# 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
LeetCode Problem Link (opens new window)
Given a linked list, remove the n-th node from the end of the list and return its head.
Advanced: Can you try to implement this with a single scan?
Example 1:
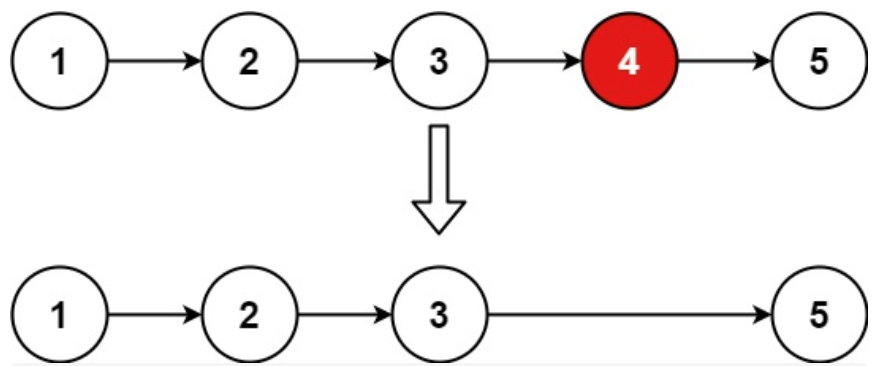
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
# Approach
The classic application of the two-pointer technique. If you want to delete the nth node from the end, let the fast pointer move n steps, and then move both fast and slow pointers at the same time until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list. Then, delete the node pointed to by the slow pointer.
This is the idea, but pay attention to some details.
Follow these steps:
Firstly, I recommend using a dummy head node, which makes the logic of deleting the actual head node easier to handle. If you're unfamiliar with virtual head nodes, check out this article: 0203.Remove Linked List Elements (opens new window)
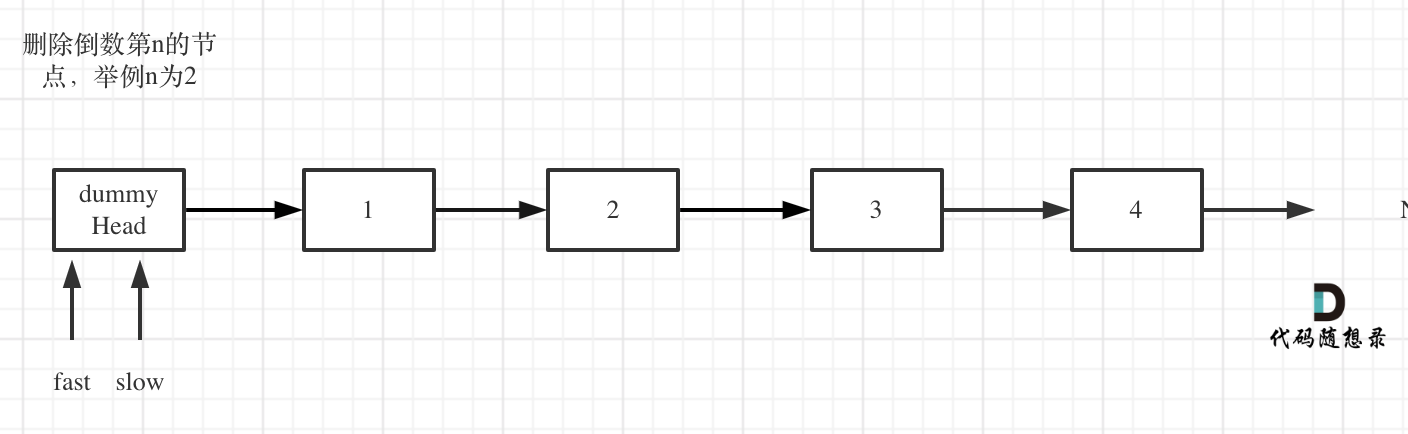
Define fast and slow pointers, both initially set to the dummy head node, as shown in the diagram:
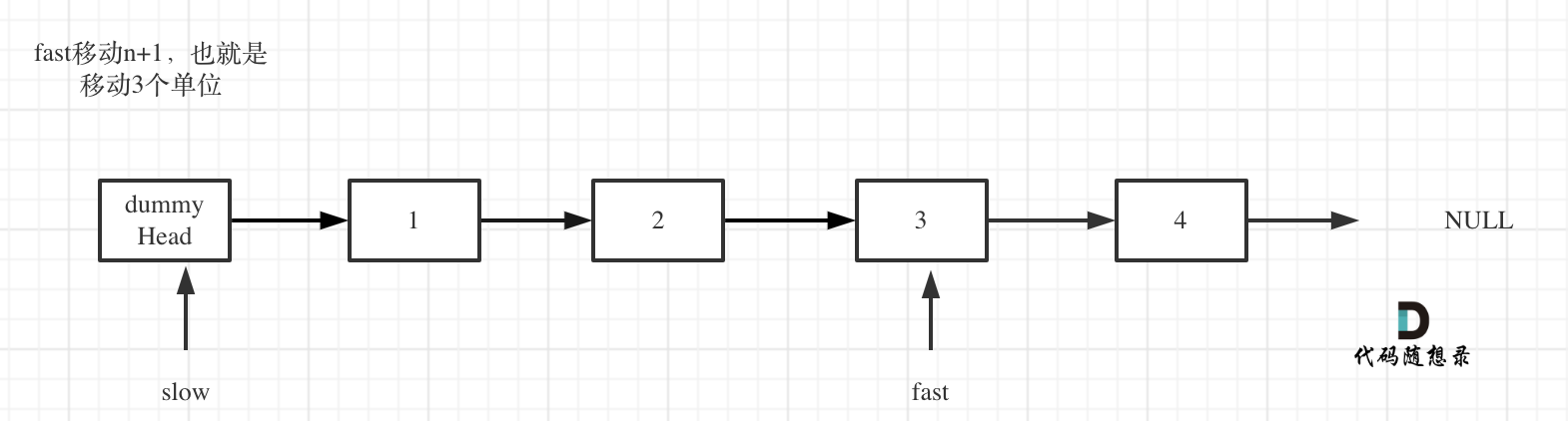
The fast pointer first moves n + 1 steps. Why n + 1? Because only in this way, when moving simultaneously, the slow pointer can point to the node before the one to be deleted (making the delete operation more convenient), as shown in the diagram:
Move fast and slow pointers simultaneously until fast reaches the end, as shown in the picture:
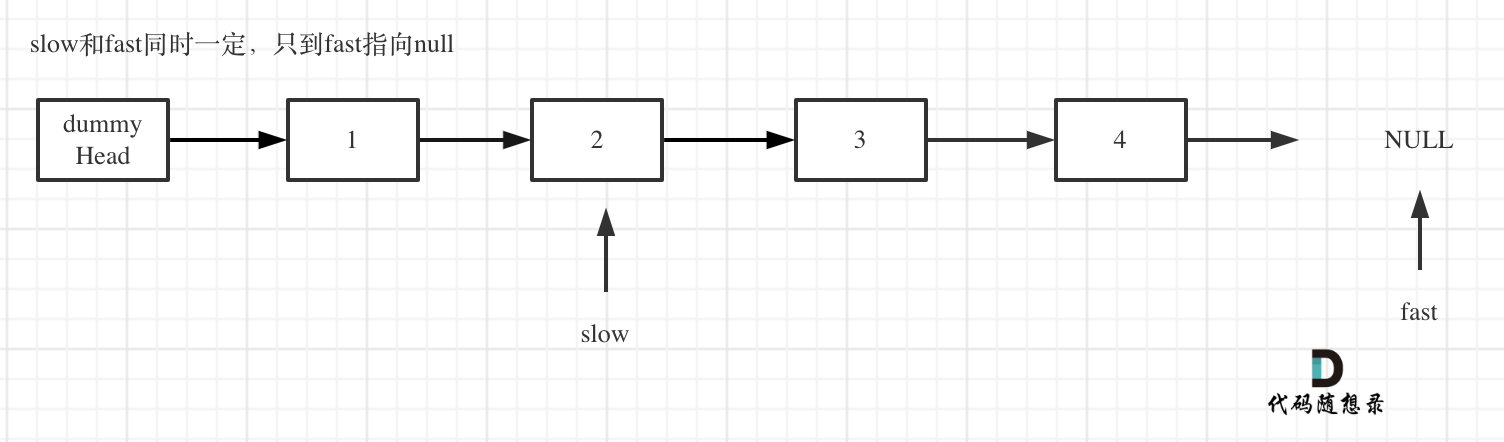
Delete the node pointed to by slow's next, as shown:
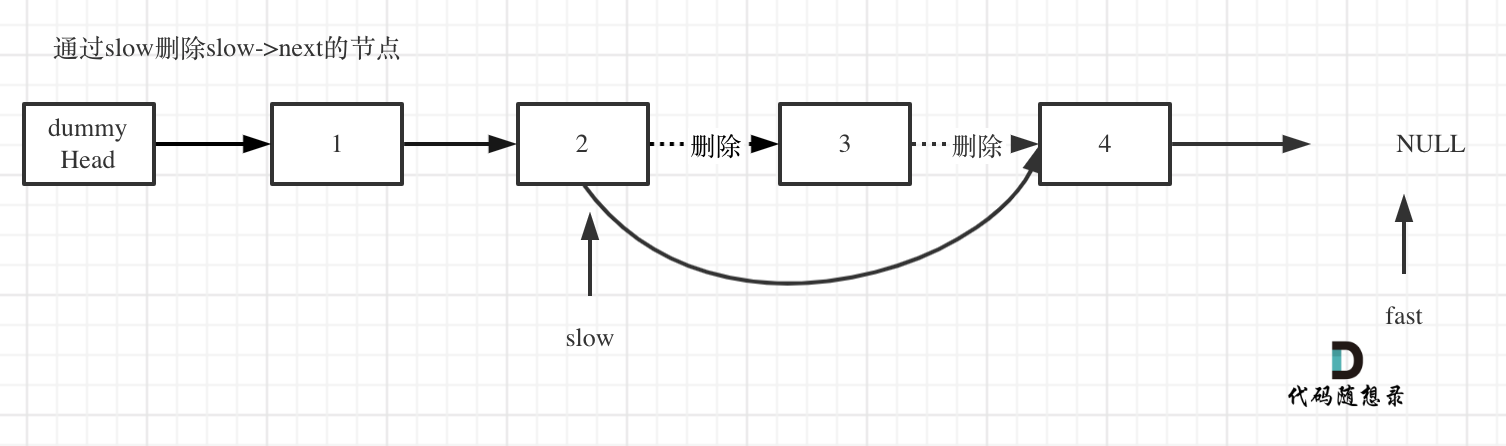
This leads to the following C++ code:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
ListNode* fast = dummyHead;
