# 143. Reorder List
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
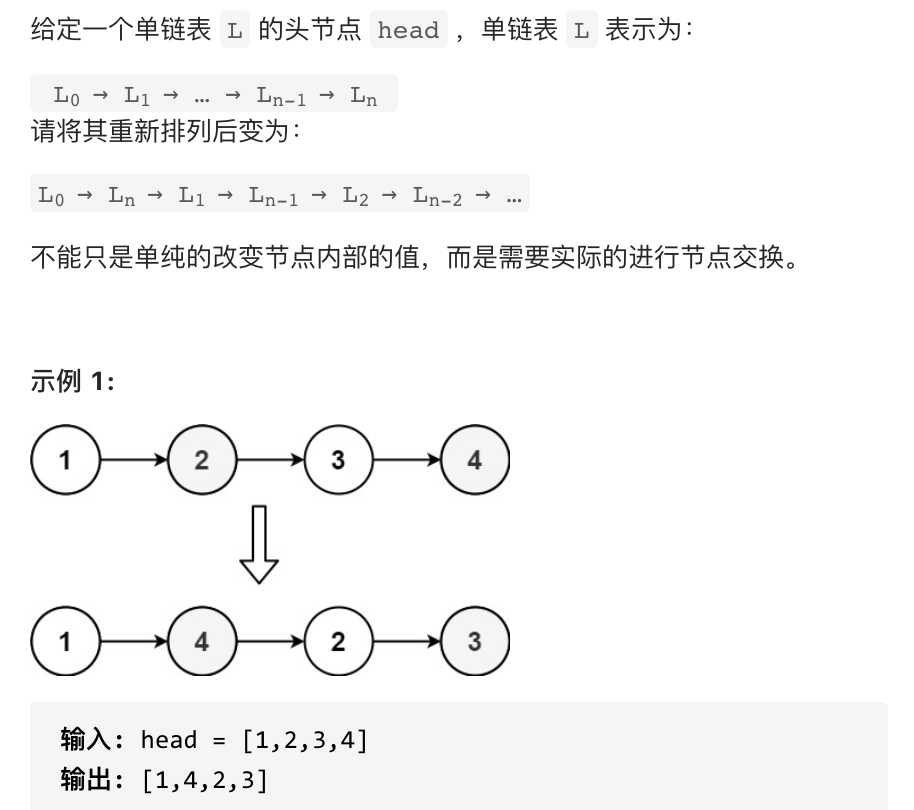
# Approach
In this article, three methods of C++ implementation will be provided:
- Array Simulation
- Deque Simulation
- Direct List Splitting
# Method 1
Put the linked list into an array, then use the two-pointer technique, one from the front and one from the back, to traverse the array and reconstruct the linked list.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
vector<ListNode*> vec;
ListNode* cur = head;
if (cur == nullptr) return;
while(cur != nullptr) {
vec.push_back(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
int i = 1;
int j = vec.size() - 1; // i and j are the two pointers from front and back
int count = 0; // counting, even numbers take from the back, odd numbers take from the front
while (i <= j) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
cur->next = vec[j];
j--;
} else {
cur->next = vec[i];
i++;
}
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
cur->next = nullptr; // Note the end
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# Method 2
Put the linked list into a deque then use the deque to pop elements from the front and the back to reconstruct the new linked list. This method is slightly easier than using an array since it avoids simulating the two-pointer mechanism from front and back.
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
deque<ListNode*> que;
ListNode* cur = head;
if (cur == nullptr) return;
while(cur->next != nullptr) {
que.push_back(cur->next);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
int count = 0; // counting, even numbers take from the back, odd numbers take from the front
ListNode* node;
while(que.size()) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
node = que.back();
que.pop_back();
} else {
node = que.front();
que.pop_front();
}
count++;
cur->next = node;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = nullptr; // Note the end
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Method 3
Split the linked list into two parts, then reverse the second linked list, and finally combine the two linked lists to form a new one.
