# 54. Spiral Matrix
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order clockwise.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
2
3
4
5
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
# Approach
The approach to solve this problem is derived from 59. Spiral Matrix II (opens new window). It is recommended to review 59. Spiral Matrix II before tackling this problem.
The same principle applies: we're simulating the clockwise spiral traversal of the rectangle. Therefore, the core is to maintain the loop invariant, adhering to the principle of left closed and right open intervals.
Simulating the process of drawing the matrix in a clockwise spiral:
- Fill the upper row from left to right
- Fill the right column from top to bottom
- Fill the lower row from right to left
- Fill the left column from bottom to top
Draw one circle at a time, as shown below:
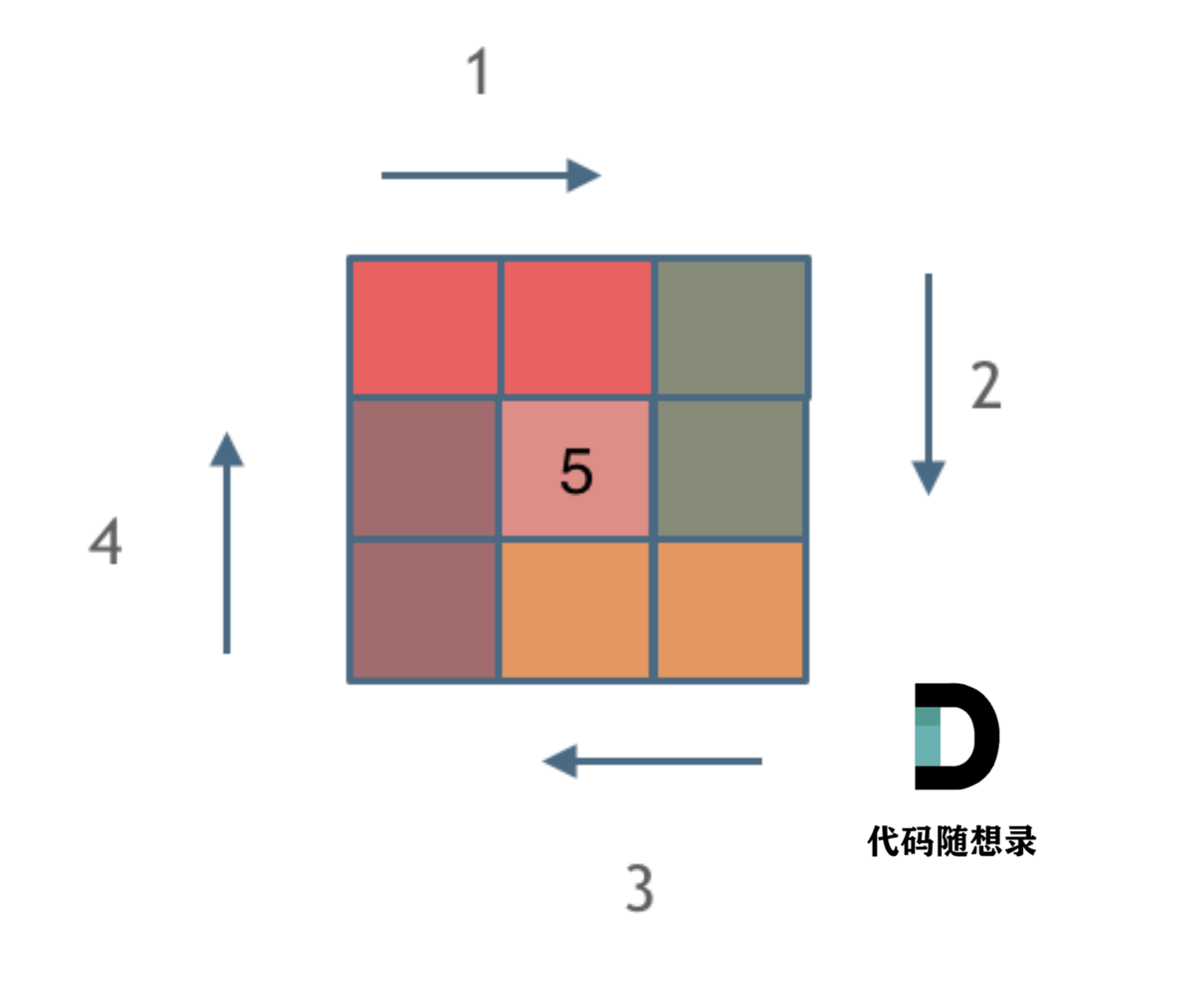
Each color represents an edge, showcasing the handling rules at each corner, where the corner is ceded to the new edge to continue drawing.