while(n-- && fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next; // fast moves one more step so that slow points to the node before the one to be deleted
while (fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
// ListNode *tmp = slow->next; // C++ memory release logic
// slow->next = tmp->next;
// delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
# Other Language Versions
# Java:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// Create a new dummy node pointing to head
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
dummyNode.next = head;
// Two pointers set to the dummy node
ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
// The two pointers must be n nodes apart
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
}
while (fastIndex != null) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
}
// Now slowIndex points to the node before the one to be deleted
// To understand this, visualize a linked list of length 3 and simulate the code
if (slowIndex.next != null) {
slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// Create a new dummy node pointing to head
ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, head);
// Invoke the remove method recursively starting from the dummy node
remove(s, n);
// Return the new list's head (ignoring the dummy node)
return s.next;
}
public int remove(ListNode p, int n) {
// Base case: if the current node is null, return 0
if (p == null) {
return 0;
}
// Recurse into the next node
int net = remove(p.next, n);
// If the current node is the n-th node from the end, proceed with deletion
if (net == n) {
p.next = p.next.next;
}
// Return the current node's total depth
return net + 1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# Python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
# Create a dummy node and set its next to the head of the list
dummy_head = ListNode(0, head)
# Set up two pointers, slow and fast, both initialized at the dummy node
slow = fast = dummy_head
# Fast pointer moves n + 1 steps ahead
for i in range(n+1):
fast = fast.next
# Move both pointers until fast reaches the end of the list
while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
# Delete the n-th node by updating the (n-1)-th node's next pointer
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy_head.next
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# Go:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummyNode := &ListNode{0, head}
fast, slow := dummyNode, dummyNode
for i := 0; i <= n; i++ { // Note the <= here; otherwise, slow would be exactly at the n-th node when fast is nil
fast = fast.Next
}
for fast != nil {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
return dummyNode.Next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# JavaScript:
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
// Create a sentinel node to simplify the logic
let dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
let fast = dummyHead;
let slow = dummyHead;
while (n--) fast = fast.next;
while (fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# TypeScript:
Version 1 (Fast and Slow Pointer Method):
function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
let newHead: ListNode | null = new ListNode(0, head);
// Based on leetcode’s definition, fast and slow need not be ListNode | null.
let slowNode: ListNode = newHead;
let fastNode: ListNode = newHead;
while(n--) {
fastNode = fastNode.next!; // fastNode.next cannot be null after moving n nodes from the virtual head.
