# 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must use only constant extra space and you may not modify the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
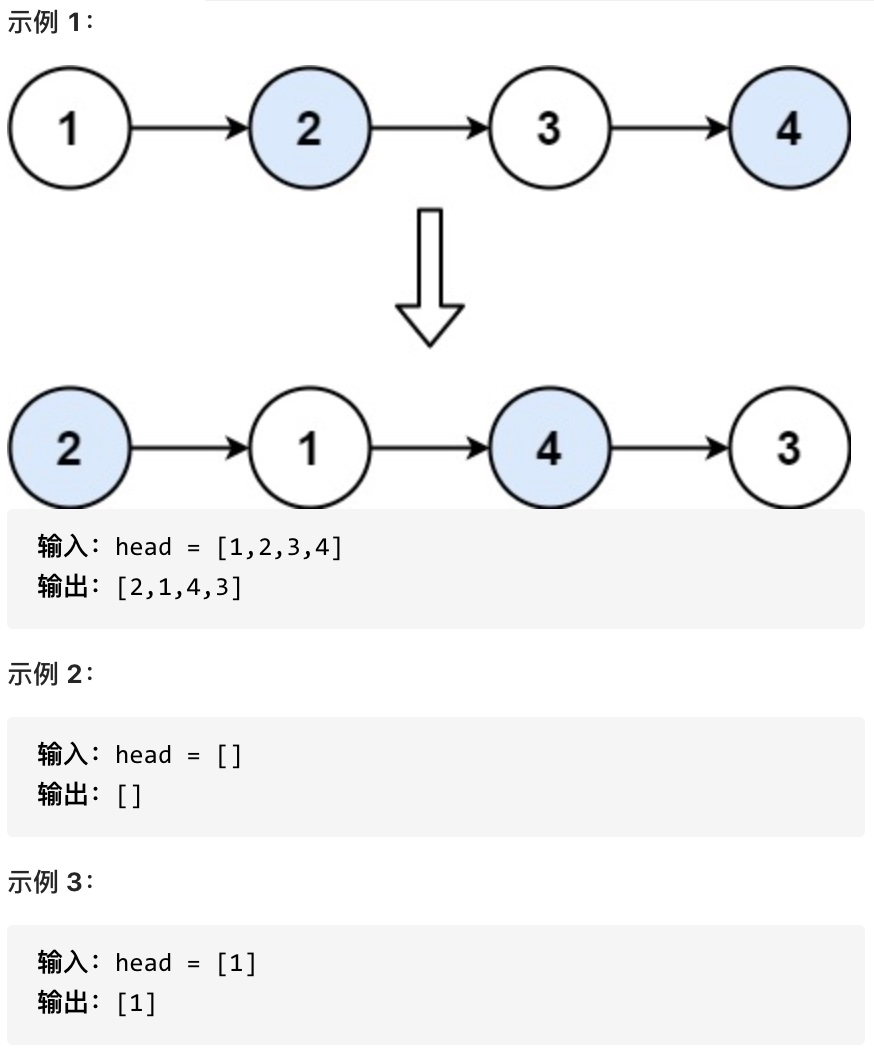
# Approach
This problem can be solved by simple simulation.
It's highly recommended to use a dummy head node. This will simplify the process significantly, otherwise, each operation targeting the head node (which doesn't have a preceding node pointing to it) would need to be handled separately.
If you are not yet familiar with operations involving a dummy head node, consider reviewing the article 0203.Remove Linked List Elements (opens new window).
Next, swap every pair of adjacent elements. It is crucial to draw a diagram here. Without a diagram, handling multiple pointers can easily become confusing, and the order of operations needs to be precise.