The difference from 59. Spiral Matrix II is that the previous problem's matrix is a square and only has the side length n as a boundary condition, whereas in this problem, we need to consider the two boundary conditions of a rectangle's length and width (m rows and n columns). Naturally, m can be equal to n, making the previous problem a special case of this problem when m == n.
Starting with the most general case, we analyze, accompanied by differences introduced by m and n:
- Calculation of loops:
The loop calculation differs slightly from the algorithm in 59. Spiral Matrix II because of the existence of two dimensions: rows and columns. The loop is determined only as
min(rows, columns), for instance, ifrows = 5andcolumns = 7, thenloop = 5 / 7 = 2. - Calculation and filling of the middle:
- Similarly, the mid calculation in this problem also differs due to the above differences.
- If
min(rows, columns)is even, there's no need to consider additional filling of the central position. - If
min(rows, columns)is odd, then the central part of the matrix is not merely[mid][mid], but there will be a special middle row or middle column left over. Whether it's the middle row or middle column depends on the size ofrowsandcolumns. Ifrows > columns, it's the middle column; otherwise, it's the middle row.
- If
Below is the C++ code, detailed with comments explaining the purpose of each step. Notice that more conditions are checked within the while loop, and the strategy used adheres uniformly to the left closed and right open principle.
Complete C++ code:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0)
return {};
int rows = matrix.size(), columns = matrix[0].size();
int total = rows * columns;
vector<int> res(total); // Use vector to define a 1D array to store the result
int startx = 0, starty = 0; // Define the starting position for each loop
int loop = min(rows, columns) / 2;
// The loop calculation is different from the algorithm in 59. Spiral Matrix II, because there are dimensions of rows and columns; one can figure out that the loop is determined by min(rows, columns). For example, if rows = 5, columns = 7, then loop = 5 / 7 = 2
int mid = min(rows, columns) / 2;
// 1. Similarly, the mid calculation in this problem also differs due to the above differences.
// 2.
// If min(rows, columns) is even, there's no need to address additional matrix center position values separately.
// If min(rows, columns) is odd, the central part of the matrix is not merely [mid][mid], but there will be a special middle row or middle column left. Whether it is a middle row or column depends on the size of rows and columns. If rows > columns, it's a middle column; otherwise, it's a middle row.
// This aspect can be difficult to understand, and readers are advised to draw their diagrams for better comprehension.
