# 127. Word Ladder
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
A transformation sequence from word beginWord to word endWord using a dictionary wordList is a sequence of words formed with the following conditions:
- The first word in the sequence is
beginWord. - The last word in the sequence is
endWord. - Only one letter can be changed at a time.
- Each intermediate word must exist in the dictionary
wordList. - Given two words,
beginWordandendWord, and a dictionarywordList, find the number of words in the shortest transformation sequence frombeginWordtoendWord. If no such sequence exists, return 0.
Example 1:
- Input:
beginWord = "hit",endWord = "cog",wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"] - Output: 5
- Explanation: One shortest transformation sequence is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog", which has a length of 5.
Example 2:
- Input:
beginWord = "hit",endWord = "cog",wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"] - Output: 0
- Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in the dictionary, so the transformation cannot be made.
# Approach
In Example 1, from the graph shown below, we can see that there are multiple paths from hit to cog. One has the shortest length of 5, and two have a length of 6.
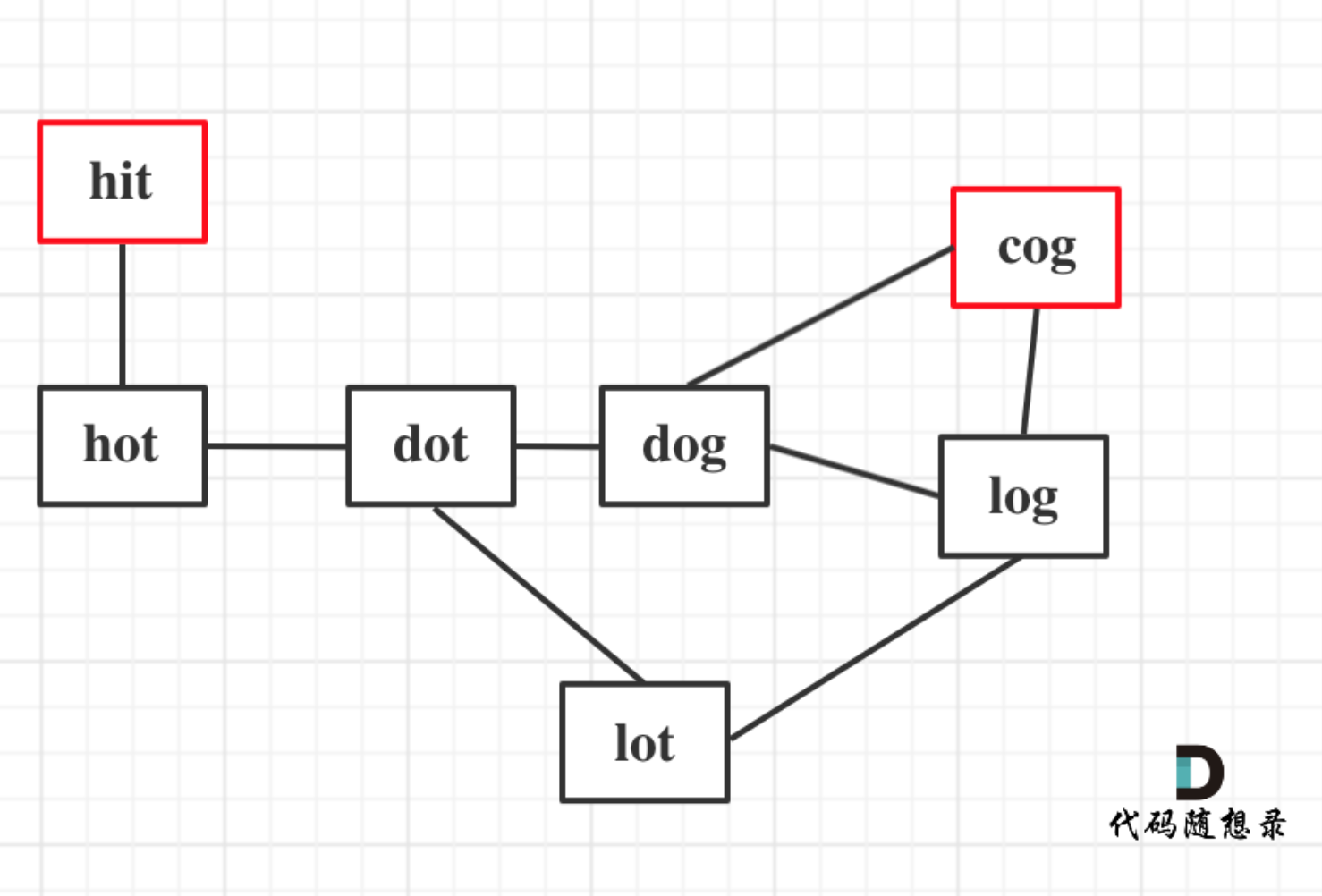
This problem only requires finding the length of the shortest path, not the path itself.
