# 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
LeetCode problem link (opens new window)
Given a perfect binary tree, where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree is defined as follows:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Advanced:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive solution does not count as extra space for this problem.
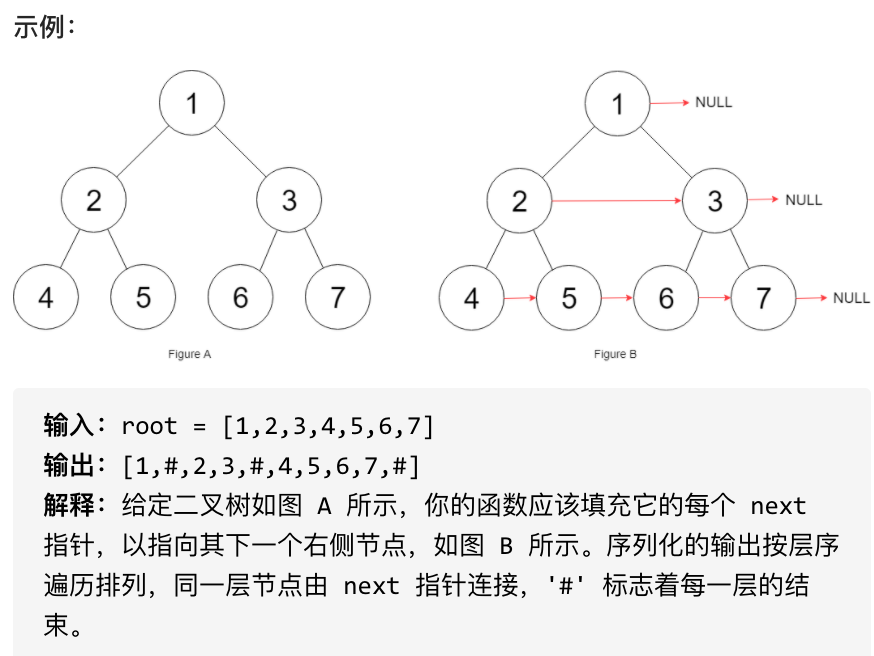
# Solution
Note the hint in the problem statement:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive solution does not count as extra space for this problem.
This essentially requires using recursion, since iterative solutions typically require a stack or queue.
# Recursion
Thinking about how to use recursion, although level-order traversal is the most straightforward, it's not easy to conceptualize a recursive approach.
As shown in the illustration, suppose the current node being processed is cur:
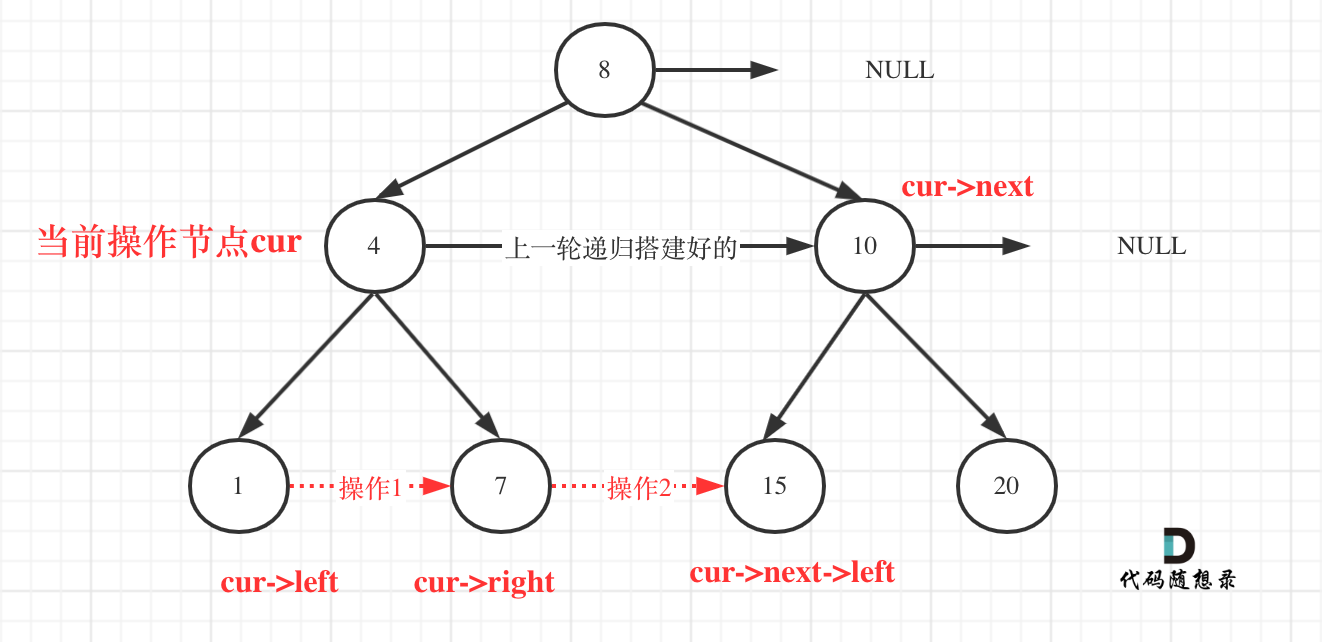
The key point is that you can use the connections established in the previous level during the recursion to connect the current level.
