# 200. Number of Islands
Problem link (opens new window)
Given a 2D grid map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), count the number of islands in the grid.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically.
You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.

Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 300
- grid[i][j] is either
'0'or'1'
# Thought Process
Note that each island is formed by horizontally and/or vertically adjacent lands only.
This means that diagonal connections are not counted. For example, in the second example, there are three islands, as shown in the following illustration:
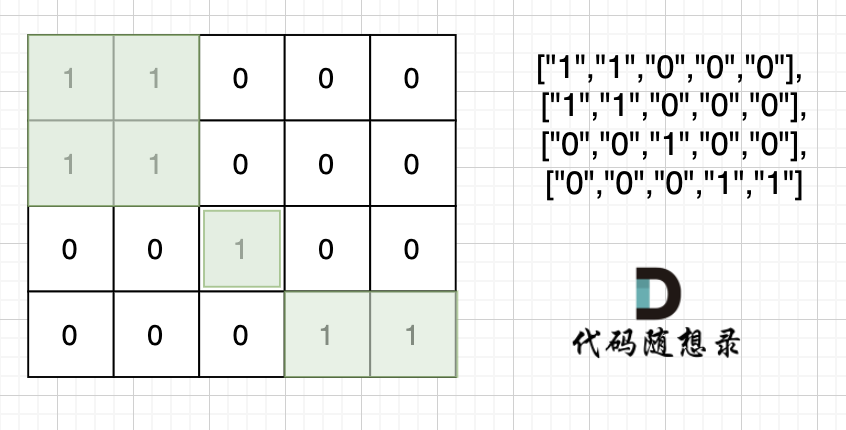
This problem can be solved using DFS, BFS, or Union Find as a basic strategy.
The approach for this problem is that when you encounter an unvisited land node, increment the counter by one, and mark all land nodes connected to this land node as visited.
When you encounter a visited land node or a water node, skip it. This way, the counter eventually reflects the number of islands.
How do you mark all land nodes connected to a given land node? You can use DFS, BFS, or Union Find.
# Breadth-First Search (BFS)
Many people encounter timeout errors when using BFS for this problem. An important detail in a breadth-first search is:
The main reason is mark the node as visited as soon as it is added to the queue, not when it is dequeued.
Some might wonder if this makes a difference.
If you mark a node as visited only when it is dequeued, as shown in the diagram below, it can cause many nodes to be re-added to the queue, leading to inefficiencies.
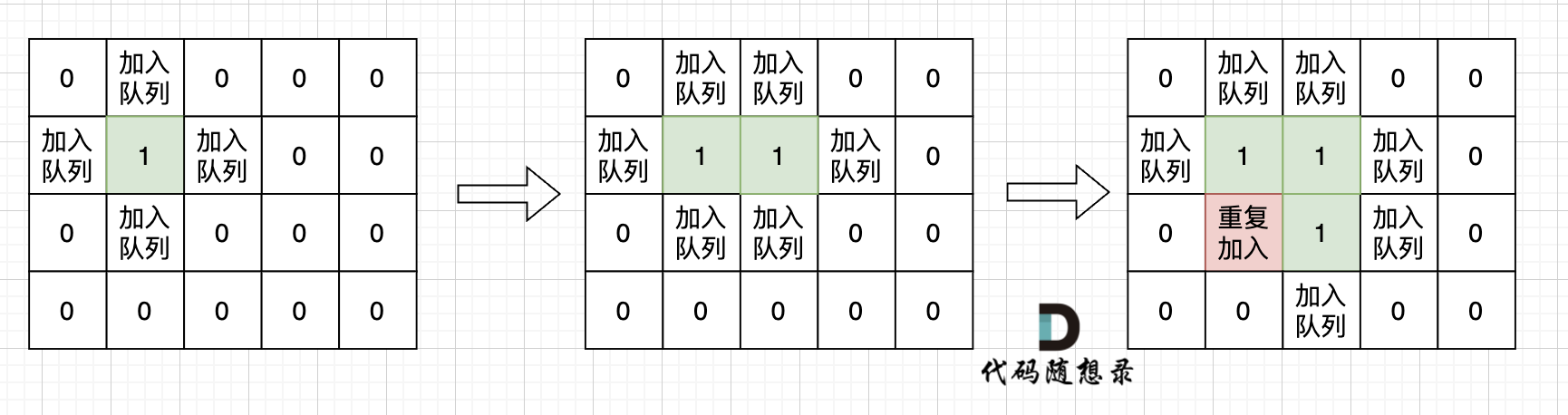
Incorrect approach (mark nodes as visited only when dequeued):
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // Four directions
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
visited[curx][cury] = true; // Only mark nodes as visited when dequeued
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // Out of bounds
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Correct approach (mark nodes as visited upon adding to the queue):
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // Four directions
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // Mark as visited when added to the queue
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // Out of bounds
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // Mark as visited when added to the queue
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
The only slight difference between these two versions is the placement of visited[x][y] = true;. This is based on the definition that nodes in the queue are already considered visited. Thus, once added to the queue, immediately mark the node as visited.