As shown in the image:
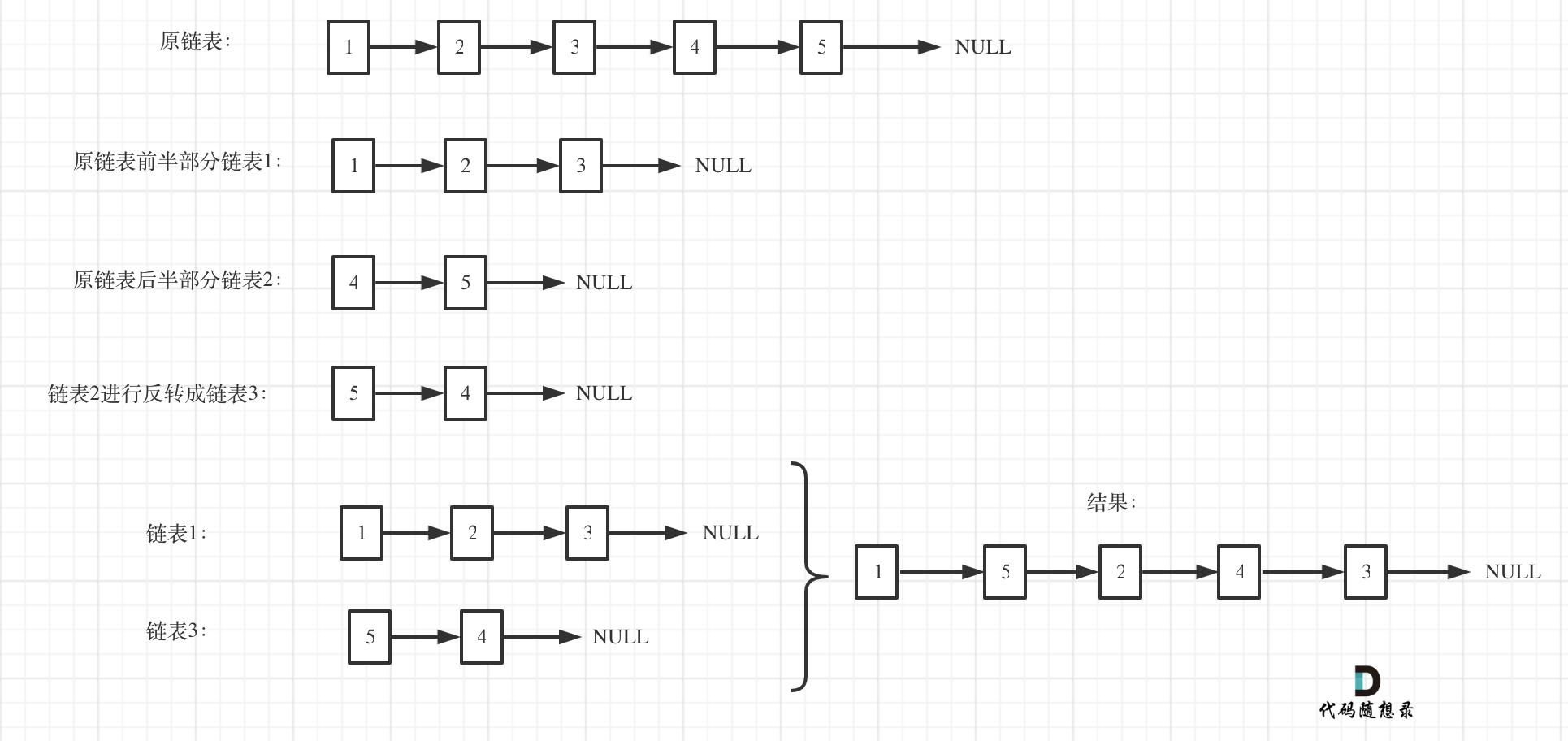
This method is relatively complex. Averaging the linked list into two appears straightforward, but there are many details when writing the code. Furthermore, there are some minor details to consider when finally combining the two linked lists into a new one.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
private:
// Reverse linked list
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // Save the next node of cur
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // Save cur's next node because we are going to change cur->next
cur->next = pre; // Reverse operation
// Update pre and cur pointers
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return;
// Use the fast and slow pointer method to divide the linked list into two parts: head1 and head2
// If the total length of the list is odd, head1 is relatively one node longer than head2
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next && fast->next->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* head1 = head;
ListNode* head2;
head2 = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
// Reverse head2
head2 = reverseList(head2);
// Interleave head1 and head2 to form the new linked list head
ListNode* cur1 = head1;
ListNode* cur2 = head2;
ListNode* cur = head;
cur1 = cur1->next;
int count = 0; // even numbers take elements from head2, odd numbers take from head1
while (cur1 && cur2) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
cur->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
} else {
cur->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
count++;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur2 != nullptr) { // Handle the end
cur->next = cur2;
}
if (cur1 != nullptr) {
cur->next = cur1;
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# Other Languages Versions
# Java
// Method 1 Java implementation using an array to store nodes
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
// Two-pointer approach
ListNode cur = head;
// ArrayList is based on an array, which allows for random access by index
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (cur != null){
list.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head; // Reset to the head
int l = 1, r = list.size() - 1; // Note the left starts from 1
int count = 0;
while (l <= r){
if (count % 2 == 0){
// Even
cur.next = list.get(r);
r--;
}else {
// Odd
cur.next = list.get(l);
l++;
}
// Move the pointer each time
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
// Terminate the tail
cur.next = null;
}
}
// Method 2: Use a deque, simplifies array operations, the code is cleaner (avoids some boundary conditions)
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
// Solve using the deque approach
Deque<ListNode> de = new LinkedList<>();
// Only take elements after the head to avoid duplication
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
de.offer(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head; // Reset to head
int count = 0;
while (!de.isEmpty()){
if (count % 2 == 0){
// Even, take from the right end of the deque
cur.next = de.pollLast();
}else {
// Odd, take from the left front of the deque
cur.next = de.poll();
}
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
cur.next = null;
}
}
// Method 3
public class ReorderList {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
// Find the midpoint
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// Right is the right half
ListNode right = slow.next;
// Disconnect left and right
slow.next = null;
// Reverse the right part
right = reverseList(right);
// The start of the left
ListNode left = head;
// Interleave left and right to form the complete list, the left list is always longer or equal in length to right, so only test right in the loop
while (right != null) {
ListNode curLeft = left.next;