For instance, when the cur node is the element 4, the logic for connecting nodes is as follows: (Note the correlation between comments "Operation 1" and "Operation 2" in the code and the illustration)
if (cur->left) cur->left->next = cur->right; // Operation 1
if (cur->right) {
if (cur->next) cur->right->next = cur->next->left; // Operation 2
else cur->right->next = NULL;
}
2
3
4
5
Understanding this, using pre-order traversal, it is not difficult to write the following code:
class Solution {
private:
void traversal(Node* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
// Center
if (cur->left) cur->left->next = cur->right; // Operation 1
if (cur->right) {
if (cur->next) cur->right->next = cur->next->left; // Operation 2
else cur->right->next = NULL;
}
traversal(cur->left); // Left
traversal(cur->right); // Right
}
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
traversal(root);
return root;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# Iteration (Level-order Traversal)
Using level-order traversal is the most straightforward approach for this problem. If you are not familiar with level-order traversal, check out this: 0102.Binary Tree Level Order Traversal (opens new window).
When traversing each level, if the node is not the last one, it points to the next node; if it is the last node, it points to nullptr.
The code is as follows:
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root != nullptr) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i != size - 1) {
node->next = que.front(); // If it's not the last Node, point to the next Node
} else node->next = nullptr; // If it's the last Node, point to nullptr
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Other Language Versions
# Java
// Recursive Method
class Solution {
public void traversal(Node cur) {
if (cur == null) return;
if (cur.left != null) cur.left.next = cur.right; // Operation 1
if (cur.right != null) {
if(cur.next != null) cur.right.next = cur.next.left; // Operation 2
else cur.right.next = null;
}
traversal(cur.left); // Left
traversal(cur.right); // Right
}
public Node connect(Node root) {
traversal(root);
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// Iterative Method
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) return root;
Queue<Node> que = new LinkedList<Node>();
que.offer(root);
Node nodePre = null;
Node node = null;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { // Start traversal of each level
if (i == 0) {
nodePre = que.peek(); // Record the head node of a level
que.poll();
node = nodePre;
} else {
node = que.peek();
que.poll();
nodePre.next = node; // Previous node in this level points to the current node
nodePre = nodePre.next;
}
if (node.left != null) que.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) que.offer(node.right);
}
nodePre.next = null; // The last node in this level points to null
}
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
// Iterative Method
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
// First node of each level
Node cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
// Since the first node of each level has been removed, change 0 to 1
while (size-- > 1) {
Node next = queue.poll();
if (next.left != null) {
queue.add(next.left);
}
if (next.right != null) {
queue.add(next.right);
}
// The current node points to the next node on the same level
cur.next = next;
// Update the current node
cur = next;
}
// In LeetCode, the last node of each level does not need to point to null
cur.next = null;
}
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Python
# Recursive Method
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
def traversal(cur: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not cur: return []
if cur.left: cur.left.next = cur.right # Operation 1
if cur.right:
if cur.next:
cur.right.next = cur.next.left # Operation 2
else:
cur.right.next = None
traversal(cur.left) # Left
traversal(cur.right) # Right
traversal(root)
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Iterative Method
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root: return
res = []
queue = [root]
while queue:
size = len(queue)
for i in range(size): # Start traversal of each level
if i==0:
nodePre = queue.pop(0) # Record the head node of the level
node = nodePre
else:
node = queue.pop(0)
nodePre.next = node # Previous node in this level points to the current node
nodePre = nodePre.next
if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
nodePre.next = None # The last node in this level points to None
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Go
// Iterative Method
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
stack := make([]*Node, 0)