Initially, the cur pointer points to the dummy head node, and then proceed with the following three steps:
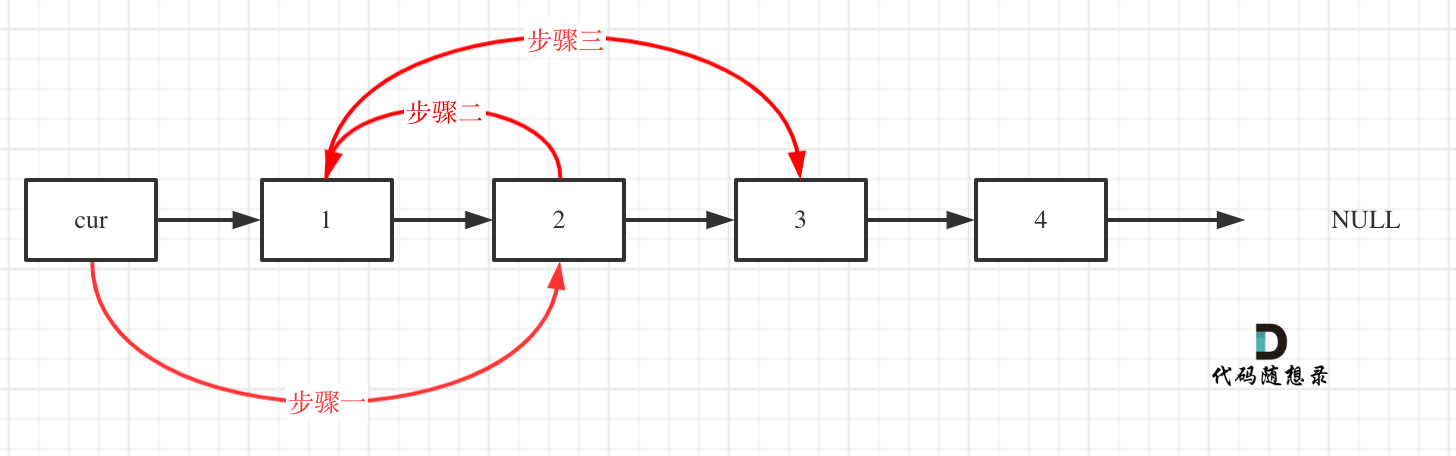
After the operations, the linked list looks like this:
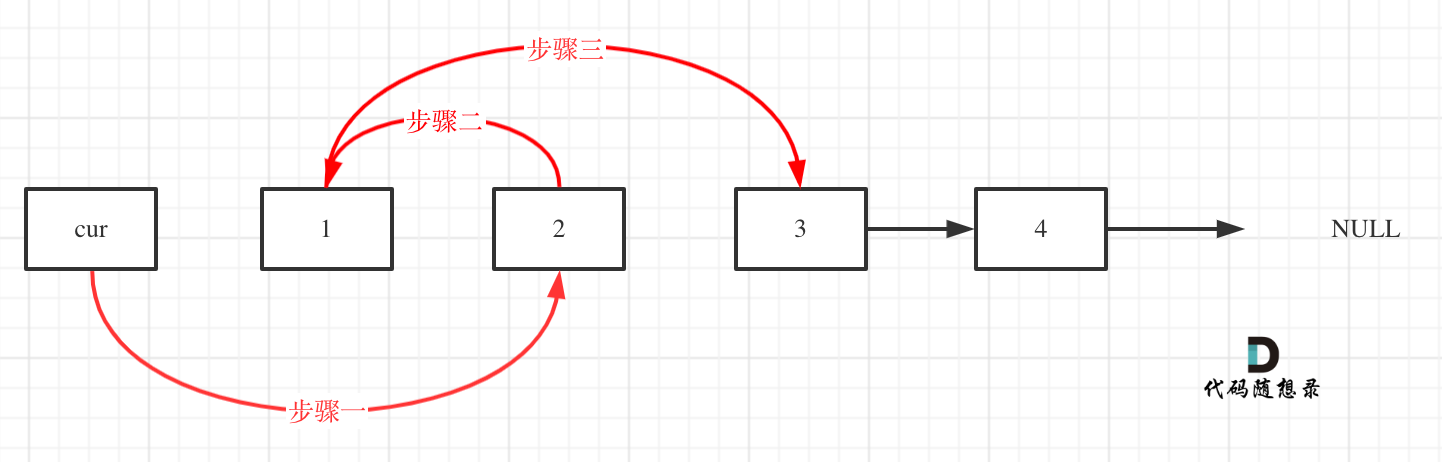
This may provide a clearer visualization:
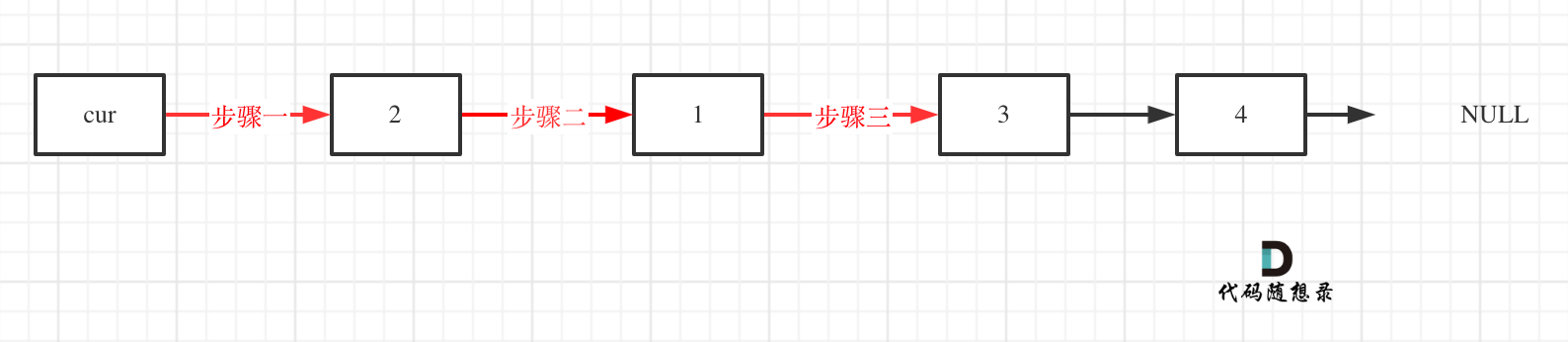
Here is the corresponding C++ code implementation: (the comments detail and align with the three steps in the diagram above)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); // Initialize a dummy head node
dummyHead->next = head; // Connect the dummy head node to the head for easier subsequent node manipulations
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next; // Save temporary node
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next->next->next; // Save another temporary node
cur->next = cur->next->next; // Step 1
cur->next->next = tmp; // Step 2
cur->next->next->next = tmp1; // Step 3
cur = cur->next->next; // Move cur forward by two nodes for the next swap
}
ListNode* result = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return result;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
# Further Discussion
Do not place too much emphasis on the runtime statistics represented on LeetCode, such as how many users your submission outperformed. These metrics are not entirely accurate.
As long as you can analyze and determine the time complexity during the coding process, that's sufficient. Regarding LeetCode's runtime metrics, just have a general look.
When I first submitted the above code, it took 8ms, which reportedly outperformed only 6.5% of other submissions, which surprised me because typically there isn’t a better approach than O(n) complexity. Upon resubmitting a few times, the results were reflected as follows:

If there are variations in execution times such as 100ms vs. 300ms, they are something to pay attention to. However, if it’s something like 4ms vs. 12ms, where one appears to outperform 80% and the other 20%, there practically isn't any difference—it’s just an estimation error on LeetCode’s part.
# Other Language Versions
# C:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
// Recursive version
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head){
// Base cases to terminate recursion: if head does not exist or if there's no next node, just return head
if(!head || !head->next)
return head;
// Create a node pointer type to store the next node of the head
struct ListNode *newHead = head->next;
// Update the node two positions ahead and link the head's next pointer to this updated list
head->next = swapPairs(newHead->next);
// Set the next node's next pointer to the old head node
newHead->next = head;
return newHead;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// Iterative version
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head){
// Using two pointers to avoid using temporary variables
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode *fakehead = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
fakehead->next = head;
ListNode* right = fakehead->next;
ListNode* left = fakehead;
while(left && right && right->next ){
left->next = right->next;
right->next = left->next->next;
left->next->next = right;
left = right;
right = left->next;
}
return fakehead->next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Java:
// Recursive version
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// Base case termination
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// Retrieve next node of the current node
ListNode next = head.next;
// Perform recursion
ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);
// Swap occurs here
next.next = head;
head.next = newNode;
return next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumyhead = new ListNode(-1); // Initialize a dummy head node
