# 234. Palindrome Linked List
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Please determine if a linked list is a palindrome.
Example 1:
- Input: 1->2
- Output: false
Example 2:
- Input: 1->2->2->1
- Output: true
# Approach
# Array Simulation
The most straightforward idea is to convert the linked list into an array and then check if it is a palindrome.
The code is relatively simple, as shown below:
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> vec;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
vec.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
// Compare the array for palindrome
for (int i = 0, j = vec.size() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (vec[i] != vec[j]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
The above code can be optimized by first calculating the length of the list, and then initializing the vector with this length to avoid reallocating space each time a new node is added.
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
int length = 0;
while (cur) {
length++;
cur = cur->next;
}
vector<int> vec(length, 0); // Initialize vector with the length to avoid reallocation
cur = head;
int index = 0;
while (cur) {
vec[index++] = cur->val;
cur = cur->next;
}
// Compare the array for palindrome
for (int i = 0, j = vec.size() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (vec[i] != vec[j]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
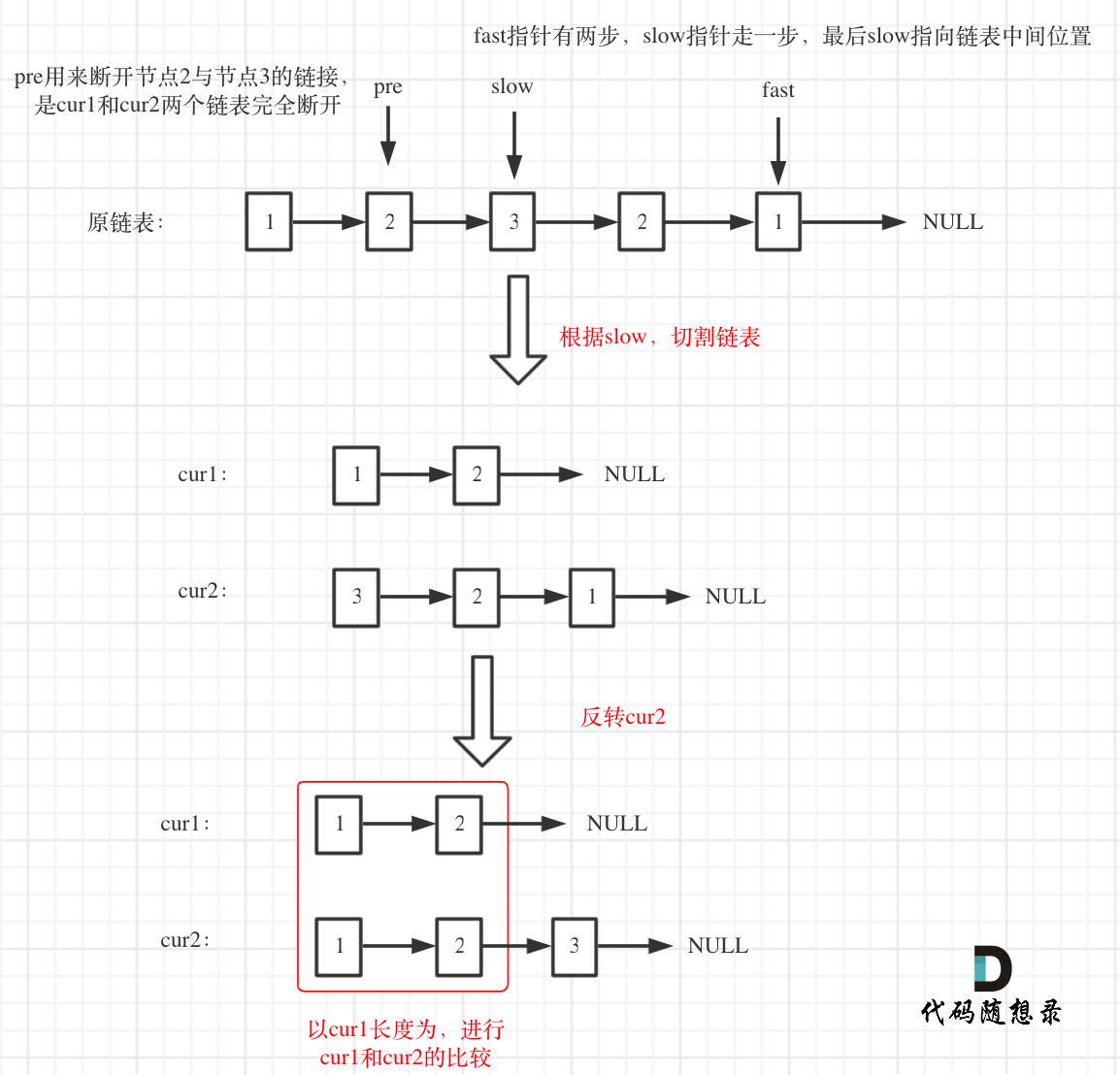
# Reverse the Second Half of the List
This involves the following steps:
- Use two pointers, one moving two steps at a time (fast) and one moving one step at a time (slow). When the fast pointer reaches the end, the slow pointer will be at the middle of the list.