left.next = right;
left = curLeft;
ListNode curRight = right.next;
right.next = left;
right = curRight;
}
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode headNode = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = headNode.next;
headNode.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
return headNode.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
# Python
# Method 2 with deque
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
d = collections.deque()
tmp = head
while tmp.next: # add all but the first element to deque
d.append(tmp.next)
tmp = tmp.next
tmp = head
while len(d): # interleave by taking reverse and forward
tmp.next = d.pop()
tmp = tmp.next
if len(d):
tmp.next = d.popleft()
tmp = tmp.next
tmp.next = None # end to null
# Method 3 with list reversal
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
if head == None or head.next == None:
return True
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
right = slow.next # split the list
slow.next = None # cut
right = self.reverseList(right) # reverse the second part
left = head
# Alternate from both parts, left is always longer or same length
while right:
curLeft = left.next
left.next = right
left = curLeft
curRight = right.next
right.next = left
right = curRight
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
pre = None
while(cur!=None):
temp = cur.next # save next
cur.next = pre # reverse
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# Go
// Method 1 Array Simulation
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
vec := make([]*ListNode, 0)
cur := head
if cur == nil {
return
}
for cur != nil {
vec = append(vec, cur)
cur = cur.Next
}
cur = head
i := 1
j := len(vec) - 1 // i, j are the two-pointer
count := 0 // count, even numbers take from the back, odd numbers take from the front
for i <= j {
if count % 2 == 0 {
cur.Next = vec[j]
j--
} else {
cur.Next = vec[i]
i++
}
cur = cur.Next
count++
}
cur.Next = nil // End
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// Method 2 Deque Simulation
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
que := make([]*ListNode, 0)
cur := head
if cur == nil {
return
}
for cur.Next != nil {
que = append(que, cur.Next)
cur = cur.Next
}
cur = head
count := 0
for len(que) > 0 {
if count % 2 == 0 {
cur.Next = que[len(que)-1]
que = que[:len(que)-1]
} else {
cur.Next = que[0]
que = que[1:]
}
count++
cur = cur.Next
}
cur.Next = nil // End
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// Method 3 Split and Reverse
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
var slow = head
var fast = head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
var right = new(ListNode)
for slow != nil {
temp := slow.Next
slow.Next = right.Next
right.Next = slow
slow = temp
}
right = right.Next
h := head
for right.Next != nil {
temp := right.Next
right.Next = h.Next
h.Next = right
h = h.Next.Next
right = temp
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# JavaScript
// Method 1 Using array to store nodes
var reorderList = function(head, s = [], tmp) {
let cur = head;
// list is an array, can use index to access
const list = [];
while(cur != null){
list.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head; // Reset to head
let l = 1, r = list.length - 1; // Left starts from 1
let count = 0;
while(l <= r){
if(count % 2 == 0){
// even
cur.next = list[r];
r--;
} else {
// odd
cur.next = list[l];
l++;
}
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
cur.next = null; // End
}
// Method 2 Using deque in JavaScript (runs slowly)
var reorderList = function(head, s = [], tmp) {
// JavaScript array used as deque
const deque = [];
let cur = head.next;
while(cur != null){
deque.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head; // Reset to head
let count = 0;
while(deque.length !== 0){
if(count % 2 == 0){
cur.next = deque.pop();
} else {
cur.next = deque.shift();