dumyhead.next = head; // Connect the dummy head node to head for easier subsequent node manipulations
ListNode cur = dumyhead;
ListNode temp; // Temporary node to save the node following the pair
ListNode firstnode; // Temporary node to save the first node of the pair
ListNode secondnode; // Temporary node to save the second node of the pair
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
temp = cur.next.next.next;
firstnode = cur.next;
secondnode = cur.next.next;
cur.next = secondnode; // Step 1
secondnode.next = firstnode; // Step 2
firstnode.next = temp; // Step 3
cur = firstnode; // Move cur forward, preparing for the next swap
}
return dumyhead.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// Swap in a different order for steps 2 and 3, removing the need for the temp node
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
ListNode node1 = cur.next; // First node in the pair
ListNode node2 = cur.next.next; // Second node in the pair
cur.next = node2; // Step 1
node1.next = node2.next; // Step 3
node2.next = node1; // Step 2
cur = cur.next.next; // Advance cur
}
return dummy.next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Python:
# Recursive version
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# Nodes to be swapped are pre and cur
pre = head
cur = head.next
next = head.next.next
cur.next = pre # Swap operation
pre.next = self.swapPairs(next) # Continue swapping the subsequent linked list
return cur
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy_head = ListNode(next=head)
current = dummy_head
# Both cur's next and next next nodes need to be present for swapping, else swapping complete
while current.next and current.next.next:
temp = current.next # Save state before modifying
temp1 = current.next.next.next
current.next = current.next.next
current.next.next = temp
temp.next = temp1
current = current.next.next
return dummy_head.next
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# Go:
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{
Next: head,
}
pre := dummy
for head != nil && head.Next != nil {
pre.Next = head.Next
next := head.Next.Next
head.Next.Next = head
head.Next = next
pre = head
head = next
}
return dummy.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// Recursive version
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
next := head.Next
head.Next = swapPairs(next.Next)
next.Next = head
return next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# JavaScript:
var swapPairs = function (head) {
let ret = new ListNode(0, head), temp = ret;
while (temp.next && temp.next.next) {
let cur = temp.next.next, pre = temp.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
temp.next = cur;
temp = pre;
}
return ret.next;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// Recursive version
var swapPairs = function (head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
let after = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(after.next);
after.next = head;
return after;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# TypeScript:
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
const dummyNode: ListNode = new ListNode(0, head);
let curNode: ListNode | null = dummyNode;
while (curNode && curNode.next && curNode.next.next) {
let firstNode: ListNode = curNode.next,
secNode: ListNode = curNode.next.next,
thirdNode: ListNode | null = curNode.next.next.next;
curNode.next = secNode;
secNode.next = firstNode;
firstNode.next = thirdNode;
curNode = firstNode;
}
return dummyNode.next;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Kotlin:
fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
val dummyNode = ListNode(0).apply {
this.next = head
}
var cur: ListNode? = dummyNode
while (cur?.next != null && cur.next?.next != null) {
val temp = cur.next
val temp2 = cur.next?.next?.next
cur?.next = cur.next?.next
cur?.next?.next = temp
cur?.next?.next?.next = temp2
cur = cur?.next?.next