Thus, there are two problems to solve:
- How do the nodes in the graph get connected?
- Finding the shortest path length from the start to the end node.
Firstly, the problem doesn't provide the connections between nodes; we have to create them ourselves under the condition of differing by one character. Hence, we need to check the relationship between nodes to determine if they only differ by one character. If they do, then they are connected.
To find the shortest path from the start to the end, Breadth-First Search (BFS) is most suitable for finding shortest paths in an undirected graph because once BFS reaches the endpoint, it guarantees the shortest path. This is because BFS searches outward in layers from the starting point.
Using Depth-First Search (DFS) in this context would be complex because it involves selecting the shortest path from multiple paths that reach the end. However, with BFS, reaching the endpoint guarantees the shortest path.
Additionally:
- This problem involves an undirected graph, so visit markers are necessary to prevent cycles!
- The provided list is an array, which can be converted into a set for faster lookup.
Below is the C++ code with detailed comments:
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
// Convert vector to unordered_set for faster lookup
unordered_set<string> wordSet(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());
// If endWord isn't in wordSet, return 0
if (wordSet.find(endWord) == wordSet.end()) return 0;
// Track whether a word has been visited
unordered_map<string, int> visitMap; // <word, path length>
// Initialize the queue
queue<string> que;
que.push(beginWord);
// Initialize visitMap
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(beginWord, 1));
while(!que.empty()) {
string word = que.front();
que.pop();
int path = visitMap[word]; // Path length for the current word
for (int i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
string newWord = word; // Use a new word for modifying one letter
for (int j = 0 ; j < 26; j++) {
newWord[i] = j + 'a';
if (newWord == endWord) return path + 1; // Found endWord, return path+1
// Check if newWord is in wordSet and hasn't been visited
if (wordSet.find(newWord) != wordSet.end()
&& visitMap.find(newWord) == visitMap.end()) {
// Add visit info
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(newWord, path + 1));
que.push(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
This problem can also be solved using Bidirectional BFS, which involves searching from both ends (head and tail). Feel free to implement it if you're interested as it won't be further explained here.
# Other Language Versions
# Java
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
HashSet<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList); // Convert to HashSet for faster lookup
if (wordSet.size() == 0 || !wordSet.contains(endWord)) { // Handle edge cases
return 0;
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // BFS Queue
queue.offer(beginWord);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // Map to track path lengths
map.put(beginWord, 1);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String word = queue.poll(); // Dequeue the front word
int path = map.get(word); // Get the path length for this word
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { // Iterate over each character
char[] chars = word.toCharArray(); // Convert word to char array for modification
for (char k = 'a'; k <= 'z'; k++) { // Replace each character with 'a' to 'z'
chars[i] = k; // Change the ith character
String newWord = String.valueOf(chars); // Form new word
if (newWord.equals(endWord)) { // If matches endWord, return current path length + 1
return path + 1;
}
if (wordSet.contains(newWord) && !map.containsKey(newWord)) { // If newWord is valid and not visited
map.put(newWord, path + 1); // Record newWord's path length
queue.offer(newWord); // Enqueue newWord
}
}
}
}
return 0; // No path found
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// Java Bidirectional BFS
class Solution {
// Check if two words differ by exactly one character
public boolean isValid(String currentWord, String chooseWord) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < currentWord.length(); i++)
if (currentWord.charAt(i) != chooseWord.charAt(i)) ++count;
return count == 1;
}
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
if (!wordList.contains(endWord)) return 0; // If endWord isn't in wordList, return 0
// ansLeft tracks the number of words formed by BFS from beginWord
// ansRight tracks the number of words formed by BFS from endWord
int ansLeft = 0, ansRight = 0;
// queueLeft is the BFS queue from beginWord
// queueRight is the BFS queue from endWord
Queue<String> queueLeft = new ArrayDeque<>(), queueRight = new ArrayDeque<>();
queueLeft.add(beginWord);
queueRight.add(endWord);
// Use hashSet to track nodes visited from both ends
Set<String> hashSetLeft = new HashSet<>(), hashSetRight = new HashSet<>();
hashSetLeft.add(beginWord);
hashSetRight.add(endWord);
