# 31. Next Permutation
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Implement a function to get the next permutation, which rearranges the given numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation.
If there is no next greater permutation, it rearranges the numbers to the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order).
You must modify the input in-place and use only constant extra space.
Example 1:
- Input:
nums = [1,2,3] - Output:
[1,3,2]
Example 2:
- Input:
nums = [3,2,1] - Output:
[1,2,3]
Example 3:
- Input:
nums = [1,1,5] - Output:
[1,5,1]
Example 4:
- Input:
nums = [1] - Output:
[1]
# Thought Process
Some may try to manually write out the sequence of permutations, but fail to do so correctly because their approach might be flawed. Here, I use the example of 1234 to list all permutations. You can refer to the pattern:
1 2 3 4
1 2 4 3
1 3 2 4
1 3 4 2
1 4 2 3
1 4 3 2
2 1 3 4
2 1 4 3
2 3 1 4
2 3 4 1
2 4 1 3
2 4 3 1
3 1 2 4
3 1 4 2
3 2 1 4
3 2 4 1
3 4 1 2
3 4 2 1
4 1 2 3
4 1 3 2
4 2 1 3
4 2 3 1
4 3 1 2
4 3 2 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
As shown:
Take 1243 as an example, the process is as follows:
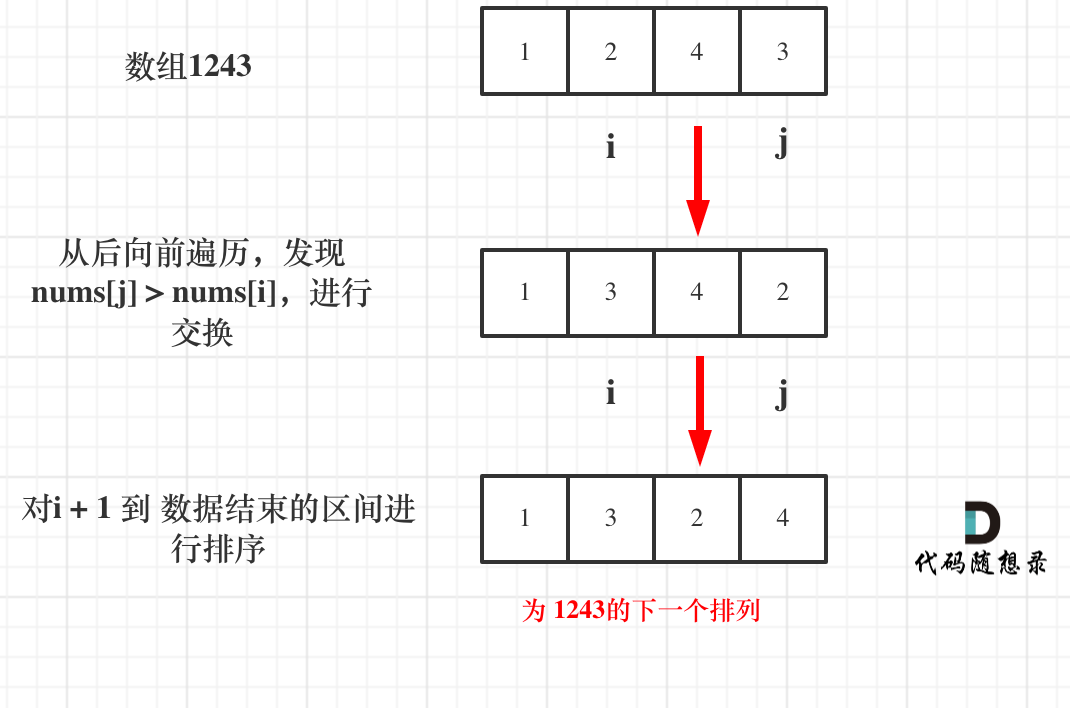
Here is the corresponding C++ code:
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
for (int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = nums.size() - 1; j > i; j--) {
if (nums[j] > nums[i]) {
swap(nums[j], nums[i]);
reverse(nums.begin() + i + 1, nums.end());
return;
}
}
}
// Reaching here means the entire array is in descending order, reverse it to get ascending order.
reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end());
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Other Language Versions
# Java
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = nums.length - 1; j > i; j--) {
if (nums[j] > nums[i]) {
// Swap
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
// Sort the elements in the range [i + 1, nums.length) in ascending order
Arrays.sort(nums, i + 1, nums.length);
return;
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(nums); // If there is no next greater permutation, rearrange the numbers to the lowest possible order (ascending order).
