# 283. Move Zeroes: Dynamic Programming: Same Pattern, Solve the Perfect Squares Again
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given an array nums, write a function to move all zeros to the end of the array while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
Example:
Input: [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]
Note:
You must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.
Minimize the total number of operations.
# Approach
Before solving this problem, you can try 0027. Remove Element (opens new window).
This problem can be solved using a brute force approach with two nested for loops, simulating the deletion of elements from the array (by overwriting).
Let's discuss the two-pointer method. If you're not familiar with the two-pointer technique, I suggest reading this summary: Double Pointers Summary (opens new window).
The two-pointer technique can achieve a time complexity of O(n) when removing elements in an array, which was explained in detail in 0027. Remove Element (opens new window). This problem follows a similar pattern.
This is equivalent to removing element 0 from the entire array, and then all elements after slowIndex are redundant removed elements of 0, which can be set to 0.
As shown in the animation:
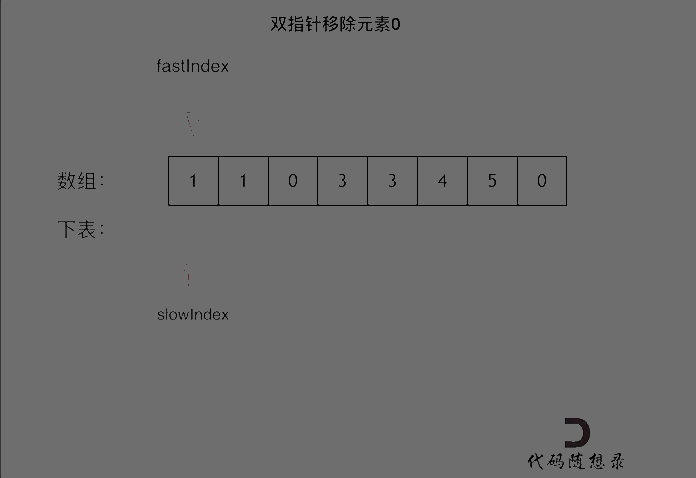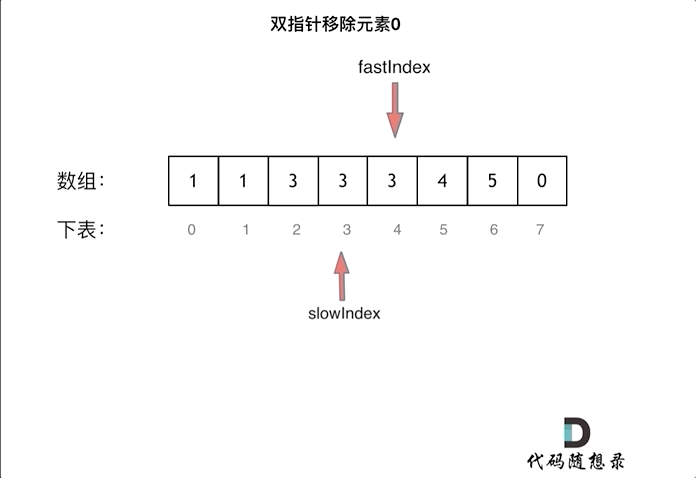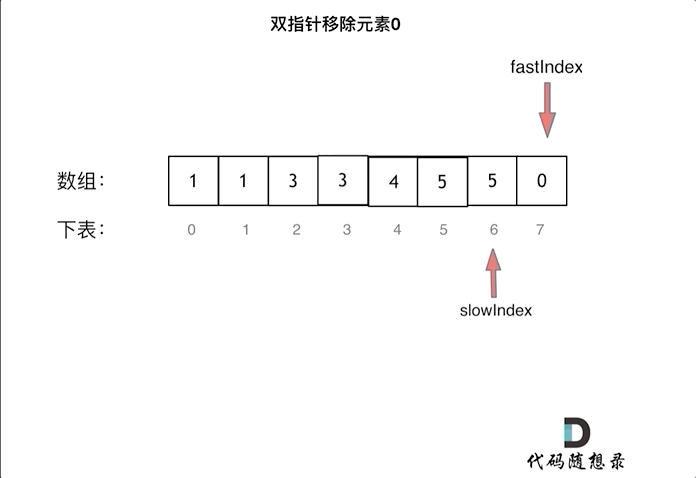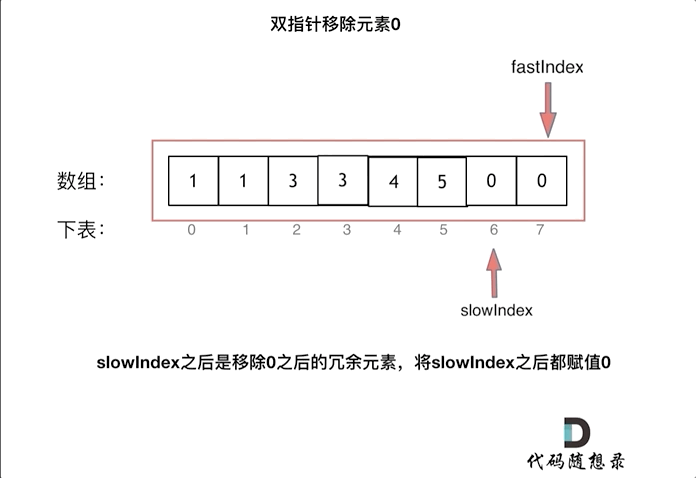
C++ code is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int slowIndex = 0;
for (int fastIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.size(); fastIndex++) {
if (nums[fastIndex] != 0) {
nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex];
}
}
// Set all redundant elements to 0
for (int i = slowIndex; i < nums.size(); i++) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int slow = 0;
for (int fast = 0; fast < nums.length; fast++) {
if (nums[fast] != 0) {
nums[slow++] = nums[fast];
}
}
// Set all following elements to 0
for (int j = slow; j < nums.length; j++) {
nums[j] = 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Python:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
slow = 0