- Use a pre pointer to record the node before the slow pointer to divide the list into two halves.
- The list is divided into two equal parts. If the list length is odd, the second half will have one more element.
- Reverse the second half of the list to get
cur2, while the first half iscur1. - Compare the nodes of
cur1andcur2sequentially forcur1's length.
As shown in the diagram:
Here is the code:
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return true;
ListNode* slow = head; // Slow pointer to find the mid position
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* pre = head; // Record the previous node of the slow pointer to divide the list
while (fast && fast->next) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = nullptr; // Divide the list
ListNode* cur1 = head; // First half
ListNode* cur2 = reverseList(slow); // Reverse the second half, if the list is odd, cur2 has one more node
// Start comparing the two lists
while (cur1) {
if (cur1->val != cur2->val) return false;
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return true;
}
// Reverse the list
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // Save the next node of cur
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // Save cur's next node, as we will change cur->next next
cur->next = pre; // Reverse operation
// Update pre and cur pointers
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# Other Language Versions
# Java
// Method 1, Using an array
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
int len = 0;
// Calculate the length of the list
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
int[] res = new int[len];
// Add elements to the array
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++){
res[i] = cur.val;
cur = cur.next;
}
// Check for palindrome
for (int i = 0, j = len - 1; i < j; i++, j--){
if (res[i] != res[j]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
// Method 2, Using fast and slow pointers
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// If the list is empty or contains only one node, return true
if (head == null && head.next == null) return true;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode pre = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
pre = slow; // Record the previous node of slow
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
pre.next = null; // Divide the two lists
// First half
ListNode cur1 = head;
// Second half. Apply list reversal
ListNode cur2 = reverseList(slow);
while (cur1 != null){
if (cur1.val != cur2.val) return false;
// Move both nodes
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return true;
}
ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
// Reverse the list
ListNode tmp = null;
ListNode pre = null;
while (head != null){
tmp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# Python
# Array simulation
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
list=[]
while head:
list.append(head.val)
head=head.next
l,r=0, len(list)-1
while l<=r:
if list[l]!=list[r]:
return False
l+=1
r-=1
return True
# Reverse the second half
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
fast = slow = head
# Find mid point including the middle element into the first half
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
node = None
# Reverse the second half of the linked list
while slow:
slow.next, slow, node = node, slow.next, slow
# Compare reversed and original half; maintain reversed list shorter than the first half
while node:
if node.val != head.val:
return False
node = node.next
head = head.next
return True
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
// Method 1, using an array
func isPalindrome(head *ListNode) bool{
// Calculate slice length to avoid frequent expansion
cur, ln := head, 0
for cur != nil {
ln++
cur = cur.Next
}
nums := make([]int, ln)
index := 0
for head != nil {
nums[index] = head.Val
index++
head = head.Next
}
// Compare palindrome slice
for i, j := 0, ln-1; i <= j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
if nums[i] != nums[j] { return false }
}
return true
}
// Method 2, fast and slow pointers
func isPalindrome(head *ListNode) bool {
if head == nil && head.Next == nil { return true }
slow := head
fast := head
pre := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
pre = slow
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
pre.Next = nil
cur1 := head
cur2 := ReverseList(slow)
for cur1 != nil {
if cur1.Val != cur2.Val { return false }
cur1 = cur1.Next
cur2 = cur2.Next
}
return true
}
func ReverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
tmp := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = tmp
}
return pre
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# JavaScript
var isPalindrome = function(head) {
const reverseList = head => {
let temp = null;
let pre = null;
while(head != null){
temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
return pre;
}
if(!head && !head.next) return true;
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
let pre = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
pre.next = null;
let cur1 = head;
let cur2 = reverseList(slow);
while(cur1 != null){
if(cur1.val != cur2.val) return false;
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return true;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# TypeScript
Array simulation
function isPalindrome(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
const helperArr: number[] = [];
let curNode: ListNode | null = head;
while (curNode !== null) {
helperArr.push(curNode.val);
curNode = curNode.next;
}
let left: number = 0,
right: number = helperArr.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (helperArr[left++] !== helperArr[right--]) return false;
}
return true;
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Reverse the second half of the list
function isPalindrome(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
if (head === null || head.next === null) return true;
let fastNode: ListNode | null = head,
slowNode: ListNode = head,
preNode: ListNode = head;
while (fastNode !== null && fastNode.next !== null) {
preNode = slowNode;
slowNode = slowNode.next!;
fastNode = fastNode.next.next;
}
preNode.next = null;
let cur1: ListNode | null = head;
let cur2: ListNode | null = reverseList(slowNode);
while (cur1 !== null) {
if (cur1.val !== cur2!.val) return false;
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2!.next;
}
return true;
};
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let curNode: ListNode | null = head,
preNode: ListNode | null = null;
while (curNode !== null) {
let tempNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next;
curNode.next = preNode;
preNode = curNode;
curNode = tempNode;
}
return preNode;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
Copyright © 2025 keetcoder