}
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
cur.next = null;
}
// Method 3 Split, Reverse and Merge
var reorderList = function(head, s = [], tmp) {
const reverseList = head => {
let headNode = new ListNode(0);
let cur = head;
let next = null;
while(cur != null){
next = cur.next;
cur.next = headNode.next;
headNode.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
return headNode.next;
}
let fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
let right = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
right = reverseList(right);
let left = head;
while (right != null) {
let curLeft = left.next;
left.next = right;
left = curLeft;
let curRight = right.next;
right.next = left;
right = curRight;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
# TypeScript
Helper Array Method:
function reorderList(head: ListNode | null): void {
if (head === null) return;
const helperArr: ListNode[] = [];
let curNode: ListNode | null = head;
while (curNode !== null) {
helperArr.push(curNode);
curNode = curNode.next;
}
let node: ListNode = head;
let left: number = 1,
right: number = helperArr.length - 1;
let count: number = 0;
while (left <= right) {
if (count % 2 === 0) {
node.next = helperArr[right--];
} else {
node.next = helperArr[left++];
}
count++;
node = node.next;
}
node.next = null;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Splitting List Method:
function reorderList(head: ListNode | null): void {
if (head === null || head.next === null) return;
let fastNode: ListNode = head,
slowNode: ListNode = head;
while (fastNode.next !== null && fastNode.next.next !== null) {
slowNode = slowNode.next!;
fastNode = fastNode.next.next;
}
let head1: ListNode | null = head;
// Reverse the second part
let head2: ListNode | null = reverseList(slowNode.next);
slowNode.next = null;
while (head2 !== null) {
const tempNode1: ListNode | null = head1!.next,
tempNode2: ListNode | null = head2.next;
head1!.next = head2;
head2.next = tempNode1;
head1 = tempNode1;
head2 = tempNode2;
}
};
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let curNode: ListNode | null = head,
preNode: ListNode | null = null;
while (curNode !== null) {
const tempNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next;
curNode.next = preNode;
preNode = curNode;
curNode = tempNode;
}
return preNode;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# C
Method 3: Reverse List
//Reverse a linked list
struct ListNode *reverseList(struct ListNode *head) {
if(!head)
return NULL;
struct ListNode *preNode = NULL, *curNode = head;
while(curNode) {
//Store curNode->next temporarily (will be updated)
struct ListNode* tempNode = curNode->next;
//Point curNode->next to preNode
curNode->next = preNode;
//Update preNode to curNode
preNode = curNode;
//Update curNode to the next node in original list
curNode = tempNode;
}
return preNode;
}
void reorderList(struct ListNode* head){
//slow pointer to mid node (last node of the first half), fast pointer as help, jumps two nodes every loop
struct ListNode *fast = head, *slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next && fast->next->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//Reverse nodes after slow->next
struct ListNode *sndLst = reverseList(slow->next);
//Disconnect the two halves
slow->next = NULL;
//Start interleaving from curNode->next, curNode initially is head, so fstList should start from head->next
struct ListNode *fstLst = head->next;
struct ListNode *curNode = head;
int count = 0;
//While nodes present in both lists
while(sndLst && fstLst) {
if(count % 2) {
curNode->next = fstLst;
fstLst = fstLst->next;
} else {
curNode->next = sndList;
sndLst = sndLst->next;
}
curNode = curNode->next;
++count;
}
//Append remaining nodes if any
if(fstLst) {
curNode->next = fstLst;
}
if(sndLst) {
curNode->next = sndLst;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