for fast in range(len(nums)):
if nums[fast] != 0:
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
slow += 1
for i in range(slow, len(nums)):
nums[i] = 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Swap variables to avoid setting zeros
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
slow, fast = 0, 0
while fast < len(nums):
if nums[fast] != 0:
nums[slow], nums[fast] = nums[fast], nums[slow]
slow += 1 # Ensures the interval [0, slow) contains no 0
fast += 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Go:
func moveZeroes(nums []int) {
slow := 0
for fast := 0; fast < len(nums); fast ++ {
if nums[fast] != 0 {
temp := nums[slow]
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
nums[fast] = temp
slow++
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# JavaScript:
var moveZeroes = function(nums) {
let slow = 0;
for(let fast = 0; fast < nums.length; fast++){
if(nums[fast] != 0){// Find non-zero elements
nums[slow] = nums[fast]; // Assign non-zero element to the index pointed by slow pointer
slow++; // Move the slow pointer to the right
}
}
// Set all following elements to 0
for(let j = slow; j < nums.length; j++){
nums[j] = 0;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# TypeScript:
function moveZeroes(nums: number[]): void {
const length: number = nums.length;
let slowIndex: number = 0,
fastIndex: number = 0;
while (fastIndex < length) {
if (nums[fastIndex] !== 0) {
nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex];
};
fastIndex++;
}
while (slowIndex < length) {
nums[slowIndex++] = 0;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# C
void moveZeroes(int* nums, int numsSize){
int fastIndex = 0, slowIndex = 0;
for (; fastIndex < numsSize; fastIndex++) {
if (nums[fastIndex] != 0) {
nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex];
}
}
// Set all following elements to 0
for (; slowIndex < numsSize; slowIndex++) {
nums[slowIndex] = 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn move_zeroes(nums: &mut Vec<i32>) {
let mut slow = 0;
for fast in 0..nums.len() {
if nums[fast] != 0 {
nums.swap(slow, fast);
slow += 1;
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