}
while(fastNode.next) { // Traverse until fastNode.next = null, which means at the end. At this point, slowNode points at the n-th from last.
fastNode = fastNode.next;
slowNode = slowNode.next!;
}
slowNode.next = slowNode.next!.next; // the n-th from last node's next is definitely not null.
return newHead.next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Version 2 (Total Node Count Method):
function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
let curNode: ListNode | null = head;
let listSize: number = 0;
while (curNode) {
curNode = curNode.next;
listSize++;
}
if (listSize === n) {
head = head.next;
} else {
curNode = head;
for (let i = 0; i < listSize - n - 1; i++) {
curNode = curNode.next;
}
curNode.next = curNode.next.next;
}
return head;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Version 3 (Reverse Recursion Method):
function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
let newHead: ListNode | null = new ListNode(0, head);
let cnt = 0;
function recur(node) {
if (node === null) return;
recur(node.next);
cnt++;
if (cnt === n + 1) {
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
recur(newHead);
return newHead.next;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Kotlin:
fun removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode?, n: Int): ListNode? {
val pre = ListNode(0).apply {
this.next = head
}
var fastNode: ListNode? = pre
var slowNode: ListNode? = pre
for (i in 0..n) {
fastNode = fastNode?.next
}
while (fastNode != null) {
slowNode = slowNode?.next
fastNode = fastNode.next
}
slowNode?.next = slowNode?.next?.next
return pre.next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Swift:
func removeNthFromEnd(_ head: ListNode?, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if n == 0 {
return head
}
let dummyHead = ListNode(-1, head)
var fast: ListNode? = dummyHead
var slow: ListNode? = dummyHead
// fast moves n ahead
for _ in 0 ..< n {
fast = fast?.next
}
while fast?.next != nil {
fast = fast?.next
slow = slow?.next
}
slow?.next = slow?.next?.next
return dummyHead.next
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# PHP:
function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
// Set a dummy head node
$dummyHead = new ListNode();
$dummyHead->next = $head;
$slow = $fast = $dummyHead;
while($n-- && $fast != null){
$fast = $fast->next;
}
// Fast moves one more step, making slow point right before the node to be deleted
$fast = $fast->next;
while ($fast != NULL) {
$fast = $fast->next;
$slow = $slow->next;
}
$slow->next = $slow->next->next;
return $dummyHead->next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Scala:
object Solution {
def removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode, n: Int): ListNode = {
val dummy = new ListNode(-1, head) // Define a dummy head node
var fast = head // Fast pointer starts at the head
var slow = dummy // Slow pointer starts at the dummy head
// Since n is immutable, we can't use while(n > 0){n -= 1}
for (i <- 0 until n) {
fast = fast.next
}
// Move fast and slow pointers until fast is null
while (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
}
// Delete slow’s next node
slow.next = slow.next.next
// Return the next of the dummy head
dummy.next
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Rust:
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, mut n: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy_head = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));
dummy_head.next = head;
let mut fast = &dummy_head.clone();
let mut slow = &mut dummy_head;
while n > 0 {
fast = fast.next.as_ref().unwrap();
n -= 1;
}
while fast.next.is_some() {
fast = fast.next.as_ref().unwrap();
slow = slow.next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
slow.next = slow.next.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
dummy_head.next
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# C:
/** c language definition for singly-linked list
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {
// Define a dummy head node and initialize it to point to head
struct ListNode* dummy = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummy->val = 0;
dummy->next = head;
// Define fast and slow pointers
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next; // Delete the n-th node from the end
head = dummy->next;
free(dummy); // Delete the dummy node
return head;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# C#:
public class Solution {
public ListNode RemoveNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummpHead = new ListNode(0);
dummpHead.next = head;
var fastNode = dummpHead;
var slowNode = dummpHead;
while(n-- != 0 && fastNode != null)
{
fastNode = fastNode.next;
}
while(fastNode.next != null)
{
fastNode = fastNode.next;
slowNode = slowNode.next;
}
slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
return dummpHead.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