}
return dummyNode.next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Swift:
func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
return head
}
let dummyHead: ListNode = ListNode(-1, head)
var current: ListNode? = dummyHead
while current?.next != nil && current?.next?.next != nil {
let temp1 = current?.next
let temp2 = current?.next?.next?.next
current?.next = current?.next?.next
current?.next?.next = temp1
current?.next?.next?.next = temp2
current = current?.next?.next
}
return dummyHead.next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Scala:
// With dummy head node
object Solution {
def swapPairs(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
var dummy = new ListNode(0, head) // Dummy head node
var pre = dummy
var cur = head
// perform swap when the next two nodes are present
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null) {
var tmp: ListNode = cur.next.next // save first node of next pair
pre.next = cur.next // Step 1
cur.next.next = cur // Step 2
cur.next = tmp // Step 3
// setup for the next swap iteration
pre = cur
cur = tmp
}
// return the node following dummy head
dummy.next
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# PHP:
// With dummy head node
function swapPairs($head) {
if ($head == null || $head->next == null) {
return $head;
}
$dummyNode = new ListNode(0, $head);
$preNode = $dummyNode; // Dummy head node
$curNode = $head;
$nextNode = $head->next;
while($curNode && $nextNode) {
$nextNextNode = $nextNode->next; // Store subsequent node
$nextNode->next = $curNode; // swap curNode and nextNode
$curNode->next = $nextNextNode;
$preNode->next = $nextNode; // Connect previous node to nextNode
// Update pointers for next iteration
$preNode = $preNode->next->next;
$curNode = $nextNextNode;
$nextNode = $nextNextNode->next;
}
return $dummyNode->next;
}
// Recursive version
function swapPairs($head)
{
// Base cases for recursion termination
if ($head === null || $head->next === null) {
return $head;
}
// Determine the new head node of the swapped sequence
$next = $head->next;
$head->next = $this->swapPairs($next->next); // Update head node's pointer
$next->next = $head; // Update pointer of the new head node
return $next; // Return the new head node after swapping
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# Rust:
// With dummy head node
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy_head = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));
dummy_head.next = head;
let mut cur = dummy_head.as_mut();
while let Some(mut node) = cur.next.take() {
if let Some(mut next) = node.next.take() {
node.next = next.next.take();
next.next = Some(node);
cur.next = Some(next);
cur = cur.next.as_mut().unwrap().next.as_mut().unwrap();
} else {
cur.next = Some(node);
cur = cur.next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
}
dummy_head.next
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// Recursive
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
if head.is_none() || head.as_ref().unwrap().next.is_none() {
return head;
}
let mut node = head.unwrap();
if let Some(mut next) = node.next.take() {
node.next = Solution::swap_pairs(next.next);
next.next = Some(node);
Some(next)
} else {
Some(node)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# C#
// With dummy head node
public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
{
var dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null)
{
ListNode tmp1 = cur.next;
ListNode tmp2 = cur.next.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = tmp1;
cur.next.next.next = tmp2;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// Recursive
public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
{
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
var cur = head.next;
head.next = SwapPairs(head.next.next);
cur.next = head;
return cur;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