stack = append(stack, root)
for len(stack) > 0 {
n := len(stack) // Record the number of nodes in the current level
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
node := stack[0] // Dequeue nodes one by one
stack = stack[1:]
if i == n - 1 { // If it's the rightmost node of this level, point next to nil
node.Next = nil
} else {
node.Next = stack[0] // If it's not the rightmost node, point next to the right node
}
if node.Left != nil { // If there is a left child, put it into the stack
stack = append(stack, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil { // If there is a right child, put it into the stack
stack = append(stack, node.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// Constant extra space, using next
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
for cur := root; cur.Left != nil; cur = cur.Left { // Traverse the leftmost nodes of each level
for node := cur; node != nil; node = node.Next { // Traverse from left to right in the current level
node.Left.Next = node.Right // Left child points next to the right child
if node.Next != nil { // If node next has a value, right child points to the left child of the next node
node.Right.Next = node.Next.Left
}
}
}
return root
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# JavaScript
const connect = root => {
if (!root) return root;
// Root node enters the queue
const Q = [root];
while (Q.length) {
const len = Q.length;
// Traverse all nodes in this level
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// Dequeue the front
const node = Q.shift();
// Connect
if (i < len - 1) {
// The new front is the right element of node
node.next = Q[0];
}
// If front left node has value, push to queue
node.left && Q.push(node.left);
// If front right node has value, push to queue
node.right && Q.push(node.right);
}
}
return root;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# TypeScript
(Note: Namespace 'Node' conflicts with the built-in type in TypeScript, here it is changed to 'NodePro')
Recursive Method:
class NodePro {
val: number
left: NodePro | null
right: NodePro | null
next: NodePro | null
constructor(val?: number, left?: NodePro, right?: NodePro, next?: NodePro) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
}
}
function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
if (root === null) return null;
root.next = null;
recur(root);
return root;
};
function recur(node: NodePro): void {
if (node.left === null || node.right === null) return;
node.left.next = node.right;
node.right.next = node.next && node.next.left;
recur(node.left);
recur(node.right);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
Iterative Method:
class NodePro {
val: number
left: NodePro | null
right: NodePro | null
next: NodePro | null
constructor(val?: number, left?: NodePro, right?: NodePro, next?: NodePro) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
}
}
function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
if (root === null) return null;
const queue: NodePro[] = [];
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length > 0) {
for (let i = 0, length = queue.length; i < length; i++) {
const curNode: NodePro = queue.shift()!;
if (i === length - 1) {
curNode.next = null;
} else {
curNode.next = queue[0];
}
if (curNode.left !== null) queue.push(curNode.left);
if (curNode.right !== null) queue.push(curNode.right);
}
}
return root;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// Recursion
public class Solution {
public Node Connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
ConnectNodes(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
private void ConnectNodes(Node node1, Node node2) {
if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
return;
}
// Connect the next of the left child to the right child
node1.next = node2;
// Recursively connect left and right children of the current node
ConnectNodes(node1.left, node1.right);
ConnectNodes(node2.left, node2.right);
// Connect the two subtrees across the parent node
ConnectNodes(node1.right, node2.left);
}
}
// Iteration
public class Solution
{
public Node Connect(Node root)
{
Queue<Node> que = new Queue<Node>();
if (root != null)
{
que.Enqueue(root);
}
while (que.Count > 0)
{
var queSize = que.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < queSize; i++)
{
var cur = que.Dequeue();
// If this node is not the last node of this level
if (i != queSize - 1)
{
// The current node points to the next node
cur.next = que.Peek();
}
// Else point to null
else
{
cur.next = null;
}
if (cur.left != null)
{
que.Enqueue(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null)
{
que.Enqueue(cur.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