int count = 0;// Used to populate every cell in the matrix
int offset = 1;// In each loop, need to control the length of each edge traversal
int i,j;
while (loop --) {
i = startx;
j = starty;
// The four following loops simulate one circle
// Simulate filling the top row from left to right (left closed, right open)
for (j = starty; j < starty + columns - offset; j++) {
res[count++] = matrix[startx][j];
}
// Simulate filling the right column from top to bottom (left closed, right open)
for (i = startx; i < startx + rows - offset; i++) {
res[count++] = matrix[i][j];
}
// Simulate filling the bottom row from right to left (left closed, right open)
for (; j > starty; j--) {
res[count++] = matrix[i][j];
}
// Simulate filling the left column from bottom to top (left closed, right open)
for (; i > startx; i--) {
res[count++] = matrix[i][starty];
}
// Starting from the second circle, the starting positions each increment. For example, the first circle starts at (0, 0), the second starts at (1, 1)
startx++;
starty++;
// Offset controls the traversal length of each edge in each circle
offset += 2;
}
// If min(rows, columns) is odd, need to handle the central matrix position separately
if (min(rows, columns) % 2) {
if(rows > columns){
for (int i = mid; i < mid + rows - columns + 1; ++i) {
res[count++] = matrix[i][mid];
}
} else {
for (int i = mid; i < mid + columns - rows + 1; ++i) {
res[count++] = matrix[mid][i];
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# Similar Problems
# Other Language Versions
# Java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
// Store the numbers in the array
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// Number of columns
int columns = matrix[0].length;
// Number of rows
int rows = matrix.length;
// Starting point for traversal
int start = 0;
// Number of loops, the smallest in value between the number of rows and columns divided by two
int loop = Math.min(rows,columns) / 2;
// The column (or row) index of the intermediate column (row) not traversed
int mid = loop;
// Termination condition
int offSet = 1;
int i, j;
while(loop-- > 0) {
// Initialize starting point
i = j = start;
// Left to right
for(; j < columns - offSet; j++)
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
// Top to bottom
for(; i < rows - offSet; i++)
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
// Right to left
for(; j > start; j--)
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
// Bottom to top
for(; i > start; i--)
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
// Change start position each loop
start++;
// Adjust termination condition
offSet++;
}
// If the smallest of the rows and columns is odd, a middle row or middle column will remain untraversed
if(Math.min(rows,columns) % 2 != 0) {
// If rows are greater than columns, there will be an intermediate column
if(rows > columns) {
// The next index of the last row of the intermediate column is mid + rows - columns + 1
for(int k = mid; k < mid + rows - columns + 1; k++) {
ans.add(matrix[k][mid]);
}
} else {// If columns are greater than or equal to rows, an intermediate row will appear
// The next index of the last column for the intermediate row is mid + columns - rows + 1
for(int k = mid; k < mid + columns - rows + 1; k++) {
ans.add(matrix[mid][k]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); // Store results
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
return res;
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int startx = 0, starty = 0; // Define the starting position for each loop
int loop = 0; // Number of loops
int offset = 1; // Control the length of traversal of each edge in each loop
while (loop < Math.min(rows, columns) / 2) {
int i = startx;
int j = starty;
// Simulate filling the top row from left to right (left closed, right open)
for (; j < columns - offset; j++) {
res.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
// Simulate filling the right column from top to bottom (left closed, right open)
for (; i < rows - offset; i++) {
res.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
// Simulate filling the bottom row from right to left (left closed, right open)
for (; j > starty; j--) {
res.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
// Simulate filling the left column from bottom to top (left closed, right open)
for (; i > startx; i--) {
res.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
// Increment the start position and number of loops, adjust traversal length
startx++;
starty++;
offset++;
loop++;
}
// If the minimum of rows or columns is odd, an untraversed part is guaranteed
// This can be understood better by drawing a diagram yourself
if (Math.min(rows, columns) % 2 == 1) {
// When rows are greater than columns, an untraversed column part remains
// Traverse it as starting position is at (startx, starty), the next position to traverse
// Traversal count is rows - columns + 1
if (rows > columns) {
for (int i = 0; i < rows - columns + 1; i++) {
res.add(matrix[startx++][starty]);
}
} else {