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Optimized time complexity to O(N), space complexity to O(1)
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
// 1. Find the first index from the end where nums[i] < nums[i+1], getting the front of the descending zone
int index = findIndex(nums);
// Check if the array is at its lowest configuration
if(index != 0){
// 2. Exchange with the smallest number greater than it in descending zone
exchange(nums,index);
}
// 3. Reverse the original descending zone to ascending
reverse(nums,index);
}
public static int findIndex(int [] nums){
for(int i = nums.length-1;i>0;i--){
if(nums[i]>nums[i-1]){
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void exchange(int [] nums, int index){
int head = nums[index-1];
for(int i = nums.length-1;i>0;i--){
if(head < nums[i]){
nums[index-1] = nums[i];
nums[i] = head;
break;
}
}
}
public static void reverse(int [] nums, int index){
for(int i = index,j = nums.length-1;i<j;i++,j--){
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# Python
Using
sorted()directly will create a new list and return it, so here's an in-place reversal function
class Solution:
def nextPermutation(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
length = len(nums)
for i in range(length - 2, -1, -1): # Start from the second to last element
if nums[i]>=nums[i+1]: continue # Pruning to remove duplicates
for j in range(length - 1, i, -1):
if nums[j] > nums[i]:
nums[j], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[j]
self.reverse(nums, i + 1, length - 1)
return
self.reverse(nums, 0, length - 1)
def reverse(self, nums: List[int], left: int, right: int) -> None:
while left < right:
nums[left], nums[right] = nums[right], nums[left]
left += 1
right -= 1
"""
265 / 265 test cases passed
Status: Passed
Execution time: 36 ms
Memory usage: 14.9 MB
"""
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# Go
// Carl's solution
func nextPermutation(nums []int) {
for i:=len(nums)-1;i>=0;i--{
for j:=len(nums)-1;j>i;j--{
if nums[j]>nums[i]{
// Swap
nums[j],nums[i]=nums[i],nums[j]
reverse(nums,0+i+1,len(nums)-1)
return
}
}
}
reverse(nums,0,len(nums)-1)
}
// A function to reverse a specified range of the target slice
func reverse(a []int,begin,end int){
for i,j:=begin,end;i<j;i,j=i+1,j-1{
a[i],a[j]=a[j],a[i]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# JavaScript
// Carl's solution (JavaScript's sort is a bit different from other languages, thought of copying the array to sort and then replace the original array to achieve ascending order for [i + 1, nums.length))
var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
for(let i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){
for(let j = nums.length - 1; j > i; j--){
if(nums[j] > nums[i]){
[nums[j],nums[i]] = [nums[i],nums[j]]; // Swap
// Deep copy of part [i + 1, nums.length) to new array `arr`
let arr = nums.slice(i+1);
// Sort `arr` in ascending order
arr.sort((a,b) => a - b);
// Replace part [i + 1, nums.length) of `nums` with `arr`
nums.splice(i+1,nums.length - i, ...arr);
return;
}
}
}
nums.sort((a,b) => a - b); // If there is no next greater permutation, rearrange the numbers to the smallest possible order (ascending order).
};
// Another approach
var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
let i = nums.length - 2;
// Iterate from right to left to get the first i where nums[i] < nums[i+1], the right part is in descending order
while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i+1]){
i--;
}
if (i >= 0){
let j = nums.length - 1;
// Iterate from right to left to get the first number greater than nums[i], as i is the first smaller to its right, there must be a number greater to its right
while (j >= 0 && nums[j] <= nums[i]){
j--;
}
// Swap the two numbers
[nums[j], nums[i]] = [nums[i], nums[j]];
}
// Reverse the right part of i
// As the right part was in descending order before, swapping a smaller number here ensures maintaining a monotonic increasing property
// Now, swapping head and tail while moving towards the center gives the minimum value of right part of i
let l = i + 1;
let r = nums.length - 1;
while (l < r){
[nums[l], nums[r]] = [nums[r], nums[l]];
l++;
r--;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
