, y));
visited[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