// This case follows similar logic to traverse the untraversed row part
for (int i = 0; i < columns - rows + 1; i++) {
res.add(matrix[startx][starty++]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
# JavaScript
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[]}
*/
var spiralOrder = function(matrix) {
let m = matrix.length
let n = matrix[0].length
let startX = startY = 0
let i = 0
let arr = new Array(m*n).fill(0)
let offset = 1
let loop = mid = Math.floor(Math.min(m,n) / 2)
while (loop--) {
let row = startX
let col = startY
// -->
for (; col < n + startY - offset; col++) {
arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
}
// down
for (; row < m + startX - offset; row++) {
arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
}
// <--
for (; col > startY; col--) {
arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
}
for (; row > startX; row--) {
arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
}
startX++
startY++
offset += 2
}
if (Math.min(m, n) % 2 === 1) {
if (n > m) {
for (let j = mid; j < mid + n - m + 1; j++) {
arr[i++] = matrix[mid][j]
}
} else {
for (let j = mid; j < mid + m - n + 1; j++) {
arr[i++] = matrix[j][mid]
}
}
}
return arr
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# Python
class Solution(object):
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if len(matrix) == 0 or len(matrix[0]) == 0 : # Check if List is empty
return []
row, col = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) # Number of rows, columns
loop = min(row, col) // 2 # Number of loops
stx, sty = 0, 0 # Starting x, y coordinates
i, j =0, 0
count = 0 # Counter
offset = 1 # Number of cells decreased each loop
result = [0] * (row * col)
while loop>0 :# Left closed, right open
i, j = stx, sty
while j < col - offset : # Left to right
result[count] = matrix[i][j]
count += 1
j += 1
while i < row - offset : # Top to bottom
result[count] = matrix[i][j]
count += 1
i += 1
while j>sty : # Right to left
result[count] = matrix[i][j]
count += 1
j -= 1
while i>stx : # Bottom to top
result[count] = matrix[i][j]
count += 1
i -= 1
stx += 1
sty += 1
offset += 1
loop -= 1
if min(row, col) % 2 == 1 : # Check if additional line filling is needed
i = stx
if row < col :
while i < stx + col - row + 1 :
result[count] = matrix[stx][i]
count += 1
i += 1
else :
while i < stx + row - col + 1 :
result[count] = matrix[i][stx]
count += 1
i += 1
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
Version 2: Define four boundaries
class Solution(object):
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not matrix:
return []
rows = len(matrix)
cols = len(matrix[0])
top, bottom, left, right = 0, rows - 1, 0, cols - 1
print_list = []
while top <= bottom and left <= right:
# Left to right
for i in range(left, right + 1):
print_list.append(matrix[top][i])
top += 1
# Top to bottom
for i in range(top, bottom + 1):
print_list.append(matrix[i][right])
right -= 1
# Right to left
if top <= bottom:
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
print_list.append(matrix[bottom][i])
bottom -= 1
# Bottom to top
if left <= right:
for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
print_list.append(matrix[i][left])
left += 1
return print_list
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# Go
func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) []int {
rows := len(matrix)
if rows == 0 {
return []int{}
}
columns := len(matrix[0])
if columns == 0 {
return []int{}
}
res := make([]int, rows * columns)
startx, starty := 0, 0 // Define the starting position for each loop
loop := min(rows, columns) / 2
mid := min(rows, columns) / 2
count := 0 // Used to populate every cell in the matrix
offset := 1 // In each loop, need to control the length of traversal of each edge
for loop > 0 {
i, j := startx, starty
// Simulate filling the top row from left to right (left closed, right open)
for ; j < starty + columns - offset; j++ {
res[count] = matrix[startx][j]
count++
}
// Simulate filling the right column from top to bottom (left closed, right open)
for ; i < startx + rows - offset; i++ {
res[count] = matrix[i][j]
count++
}
// Simulate filling the bottom row from right to left (left closed, right open)
for ; j > starty; j-- {
res[count] = matrix[i][j]
count++
}
// Simulate filling the left column from bottom to top (left closed, right open)
for ; i > startx; i-- {
res[count] = matrix[i][starty]
count++
}
// Starting from the second circle, the starting positions each increment. For example, the first circle starts at (0, 0), the second starts at (1, 1)
startx++
starty++
// Offset controls the traversal length of each edge in each circle
offset += 2
loop--
}
// If min(rows, columns) is odd, need to handle the central matrix position separately
if min(rows, columns) % 2 == 1 {
if rows > columns {
for i := mid; i < mid + rows - columns + 1; i++ {
res[count] = matrix[i][mid]
count++
}
} else {
for i := mid; i < mid + columns - rows + 1; i++ {
res[count] = matrix[mid][i]
count++
}
}
}
return res
}
func min(x, y int) int {
if x < y {
return x
}
return y
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