Complete BFS solution:
class Solution {
private:
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // Four directions
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // Mark as visited when added to the queue
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // Out of bounds
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // Mark as visited when added to the queue
}
}
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
result++; // Increment for each new unvisited land
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // Mark all connected lands as visited
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# Implementations in Other Languages
# Java
class Solution {
boolean[][] visited;
int[][] move = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
visited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
bfs(grid, i, j);
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
// Visit all lands in this island
public void bfs(char[][] grid, int y, int x) {
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{y, x});
visited[y][x] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int m = cur[0];
int n = cur[1];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nexty = m + move[i][0];
int nextx = n + move[i][1];
if(nextx < 0 || nexty == grid.length || nexty < 0 || nextx == grid[0].length) continue;
if(!visited[nexty][nextx] && grid[nexty][nextx] == '1') {
queue.offer(new int[]{nexty, nextx});
visited[nexty][nextx] = true; // Mark as visited upon entering the queue
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# Python
BFS solution
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.dirs = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
m = len(grid)
n = len(grid[0])
visited = [[False]*n for _ in range(m)]
res = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if visited[i][j] == False and grid[i][j] == '1':
res += 1
self.bfs(grid, i, j, visited) # Call bfs within this condition
return res
def bfs(self, grid, i, j, visited):
q = deque()
q.append((i,j))
visited[i][j] = True
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
for k in range(4):
next_i = x + self.dirs[k][0]
next_j = y + self.dirs[k][1]
if next_i < 0 or next_i >= len(grid):
continue
if next_j < 0 or next_j >= len(grid[0]):
continue
if visited[next_i][next_j]:
continue
if grid[next_i][next_j] == '0':
continue
q.append((next_i, next_j))
visited[next_i][next_j] = True
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# JavaScript
var numIslands = function (grid) {
let dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]; // Four directions
let bfs = (grid, visited, x, y) => {
let queue = [];
queue.push([x, y]);
visited[x][y] = true;
while (queue.length) {
let top = queue.shift();// Dequeue
console.log(top)
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nextX = top[0] + dir[i][0]
let nextY = top[1] + dir[i][1]
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY < 0 || nextY >= grid[0].length)
continue;
if (!visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] === "1") {
queue.push([nextX, nextY])
visited[nextX][nextY] = true
}
}
}
}
let visited = new Array(grid.length).fill().map(() => Array(grid[0].length).fill(false))
let res = 0
for (let i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] === "1") {
++res;
bfs(grid, visited, i, j);
}
}
}
return res
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# TypeScript
function numIslands2(grid: string[][]): number {
// Four directions
const dir: number[][] = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]];
const [m, n]: [number, number] = [grid.length, grid[0].length];
function dfs(grid: string[][], visited: boolean[][], x: number, y: number) {
const queue: number[][] = [[x, y]];
while (queue.length !== 0) {
// Dequeue
const top: number[] = queue.shift()!;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const nextX: number = top[0] + dir[i][0];
const nextY: number = top[1] + dir[i][1];
// Out of bounds
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= m || nextY < 0 || nextY >= n) {
continue;
}
if (!visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] === '1') {
queue.push([nextX, nextY]);
// Mark as visited when added to the queue
visited[nextX][nextY] = true;
}
}
}
}
const visited: boolean[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, _ => new Array(n).fill(false));
let result = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let k = 0; k < n; k++) {
if (!visited[i][k] && grid[i][k] === '1') {
++result; // Increment for each new unvisited land
visited[i][k] = true;
dfs(grid, visited, i, k); // Mark all connected lands as visited
}
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# Go
var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}
func numIslands(grid [][]byte) int {
res := 0
visited := make([][]bool, len(grid))
for i := 0; i < len(grid); i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, len(grid[0]))
}
for i, rows := range grid {
for j, v := range rows {
if v == '1' && !visited[i][j] {
res++
bfs(grid, visited, i, j)
}
}
}
return res
}
func bfs(grid [][]byte, visited [][]bool, i, j int) {
queue := [][2]int{{i, j}}
visited[i][j] = true // Mark as visited, doing it inside the loop leads to repetitions
for len(queue) > 0 {
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
x, y := cur[0]+d[0], cur[1]+d[1]
if x < 0 || x >= len(grid) || y < 0 || y >= len(grid[0]) {
continue
}
if grid[x][y] == '1' && !visited[x][y] {
visited[x][y] = true
queue = append(queue, [2]int{x, y})
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# Rust
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
const DIRECTIONS: [(i32, i32); 4] = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)];
pub fn num_islands(grid: Vec<Vec<char>>) -> i32 {
let mut visited = vec![vec![false; grid[0].len()]; grid.len()];
let mut res = 0;
for (i, chars) in grid.iter().enumerate() {
for (j, &c) in chars.iter().enumerate() {
if !visited[i][j] && c == '1' {
res += 1;
Self::bfs(&grid, &mut visited, (i as i32, j as i32));
}
}
}
res
}
pub fn bfs(grid: &Vec<Vec<char>>, visited: &mut Vec<Vec<bool>>, (x, y): (i32, i32)) {
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back((x, y));
visited[x as usize][y as usize] = true;
while let Some((cur_x, cur_y)) = queue.pop_front() {
for (dx, dy) in Self::DIRECTIONS {
let (nx, ny) = (cur_x + dx, cur_y + dy);
if nx < 0 || nx >= grid.len() as i32 || ny < 0 || ny >= grid[0].len() as i32 {
continue;
}
let (nx, ny) = (nx as usize, ny as usize);
if grid[nx][ny] == '1' && !visited[nx][ny] {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
queue.push_back((nx as i32, ny as i32));
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