// As long as either queue is not empty
while (!queueLeft.isEmpty() && !queueRight.isEmpty()) {
++ansLeft;
int size = queueLeft.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String currentWord = queueLeft.poll();
// If hashSetRight contains currentWord, it's crossed over to endWord
if (hashSetRight.contains(currentWord)) return ansRight + ansLeft;
for (String chooseWord : wordList) {
if (hashSetLeft.contains(chooseWord) || !isValid(currentWord, chooseWord)) continue;
hashSetLeft.add(chooseWord);
queueLeft.add(chooseWord);
}
}
++ansRight;
size = queueRight.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String currentWord = queueRight.poll();
// If hashSetLeft contains currentWord, it's crossed over to beginWord
if (hashSetLeft.contains(currentWord)) return ansLeft + ansRight;
for (String chooseWord : wordList) {
if (hashSetRight.contains(chooseWord) || !isValid(currentWord, chooseWord)) continue;
hashSetRight.add(chooseWord);
queueRight.add(chooseWord);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# Python
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
wordSet = set(wordList)
if len(wordSet)== 0 or endWord not in wordSet:
return 0
mapping = {beginWord:1}
queue = deque([beginWord])
while queue:
word = queue.popleft()
path = mapping[word]
for i in range(len(word)):
word_list = list(word)
for j in range(26):
word_list[i] = chr(ord('a')+j)
newWord = "".join(word_list)
if newWord == endWord:
return path+1
if newWord in wordSet and newWord not in mapping:
mapping[newWord] = path+1
queue.append(newWord)
return 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Go
func ladderLength(beginWord string, endWord string, wordList []string) int {
wordMap, que, depth := getWordMap(wordList, beginWord), []string{beginWord}, 0
for len(que) > 0 {
depth++
qLen := len(que) // Length of the queue
for i := 0; i < qLen; i++ {
word := que[0]
que = que[1:] // Dequeue the front word
candidates := getCandidates(word)
for _, candidate := range candidates {
if _, exist := wordMap[candidate]; exist { // Check candidates against wordMap
if candidate == endWord {
return depth + 1
}
delete(wordMap, candidate) // Delete used words to avoid revisiting
que = append(que, candidate)
}
}
}
}
return 0
}
// Create a map of words for faster lookup
func getWordMap(wordList []string, beginWord string) map[string]int {
wordMap := make(map[string]int)
for i, word := range wordList {
if _, exist := wordMap[word]; !exist {
if word != beginWord {
wordMap[word] = i
}
}
}
return wordMap
}
// Generate candidates by replacing each character
func getCandidates(word string) []string {
var res []string
for i := 0; i < 26; i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(word); j++ {
if word[j] != byte(int('a')+i) {
res = append(res, word[:j]+string(int('a')+i)+word[j+1:])
}
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# JavaScript
var ladderLength = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
// Convert wordList to Set for faster lookup
const wordSet = new Set(wordList);
// If endWord isn't in wordSet, return 0
if (wordSet.size === 0 || !wordSet.has(endWord)) return 0;
// Track whether a word has been visited
const visitMap = new Map();// <word, path length>
// Initialize queue
const queue = [];
queue.push(beginWord);
// Initialize visitMap
visitMap.set(beginWord, 1);
while(queue.length !== 0){
let word = queue.shift(); // Dequeue the front word
let path = visitMap.get(word); // Path length for current word
for(let i = 0; i < word.length; i++){ // Iterate each character of the word
for (let c = 97; c <= 122; c++) { // Iterate 'a' to 'z'
// Form new word by changing one character
let newWord = word.slice(0, i) + String.fromCharCode(c) + word.slice(i + 1);
if(newWord === endWord) return path + 1; // Found endWord, return path+1
// If newWord is in wordSet and hasn't been visited
if(wordSet.has(newWord) && !visitMap.has(newWord)) {
// Add visit info
visitMap.set(newWord, path + 1);
queue.push(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# TypeScript
function ladderLength(
beginWord: string,
endWord: string,
wordList: string[]
): number {
const words = new Set(wordList);
if (!words.has(endWord)) return 0;
if (beginWord.length === 1) return 2;
let current = new Set([beginWord]);
let rightcurrent = new Set([endWord]);
words.delete(endWord);
let step = 1;
while (current.size) {
if (current.size > rightcurrent.size) {
[current, rightcurrent] = [rightcurrent, current];
}
const temp: Set<string> = new Set();
for (const word of current) {
for (const right of rightcurrent) {
if (diffonechar(word, right)) {
return step + 1;
}
}
for (const other of words) {
if (diffonechar(other, word)) {
temp.add(other);
words.delete(other);
}
}
}
if (temp.size === 0) return 0;
current = temp;
step = step + 1;
}
return 0;
}
function diffonechar(word1: string, word2: string): boolean {
let changes = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < word1.length; i++) {
if (word1[i] != word2[i]) changes += 1;
}
return changes === 1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
